Abstract
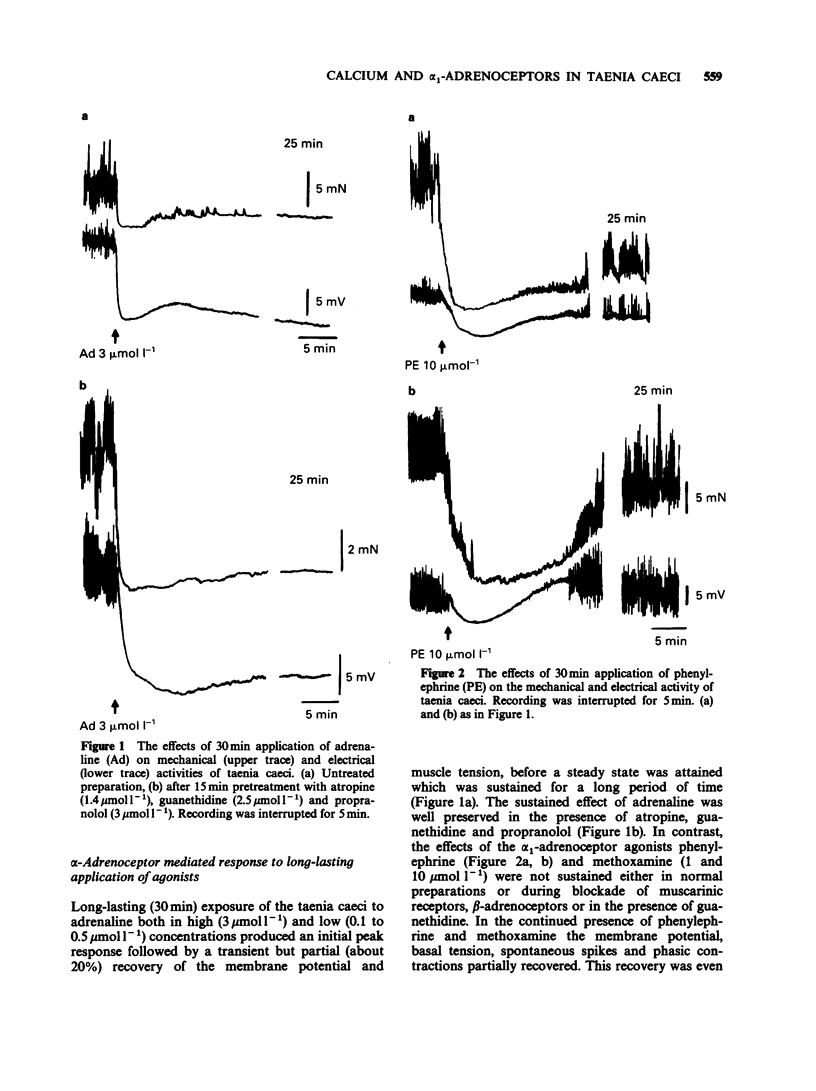
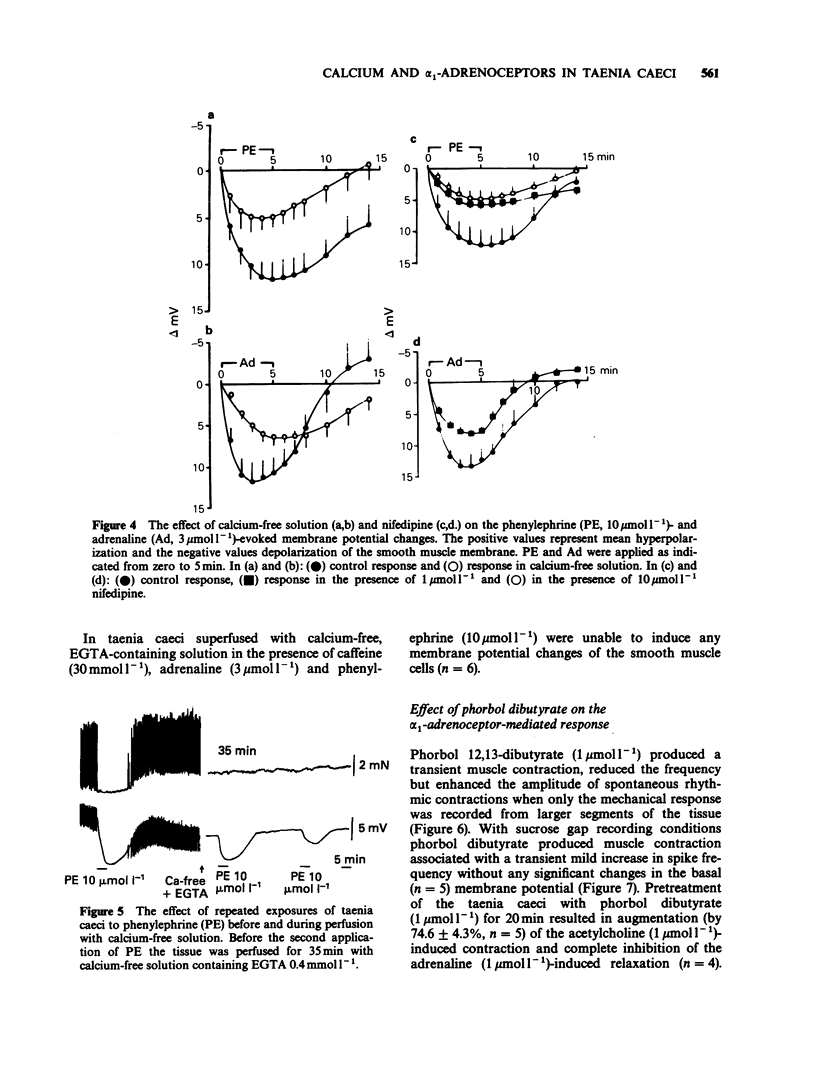
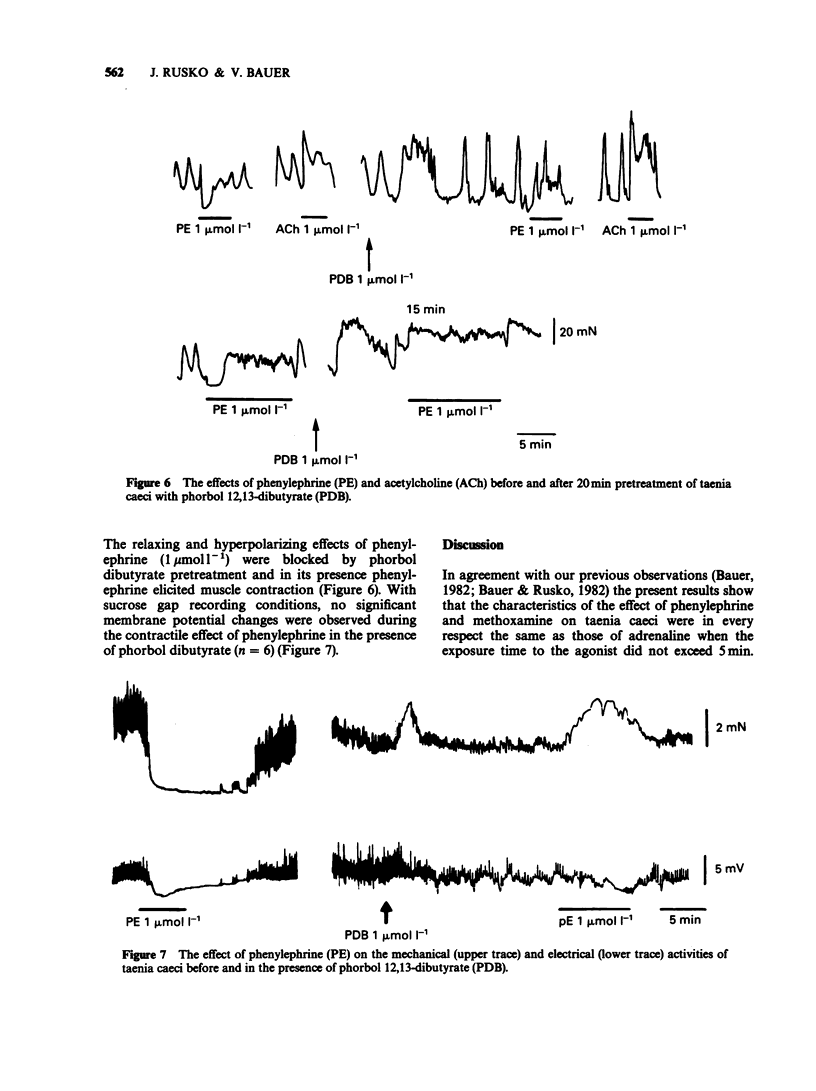
1. The actions of phenylephrine (0.1-100 mumol l-1) and methoxamine (0.1-100 mumol l-1) were compared with that of adrenaline (0.01-10 mumol l-1) using the single sucrose gap method and mechanical recording in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Drugs were applied for variable periods of time. 2. The characteristics of the inhibitory effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists were the same when exposure time did not exceed 5 min. When the exposure was prolonged, in contrast to the sustained effects of adrenaline (0.1-3 mumol l-1), phenylephrine and methoxamine (1-10 mumol l-1) produced a transient inhibitory action. 3. During the delayed recovery phase of phenylephrine, adrenaline preserved its ability to suppress the spontaneous electrical and mechanical activities of the taenia both when phenylephrine was replaced by adrenaline or when adrenaline was applied in addition to phenylephrine. All the above effects were found in untreated preparations, as well as during blockade of muscarinic cholinoceptors by atropine (1.4 mumol l-1), beta-adrenoceptors by propranolol (3 mumol l-1) and release of endogenous catecholamines by guanethidine (2.5 mumol l-1). 4. In the presence of phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate adrenaline ceased to be effective, while the inhibitory action of phenylephrine was converted to a contraction. 