Abstract
1. A new nonpeptide kappa-opioid compound, a cyclohexyl benzeneacetamide derivative (PD117302), has been synthesized and its affinity for the different types of opioid receptor determined. The ability of PD117302 to modify the activity of the electrically-stimulated guinea-pig ileum and rabbit vas deferens has also been evaluated. 2. In binding studies using guinea-pig brain homogenates, unlabelled PD117302 had a high affinity (Ki = 3.7 nM) at [3H]-etorphine labelled kappa sites and a low affinity at [3H]-[D-Ala2, MePhe4, glyol5]-enkephalin ([3H]-DAGOL) labelled mu sites (Ki = 408 nM) and [3H]-SKF 10047 labelled sigma sites (Ki = 1.8 microM). In bioassay studies, PD117302 was a potent agonist, producing a maximum inhibition of the electrically-evoked contractions of the guinea-pig ileum (IC50 = 1.1 nM) and rabbit vas deferens (IC50 = 45 nM) which was naloxone-reversible. 3. In guinea-pig brain, [3H]-PD117302 bound to a high-affinity opioid binding site with a KD of 2.7 nM and a Bmax of 3.4 pmol g-1 wet weight. The Bmax was found to be less than 50% of the Bmax values for [3H]-etorphine and [3H]-bremazocine suggesting that [3H]-PD117302 may be a specific ligand for a subtype of kappa receptor. [3H]-PD117302 also bound with micromolar affinity to a non-opioid binding site. 4. Kinetic studies found that [3H]-PD117302-specific binding to the high affinity site was saturable, reaching equilibrium within 20 min at 4 degrees C, and reversible, with a half-life of dissociation of 3.9 min.