Abstract
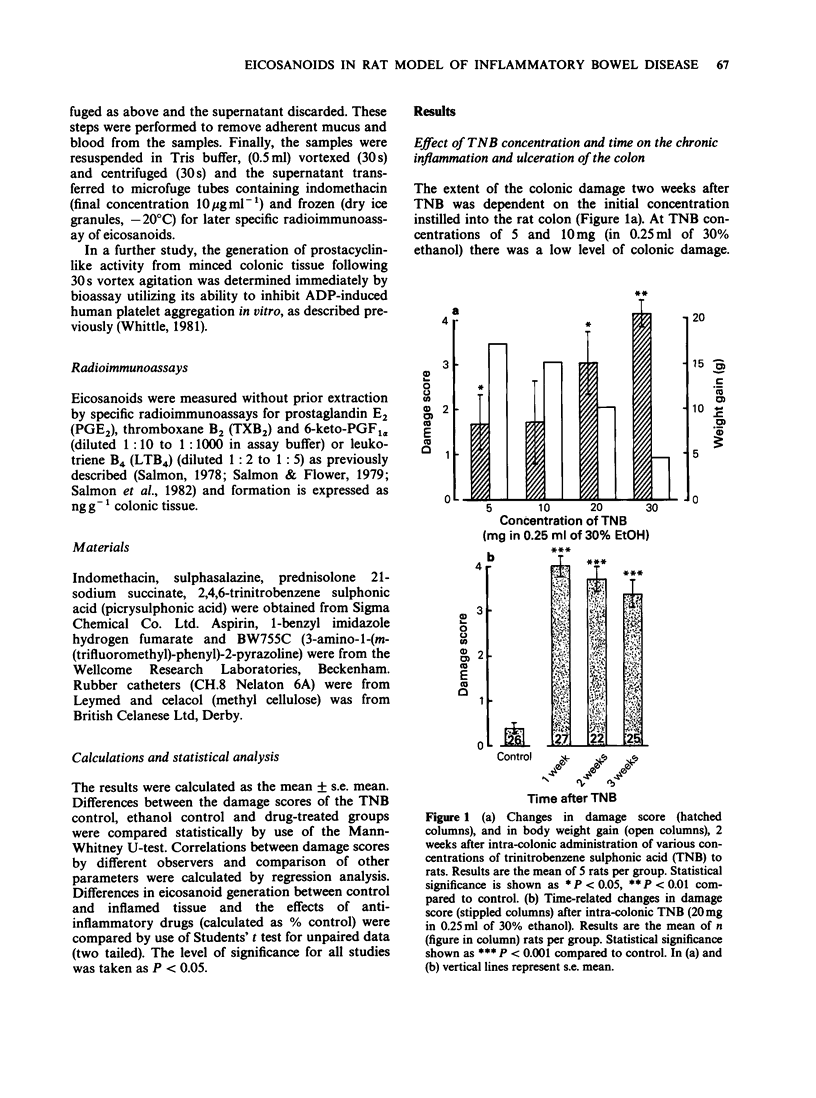
1. The effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on eicosanoid formation and colonic damage in a chronic model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in the rat were investigated. 2. A single colonic instillation of the hapten, trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNB) resulted in ulceration and inflammation which persisted for 3 weeks. 3. The macroscopic colonic damage, present 3 weeks after TNB, was correlated with an increase in immunoreactive 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (6-keto-PGF1 alpha) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) synthesis by the rat colon. 4. Anti-inflammatory drugs were administered 2 weeks after TNB, when there was substantial colonic damage, and continued for a week. The experimental drug BW755C inhibited the increased formation of 6-keto-PGF1 alpha and LTB4 by the inflamed colon. Indomethacin and aspirin markedly inhibited prostanoid formation in both inflamed and control colon. Sulphasalazine or prednisolone also inhibited the formation of 6-keto-PGF1 alpha but the effects were less marked. 5. None of the anti-inflammatory drugs significantly reduced the colonic damage induced by TNB. 6. The results suggest that eicosanoids, including LTB4, have only a minor role in maintaining the chronic macroscopic damage induced in the rat colon by TNB. The role of such eicosanoids in the underlying infiltration and activity of inflammatory cells in this model of IBD, however, is not known.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Hawkey C. J., Whittle B. J. Biosynthesis of lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase products from [14C]-arachidonic acid by human colonic mucosa. Gut. 1983 Dec;24(12):1176–1182. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.12.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Whittle B. J. Increased metabolism of arachidonic acid in an immune model of colitis in guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):439–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. R., Brash A. R., Conolly M. E., Lennard-Jones J. E. Studies of prostaglandins and sulphasalazine in ulcerative colitis. Prostaglandins Med. 1981 Feb;6(2):165–182. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(81)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. W., Smith P. R., Swan C. H. Determination of prostaglandin synthetase activity in rectal biopsy material and its significance in colonic disease. Gut. 1978 Oct;19(10):875–877. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.10.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. J., Boughton-Smith N. K., Whittle B. J. Modulation of human colonic arachidonic acid metabolism by sulfasalazine. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Dec;30(12):1161–1165. doi: 10.1007/BF01314051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Eakins K. E., Mugridge K. G., Moncada S., Vane J. R. The effects of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs on leukocyte migration in carrageenin-induced inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 22;66(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Eicosanoids in inflammation. Ann Clin Res. 1984;16(5-6):287–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Karmeli F., Sharon P., Zor U., Cohen F., Rachmilewitz D. Enhanced thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin production by cultured rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis and its inhibition by steroids and sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. 1981 Sep;81(3):444–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris A. A., Lewis A. J., Zeitlin I. J. Changes in colonic tissue levels of inflammatory mediators in a guinea-pig model of immune colitis. Agents Actions. 1982 Apr;12(1-2):243–246. doi: 10.1007/BF01965154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppercorn M. A., Goldman P. Distribution studies of salicylazosulfapyridine and its metabolites. Gastroenterology. 1973 Feb;64(2):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A. A radioimmunoassay for 6-keto-prostaglandin F1alpha. Prostaglandins. 1978 Mar;15(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Simmons P. M., Moncada S. The effects of BW755C and other anti-inflammatory drugs on eicosanoid concentrations and leukocyte accumulation in experimentally-induced acute inflammation. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;35(12):808–813. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1983.tb02901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Simmons P. M., Palmer R. M. A radioimmunoassay for leukotriene B4. Prostaglandins. 1982 Aug;24(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Ligumsky M., Rachmilewitz D., Zor U. Role of prostaglandins in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):638–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Metabolism of arachidonic acid in acetic acid colitis in rats. Similarity to human inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Temporal relationship between cyclooxygenase inhibition, as measured by prostacyclin biosynthesis, and the gastrointestinal damage induced by indomethacin in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jan;80(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser R. D., Nast C. C., Lee M., Kao H. W., Duke R. In vivo production of leukotriene B4 and leukotriene C4 in rabbit colitis. Relationship to inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90836-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



