Abstract
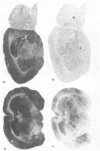
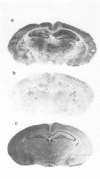
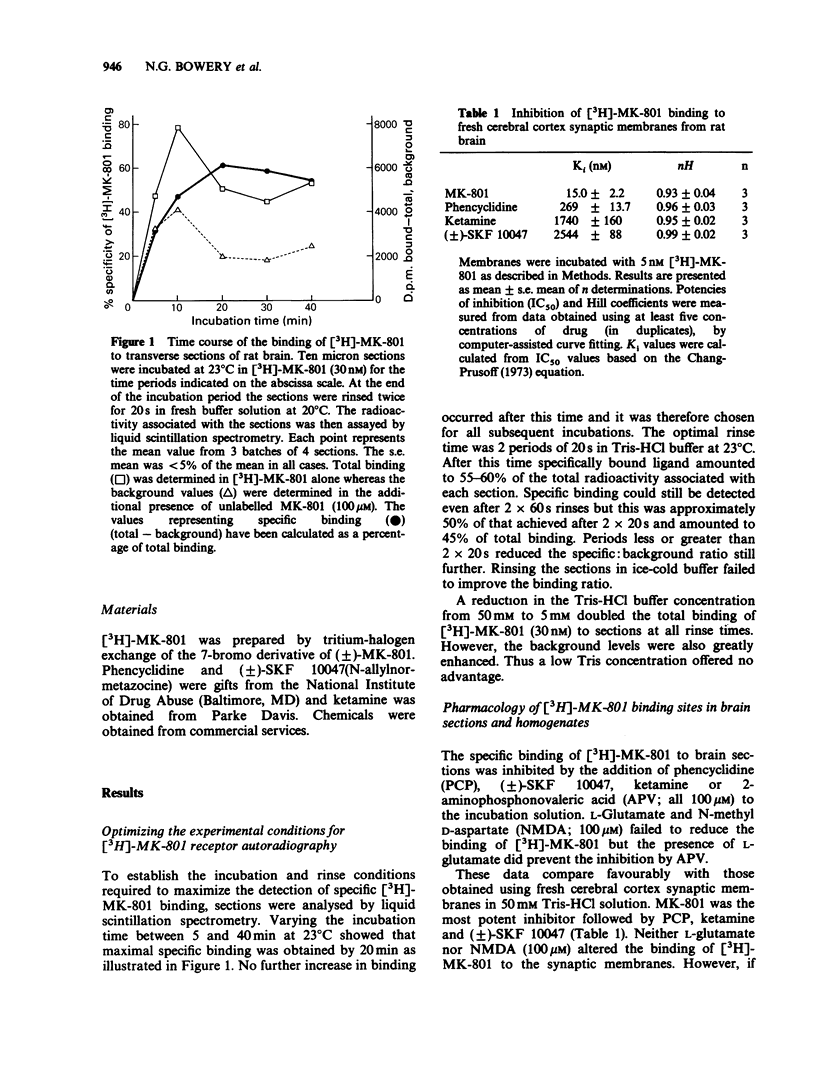
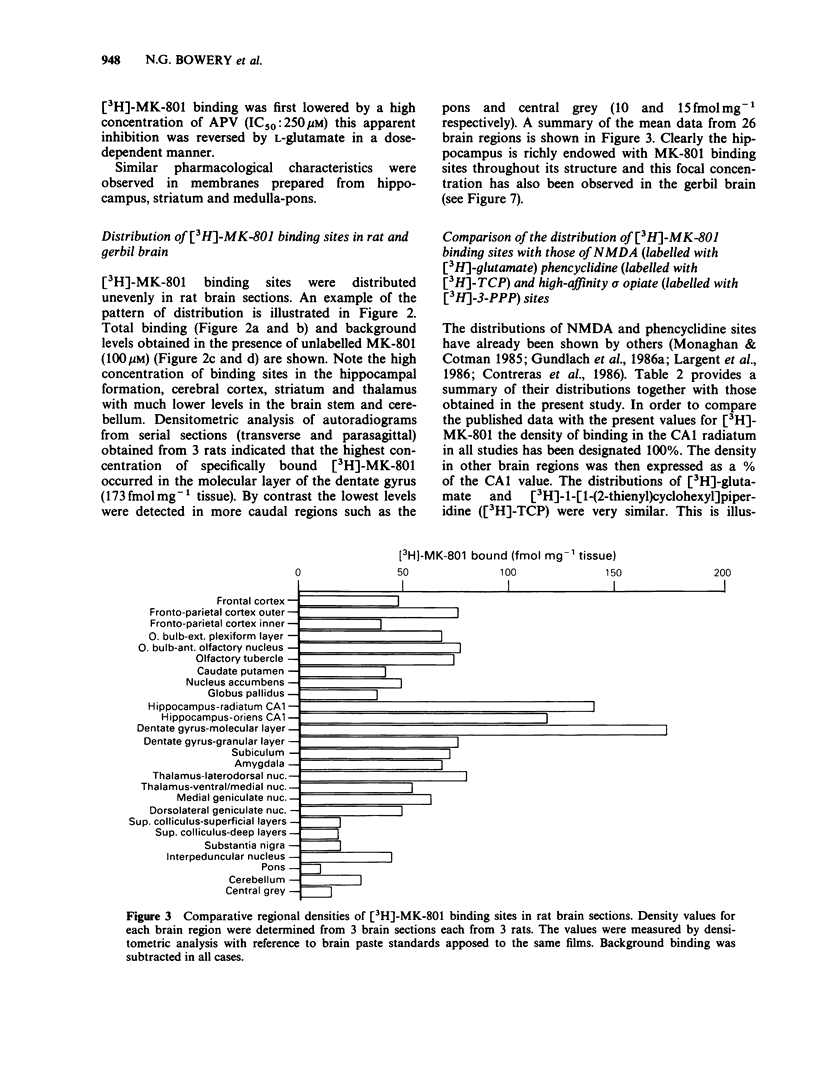
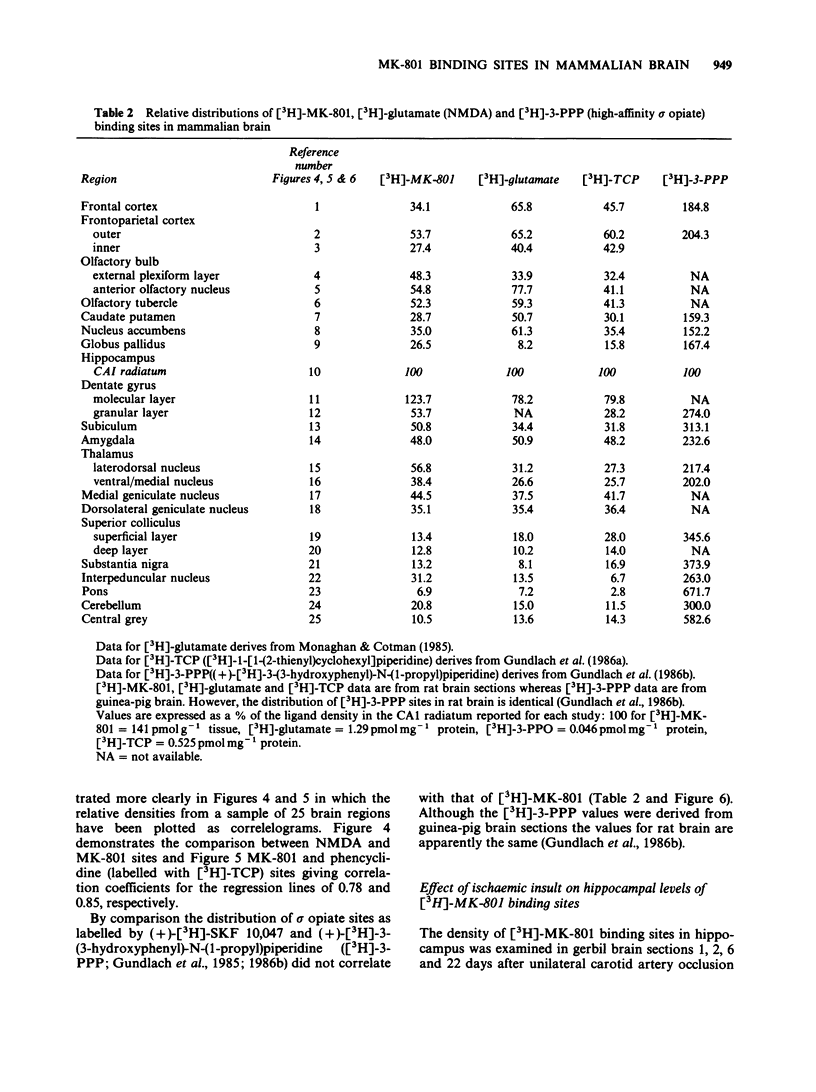
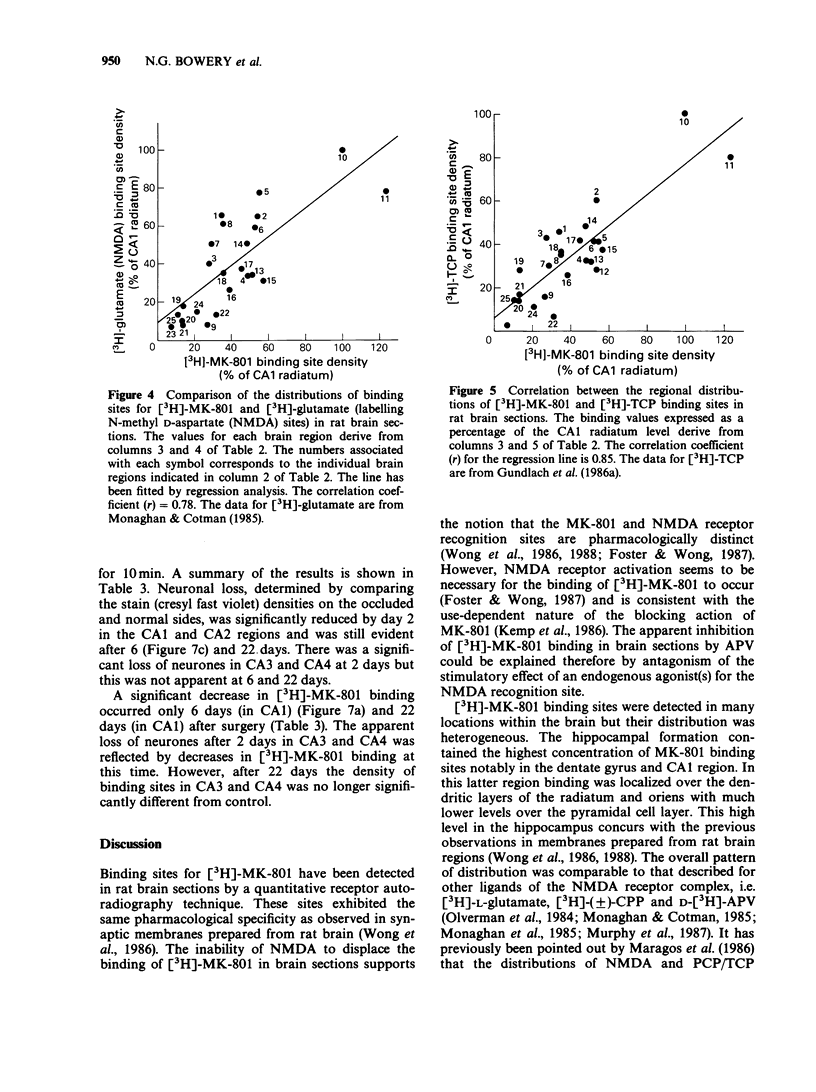
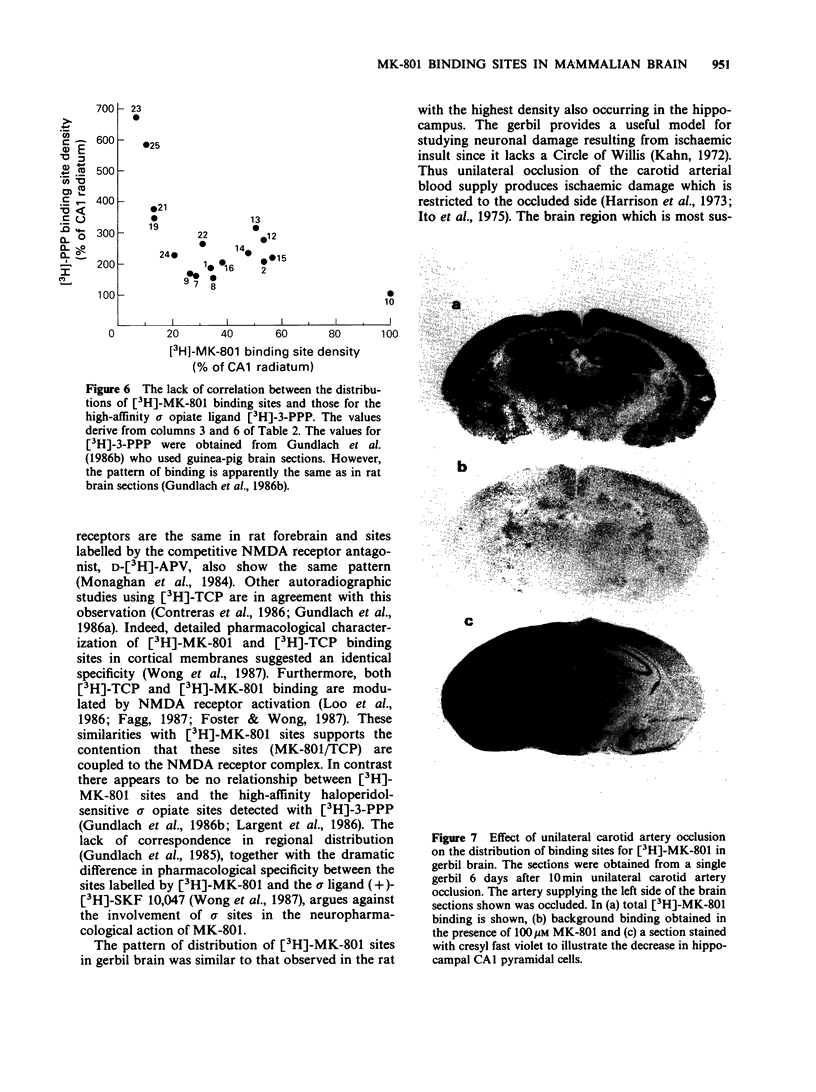
1. An in vitro receptor autoradiography procedure is described for visualizing binding sites for the excitatory amino acid antagonist radiolabelled MK-801, in rat and gerbil brain sections. 