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


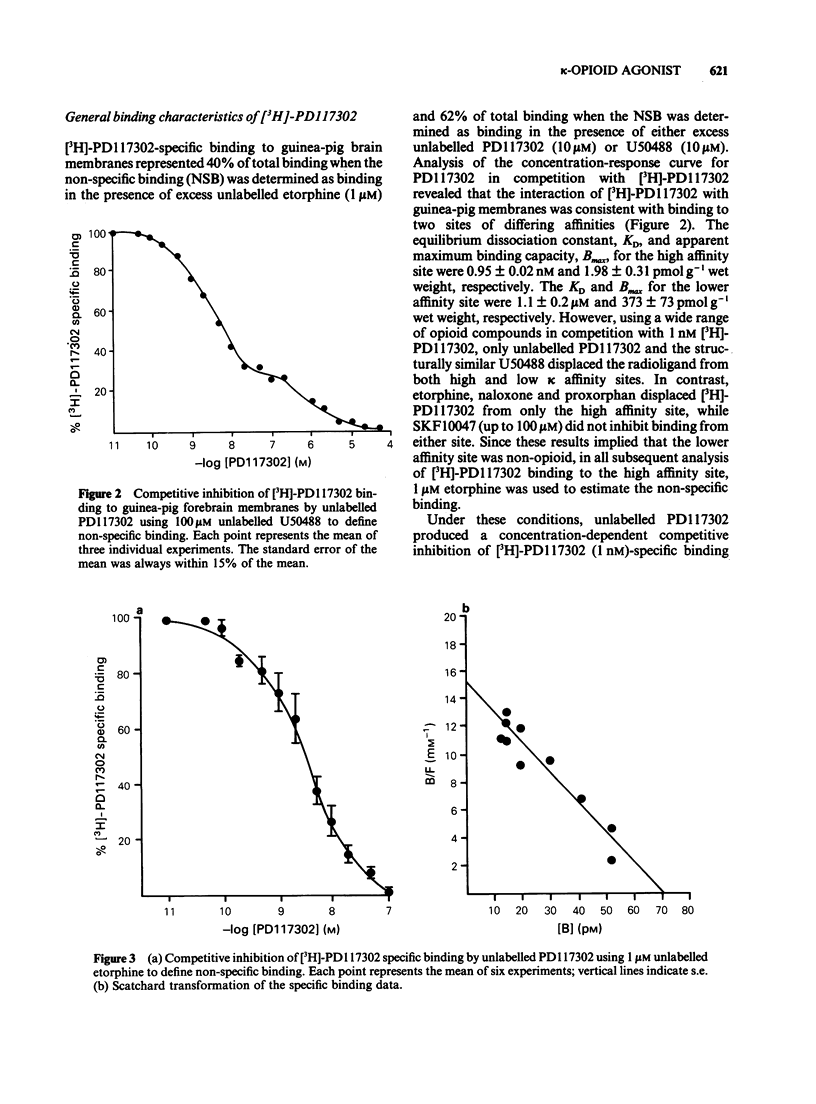
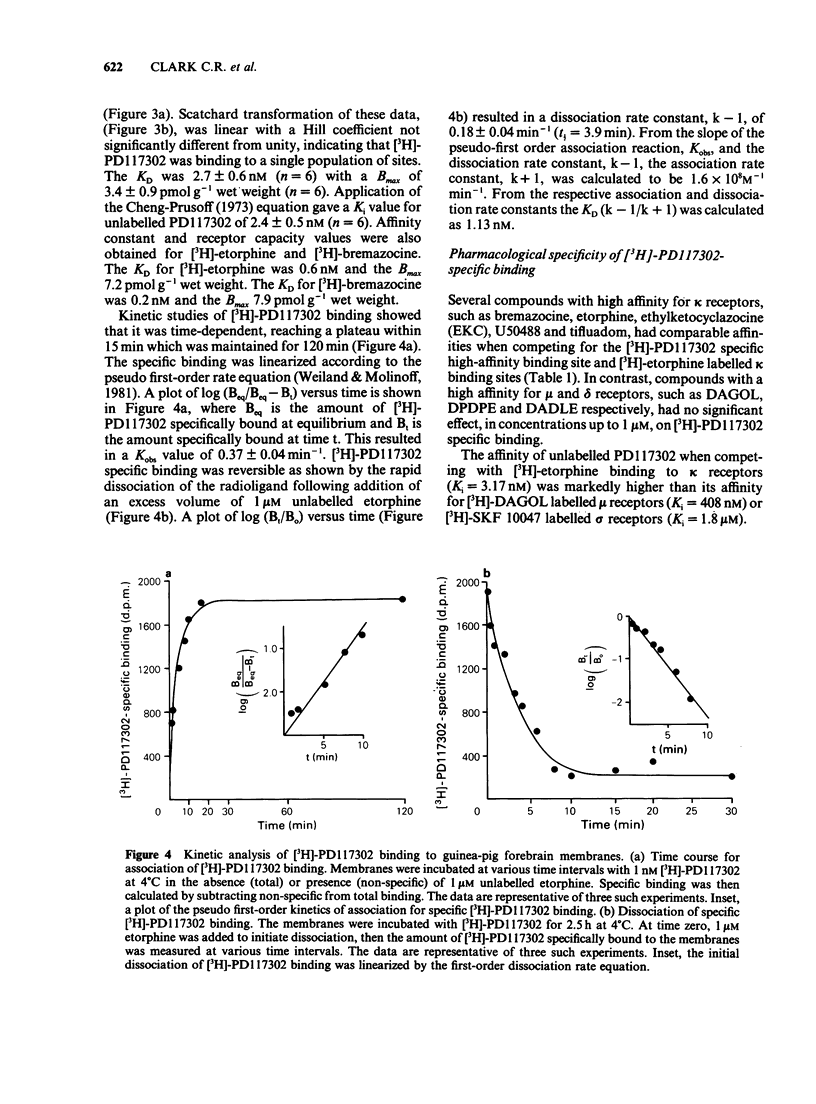
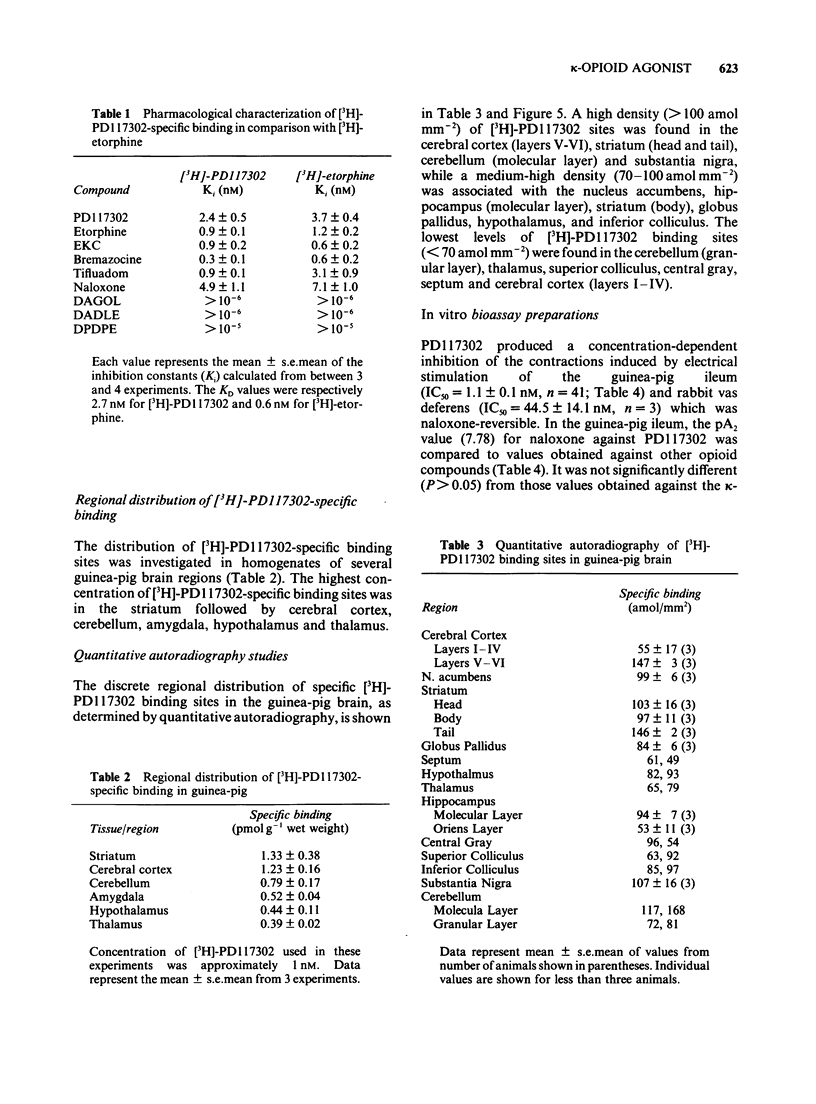
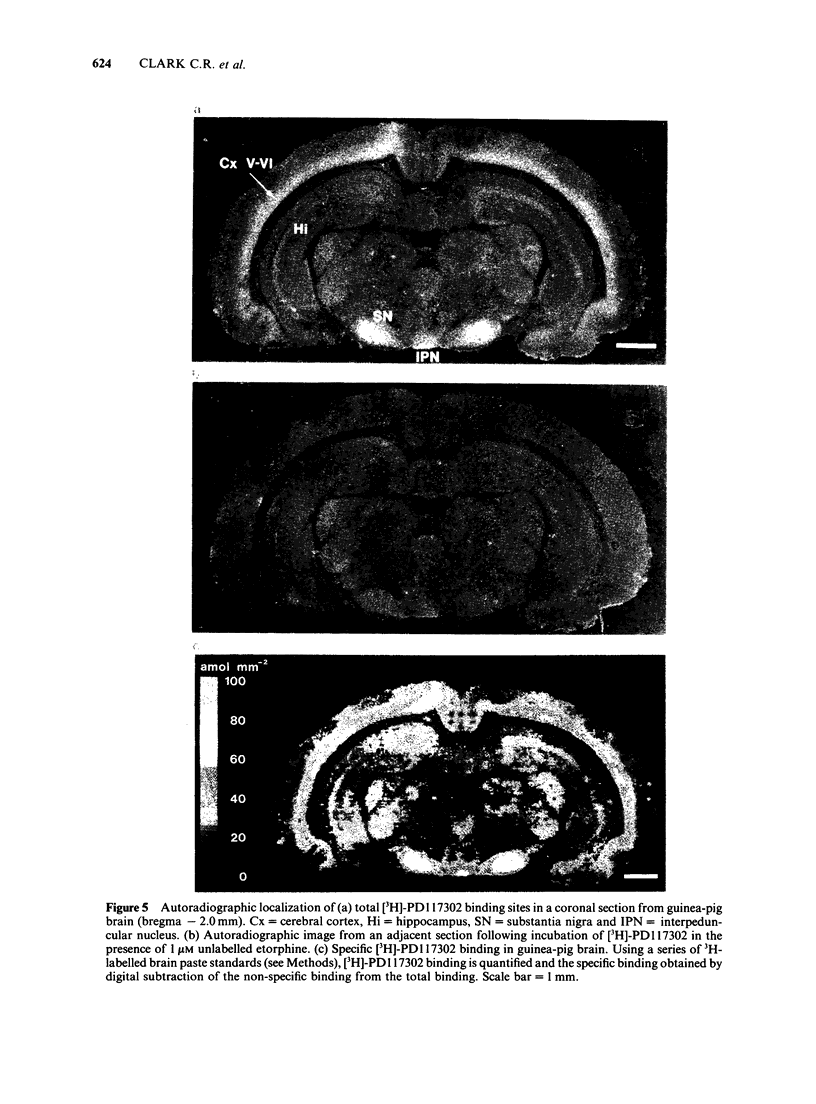


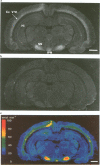
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Attali B., Mazarguil H., Cros J. Characterization of [3H]-etorphine binding in guinea-pig striatum after blockade of mu and delta sites. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1287–1290. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischel S. V., Medzihradsky F. Interaction between [3H]ethylketocyclazocine and [3H]etorphine and opioid receptors in membranes from rat brain. A kinetic analysis. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Apr;25(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote R. W., Maurer R. Autoradiographic localization of opiate kappa-receptors in the guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 5;85(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P. E., Martin W. R. The effects of morphine and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent, morphine-dependent and