5. In calcium-free conditions in the presence of EGTA (0.4 mmol l-1) the initial hyperpolarization induced by adrenaline and phenylephrine was significantly reduced and with repeated applications of the agonists the inhibitory response disappeared. Similar results were obtained using tissues treated with nifedipine (1 and 10 mumol l-1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allgaier C., Hertting G. Polymyxin B, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, diminishes the release of noradrenaline and the enhancement of release caused by phorbol 12,13-butyrate. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;334(2):218–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00505825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V. Effects of 3,4-diaminopyridine and tetraethylammonium on the pre- and post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor mediated inhibitory actions of noradrenaline in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Calcium requirement for the alpha-action of catecholamines on guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Jun 15;197(1128):271–284. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Effect of calcium, barium and manganese on the action of adrenaline in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):121–136. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Increase of membrane conductance by adrenaline in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):89–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Suppression of spontaneous spike generation by catecholamines in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):103–119. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauvin C., Loutzenhiser R., Van Breemen C. Mechanisms of calcium antagonist-induced vasodilation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:373–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A. Calcium and the action of adrenaline, adenosine triphosphate and carbachol on guinea-pig taenia caeci. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:423–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A. Calcium and the alpha-action of catecholamines on guinea-pig taenia caeci. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:109–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egashira K. Hyperpolarization by noradrenaline in guinea pig liver cells: effects of ouabain and external Ca2+. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(3):473–485. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhurst A. S., Whittaker M. L., Ehlert F. J. Interactions of D600 (methoxyverapamil) and local anesthetics with rat brain alpha-adrenergic and muscarinic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;29(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis R. A., Scriabine A. Sites of action of Ca2+ channel inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 1;32(23):3499–3507. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelemans A., Den Hertog A. Changes in membrane potential and phosphoinositides during alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 13;133(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Biphasic modulation of potassium release in rat parotid gland by carbachol and phenylephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough N. L., Carrier G. O. Nifedipine and alpha adrenoceptors in rat aorta. II. Role of extracellular calcium in enhanced alpha-2 adrenoceptor-mediated contraction in diabetes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):603–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Relief of Na+ block of Ca2+-activated K+ channels by external cations. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):187–199. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


