Abstract
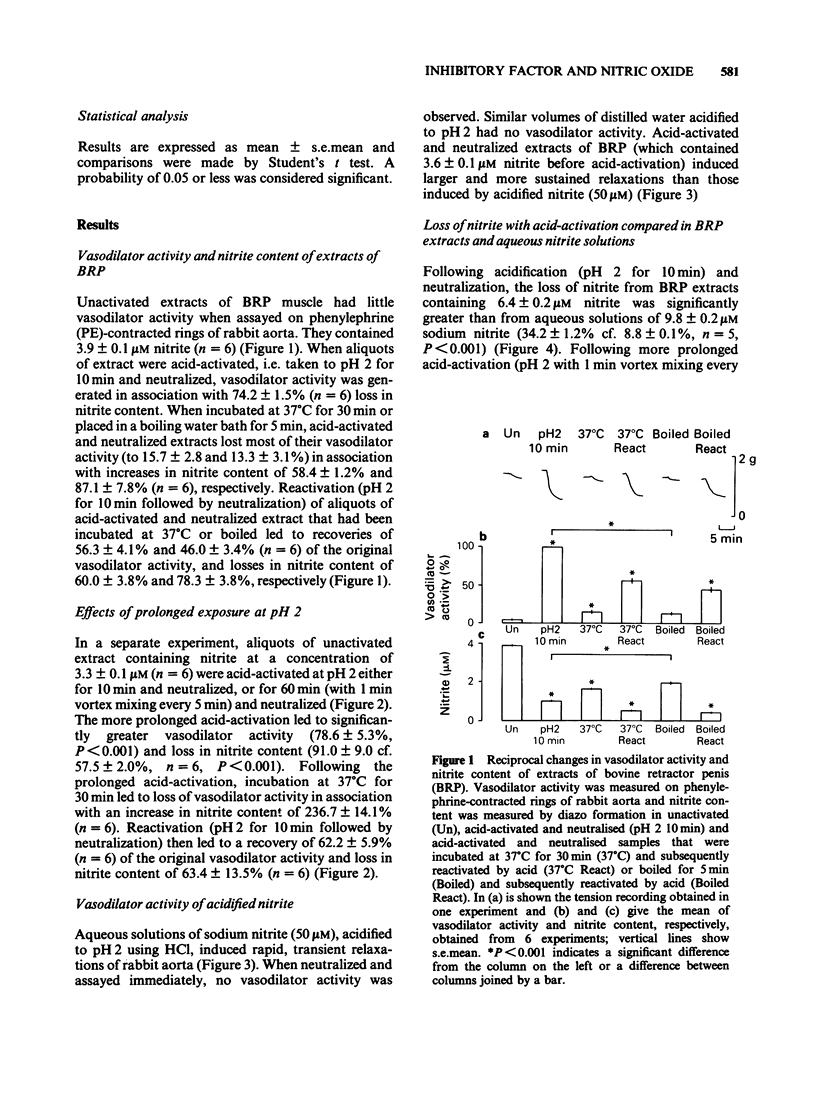
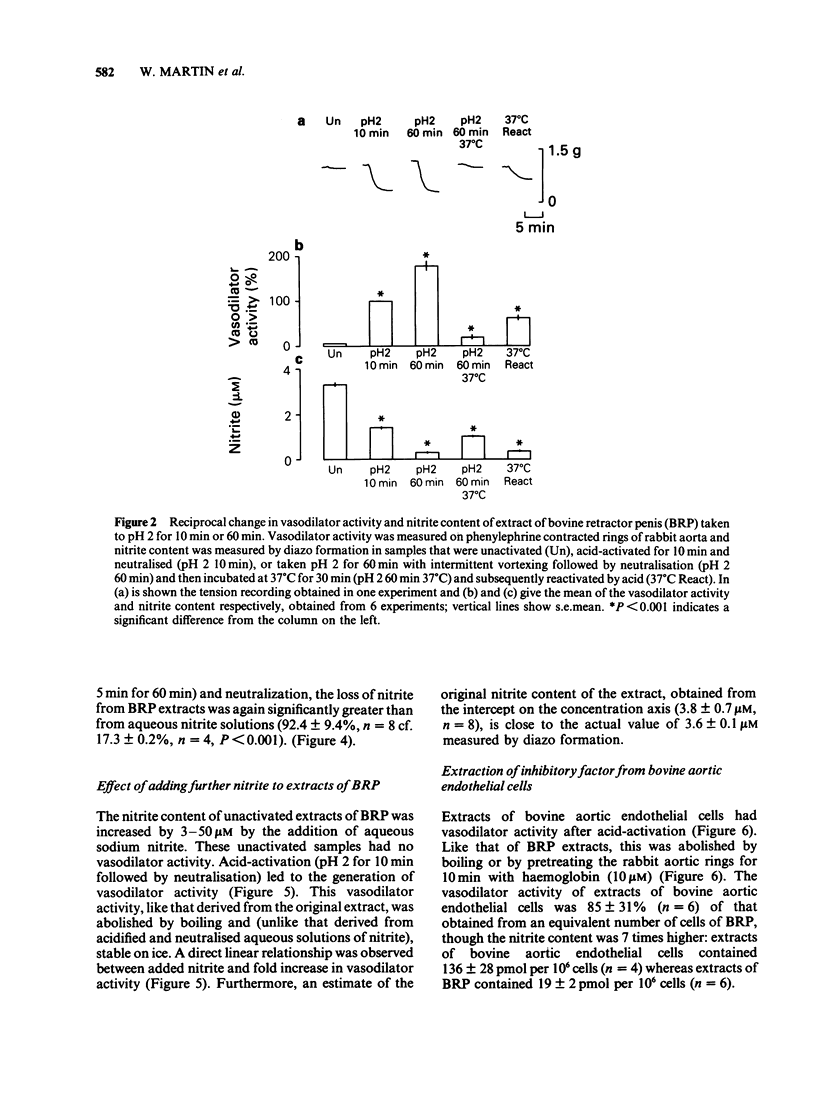
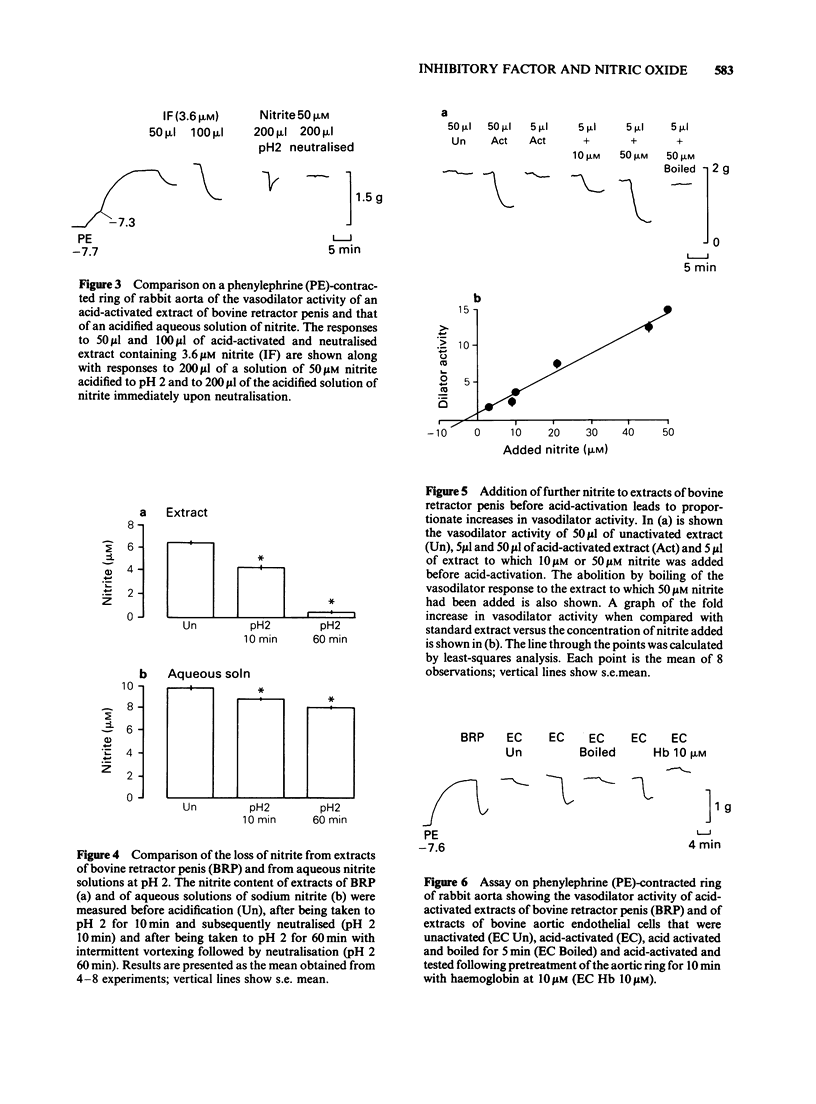
1. Unactivated extracts of bovine retractor penis (BRP) contains 3-7 microM nitrite. Acid-activation of these extracts at pH 2 for 10 min followed by neutralization generates the active form of inhibitory factor (IF; assayed by its vasodilator action on rabbit aorta), and is associated with partial loss of nitrite. 2. Increasing the time of acid-activation at pH 2 from 10 to 60 min with intermittent vortex mixing generates greater vasodilator activity and increases nitrite loss. 3. When acid-activated and neutralized extracts are incubated at 37 degrees C or 30 min or boiled for 5 min, vasodilator activity is lost and nitrite content increased. Reactivation of these samples at pH 2 for 10 min followed by neutralization leads to partial recoveries of vasodilator activity with loss in nitrite content. 4. Addition of sodium nitrite to BRP extracts increases acid-activatable vasodilator activity pro rata. 5. Acid-activation of aqueous sodium nitrite solutions results in less loss of nitrite and generation of less vasodilator activity than BRP extracts. Vasodilatation is only transient and is rapidly abolished on neutralization, whereas responses to acid-activated BRP extracts are more prolonged and activity is stable on ice. 6. Bovine aortic endothelial cells yield vasodilator activity that is indistinguishable from that isolated from BRP. It is activated by acid, stable on ice, abolished by boiling or by haemoglobin, and appears to be due to the generation of nitric oxide (NO) from nitrite.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Killick S. W., Aboo Aar M. Extraction from ox retractor penis of an inhibitory substance which mimics its atropine-resistant neurogenic relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;54(3):409–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. M., Kobus S. M., Brien J. F., Nakatsu K., Marks G. S. Requirement for reduced, unliganded hemoprotein for