cyclazocine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jul;198(1):66–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Comparison of the binding characteristics of tritiated opiates and opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;70(3):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb08727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W. Spectrum of the mu, delta- and kappa-binding sites in homogenates of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H. Kappa opiate receptors localized by autoradiography to deep layers of cerebral cortex: relation to sedative effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M., Waterfield A. A. Assessment in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens of benzomorphans which have strong antinociceptive activity but do not substitute for morphine in the dependent monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Types of opioid receptors: relation to antinociception. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Feb 19;308(1136):291–297. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Mickelson M. M., McCall J. M., Von Voigtlander P. F. [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton G. E., Johnson M. A., Meecham K. G., Hill R. G., Hughes J. Pharmacological profile of PD 117302, a selective kappa-opioid agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;92(4):915–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Lewis M. E., Khachaturian H., Akil H., Watson S. J. Pharmacological and anatomical evidence of selective mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 3;399(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90601-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W. Multiple opiate receptors: [3H]ethylketocyclazocine receptor binding and ketocyclazocine analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3691–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. E., Foote R. W., Maurer R., Kosterlitz H. W. Opioid binding sites of the kappa-type in guinea-pig cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1984 Jun;12(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. B. A classification of opiate receptors that mediate antinociception in animals. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton N., Sewell R. D., Spencer P. S. Analgesic actions of mu- and kappa-opiate agonists in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Apr;262(2):199–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Takemori A. E. Relative involvement of mu, kappa and delta receptor mechanisms in opiate-mediated antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: I. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]