Abstract
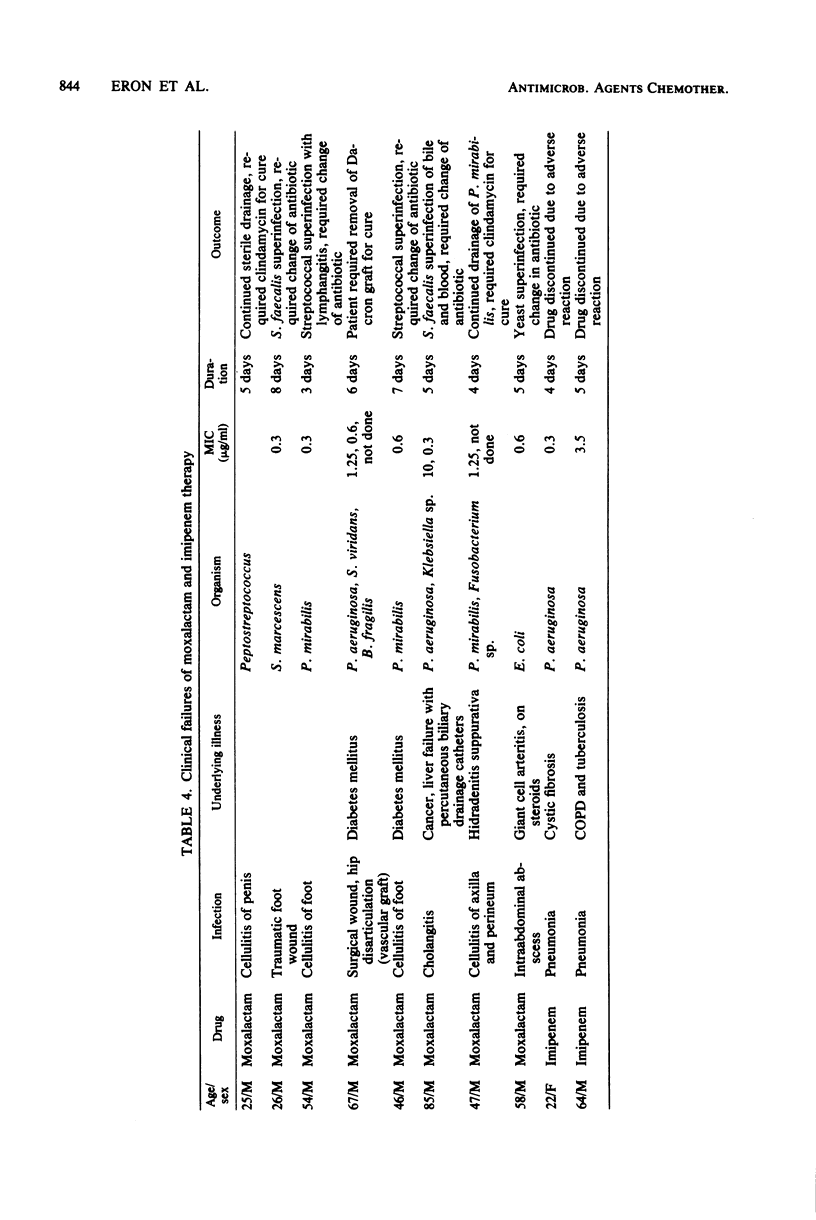
Imipenem (formerly imipemide, N-formimidoyl thienamycin, or MK0787) was compared to moxalactam in a randomized therapeutic trial involving 39 evaluable patients with serious bacterial infections. Of those treated with imipenem, 89% were cured or improved versus 60% for moxalactam (P = 0.06). Although mucocutaneous fungal infections occurred in both groups (25 and 10%, respectively), Streptococcus faecalis superinfection was seen in two patients in the moxalactam group only. Adverse drug reactions occurred with both drugs, although bleeding occurred in three patients treated with moxalactam.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corrado M. L., Landesman S. H., Cherubin C. E. Influence of inoculum size on activity of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, moxalactam, piperacillin, and N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):893–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., Goldenberg R. I., Park C. H., Poretz D. M. Ceftazidime therapy of serious bacterial infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):236–241. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathisen G. E., Meyer R. D., Thompson J. M., Finegold S. M. Clinical evaluation of moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):780–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Barza M. Clinical experience with Moxalactam in the treatment of pseudomonal and nonpseudomonal infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Alestig K., Björnegård B., Burman L. A., Ferber F., Huber J. L., Jones K. H., Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Kropp H. Urinary recovery of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) as affected by coadministration of N-formimidoyl thienamycin dehydropeptidase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):300–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt R., Ehrlich S. L., Afarian J., O'Brien T. F., Pennington J. E., Kass E. H. Moxalactam therapy of infections caused by cephalothin-resistant bacteria: influence of serum inhibitory activity on clinical response and acquisition of antibiotic resistance during therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzer W., Pegram P. S., Jr, McCall C. E. Clinical evaluation of moxalactam: evidence of decreased efficacy in gram-positive aerobic infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):565–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K. E., Cleary T. J., Finegold S. M., Hill G. B., Iannini P. B., McCloskey R. V. Susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States in 1981. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):536–540. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitekamp M. R., Aber R. C. Prolonged bleeding times and bleeding diathesis associated with moxalactam administration. JAMA. 1983 Jan 7;249(1):69–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L. Enterococcal superinfection and colonization after therapy with moxalactam, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):784–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