the hemoglobin- and myoglobin-mediated biotransformation of glyceryl trinitrate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 May;237(2):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A., Drummond A. H. Cyclic GMP mediates neurogenic relaxation in the bovine retractor penis muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):665–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A., Gillespie J. S., Martin W. The inhibitory material in extracts from the bovine retractor penis muscle is not an adenine nucleotide. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):327–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A., Gillespie J. S., Pollock D. Oxyhaemoglobin blocks non-adrenergic non-cholinergic inhibition in the bovine retractor penis muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 19;85(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braughler J. M., Mittal C. K., Murad F. Effects of thiols, sugars, and proteins on nitric oxide activation of guanylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12450–12454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A., Campbell J. H., Campbell G. R. Release and properties of endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from endothelial cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jun;123(3):310–320. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., ROUGHTON F. J. The kinetics and equilibria of the reactions of nitric oxide with sheep haemoglobin. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):507–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Hunter J. C., Martin W. Some physical and chemical properties of the smooth muscle inhibitory factor in extracts of the bovine retractor penis muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:111–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Martin W. A smooth muscle inhibitory material from the bovine retractor penis and rat anococcygeus muscles. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:55–64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta: relationship to stimulation of 86Rb efflux from isolated endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Henderson A. H. Evidence that cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 7;112(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90496-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Barry B. K., McNamara D. B., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. J. Coronary arterial relaxation and guanylate cyclase activation by cigarette smoke, N'-nitrosonornicotine and nitric oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jul;214(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J., Poole R. K. The respiratory chains of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):222–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.222-271.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSANE J. M., ROBINS E. The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Furchgott R. F., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors induce endothelium-dependent relaxation of rat and rabbit aorta by potentiating the effects of spontaneously released endothelium-derived relaxing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 May;237(2):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Smith J. A., White D. G. The mechanisms by which haemoglobin inhibits the relaxation of rabbit aorta induced by nitrovasodilators, nitric oxide, or bovine retractor penis inhibitory factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):563–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. J., Fridovich I., Makhoul R. G., Hagen P. O. Stabilization and partial characterization of endothelium-derived relaxing factor from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):689–696. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Mortara M., Whitaker C. Methods for microcarrier culture of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells avoiding the use of enzymes. Tissue Cell. 1980;12(4):619–635. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