2. Ten micron sections were labelled by incubation at room temperature for 20 min in 30 nM [3H]-MK-801. This was followed by 2 rinses for 20 s in fresh buffer solution. Specifically bound ligand determined with 100 microM unlabelled MK-801 amounted to 55-60% of total. 3. Phencyclidine, (+/-)-SKF 10047, ketamine and 2-aminophosphonovaleric acid (APV) (all 100 microM) prevented the specific binding of [3H]-MK-801. L-Glutamate and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) (100 microM) had no effect. However, L-glutamate prevented the inhibition by APV. 4. The highest concentrations of [3H]-MK-801 binding sites occurred in the hippocampal formation, cerebral cortex, olfactory bulb and thalamus. Very low levels were detected in the brain stem and cerebellum. 5. The distribution of [3H]-MK-801 binding sites was comparable to that of NMDA sites and phencyclidine sites (labelled with [3H]-TCP) but not with high-affinity sigma sites labelled with [3H]-3-PPP. 6. The density of [3H]-MK-801 binding sites in the gerbil hippocampus was examined 1, 2, 6 and 22 days after unilateral carotid artery occlusion for 10 min. Only at 6 and 22 days was the binding reduced (by 36% and 46% respectively) in the CA1 region whereas a significant neuronal loss was apparent at day 2. In CA2 a decrease in binding was only evident at day 22. 7. These results indicate that binding sites for [3H]-MK-801 can be detected in mammalian brain sections by receptor autoradiography. Their distribution supports an association with the NMDA receptor complex and the loss in the hippocampus after carotid artery occlusion indicates their presence on pyramidal cells is vulnerable to ischaemic insult.
Full text
PDF

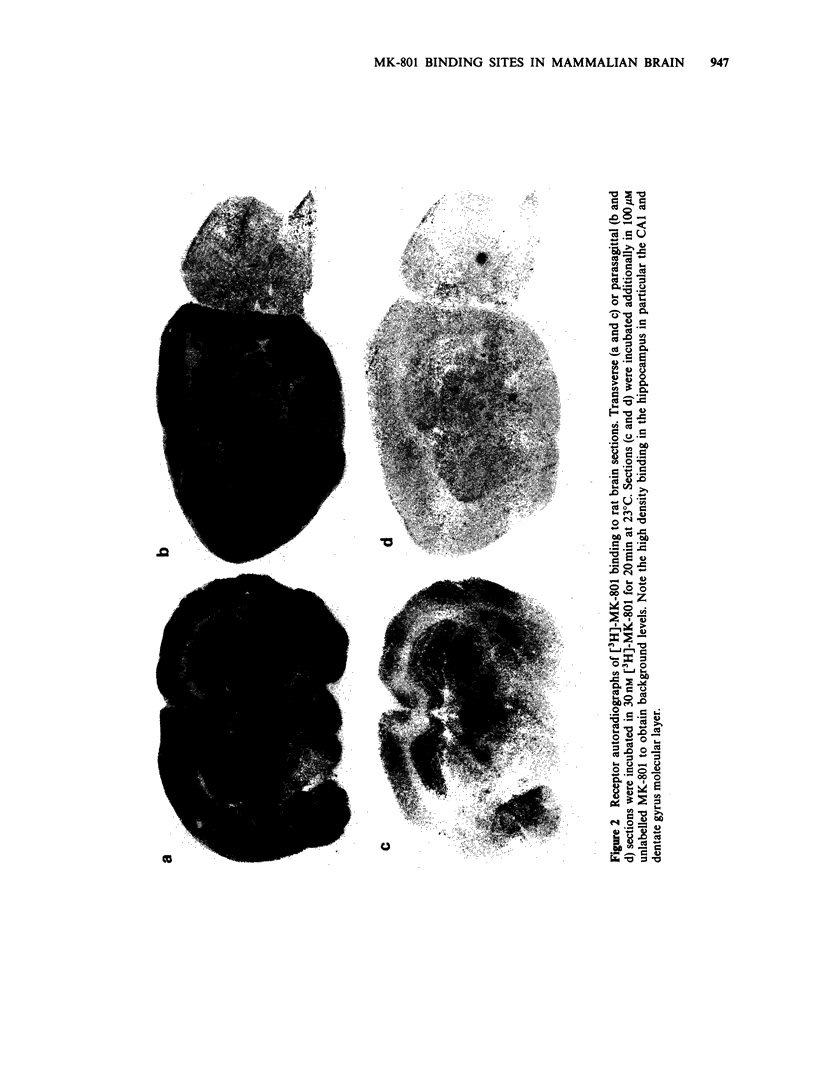



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras P. C., Quirion R., O'Donohue T. L. Autoradiographic distribution of phencyclidine receptors in the rat brain using [3H]1-(1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl)piperidine ([3H]TCP). Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 18;67(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E. Phencyclidine and related drugs bind to the activated N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-channel complex in rat brain membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 6;76(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90719-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Gill R., Kemp J. A., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 prevents N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal degeneration in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 19;76(3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Wong E. H. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801 binds to the activated state of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 protects against ischemia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in the gerbil. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3343–3349. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach A. L., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. Autoradiographic localization of sigma receptor binding sites in guinea pig and rat central nervous system with (+)3H-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1757–1770. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01757.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach A. L., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. Phencyclidine (PCP) receptors: autoradiographic localization in brain with the selective ligand, [3H]TCP. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 29;386(1-2):266–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach A. L., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. Phencyclidine and sigma opiate receptors in brain: biochemical and autoradiographical differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):465–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Ganong A. H., Monaghan D. T., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Action of 3-((+/-)-2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)-propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP): a new and highly potent antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Brownbill D., Lewis P. D., Russell R. W. Cerebral edema following carotid artery ligation in the gerbil. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):389–391. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240049008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito U., Spatz M., Walker J. T., Jr, Klatzo I. Experimental cerebral ischemia in mongolian gerbils. I. Light microscopic observations. Acta Neuropathol. 1975 Aug 27;32(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00696570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn K. The natural course of experimental cerebral infarction in the gerbil. Neurology. 1972 May;22(5):510–515. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Gundlach A. L., Snyder S. H. Pharmacological and autoradiographic discrimination of sigma and phencyclidine receptor binding sites in brain with (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047, (+)-[3H]-3-[3-hydroxyphenyl]-N-(1-propyl)piperidine and [3H]-1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo P., Braunwalder A., Lehmann J., Williams M. Radioligand binding to central phencyclidine recognition sites is dependent on excitatory amino acid receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 29;123(3):467–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90726-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragos W. F., Chu D. C., Greenamyre J. T., Penney J. B., Young A. B. High correlation between the localization of [3H]TCP binding and NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 9;123(1):173–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H. Receptors for the excitatory amino acids in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;20(3-4):251–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. Possible therapeutic applications of antagonists of excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Feb;68(2):113–122. doi: 10.1042/cs0680113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Distribution of N-methyl-D-aspartate-sensitive L-[3H]glutamate-binding sites in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1985 Nov;5(11):2909–2919. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02909.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Cotman C. W. L-[3H]Glutamate binds to kainate-, NMDA- and AMPA-sensitive binding sites: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 12;340(2):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90936-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Olverman H. J., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Autoradiography of D-2-[3H]amino-5-phosphonopentanoate binding sites in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Dec 21;52(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Schneider J., Boehm C., Lehmann J., Williams M. Binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid to rat brain membranes: a selective, high-affinity ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):778–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Collins J. F., Stone T. W. Isomers of 2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoic acid as antagonists of neuronal excitants. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Sep 20;32(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Kogure K., Kato H., Ohtomo H. Disturbed Ca2+ homeostasis in the gerbil hippocampus following brief transient ischemia. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 5;364(2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90850-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker H., Morelli M., Deshmukh P., Yamamura H. I. [3H]Ro5-4864 benzodiazepine binding in the kainate lesioned striatum and Huntington's diseased basal ganglia. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 30;248(2):396–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90602-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J., Palacios J. M. Quantitative receptor autoradiography using [3H]ultrofilm: application to multiple benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N. [3H]MK-801 labels a site on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel complex in rat brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):274–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]