Abstract
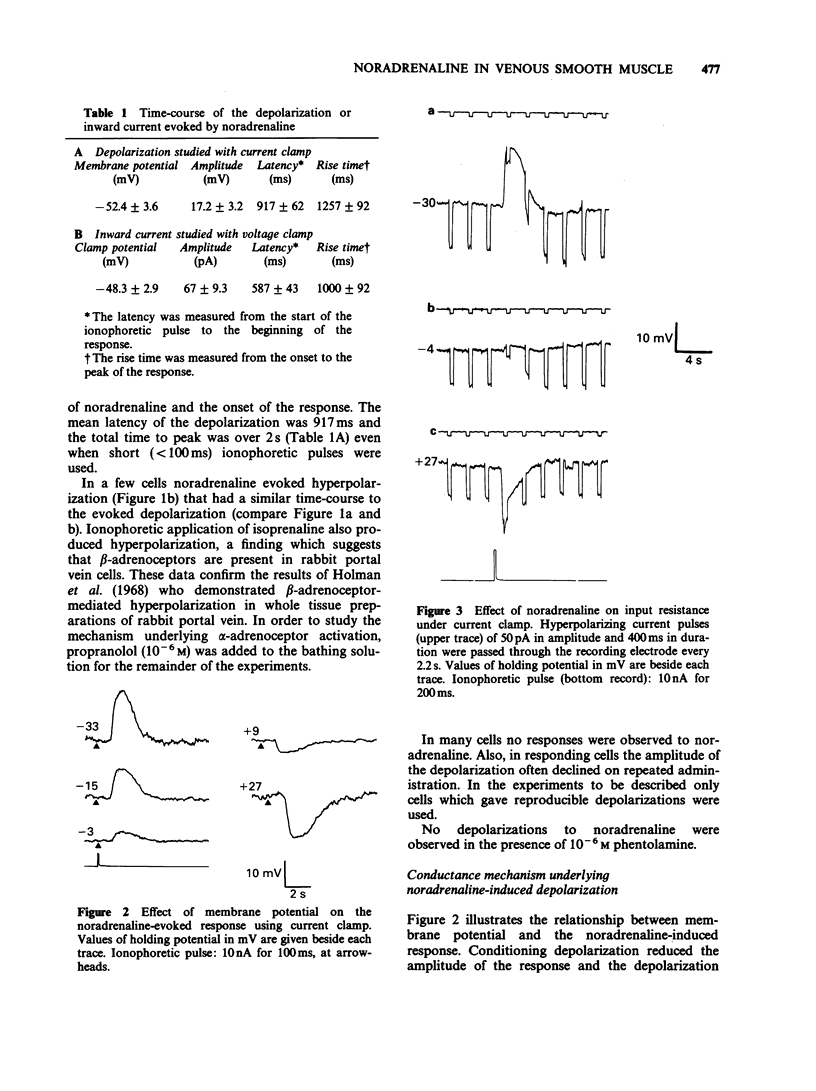
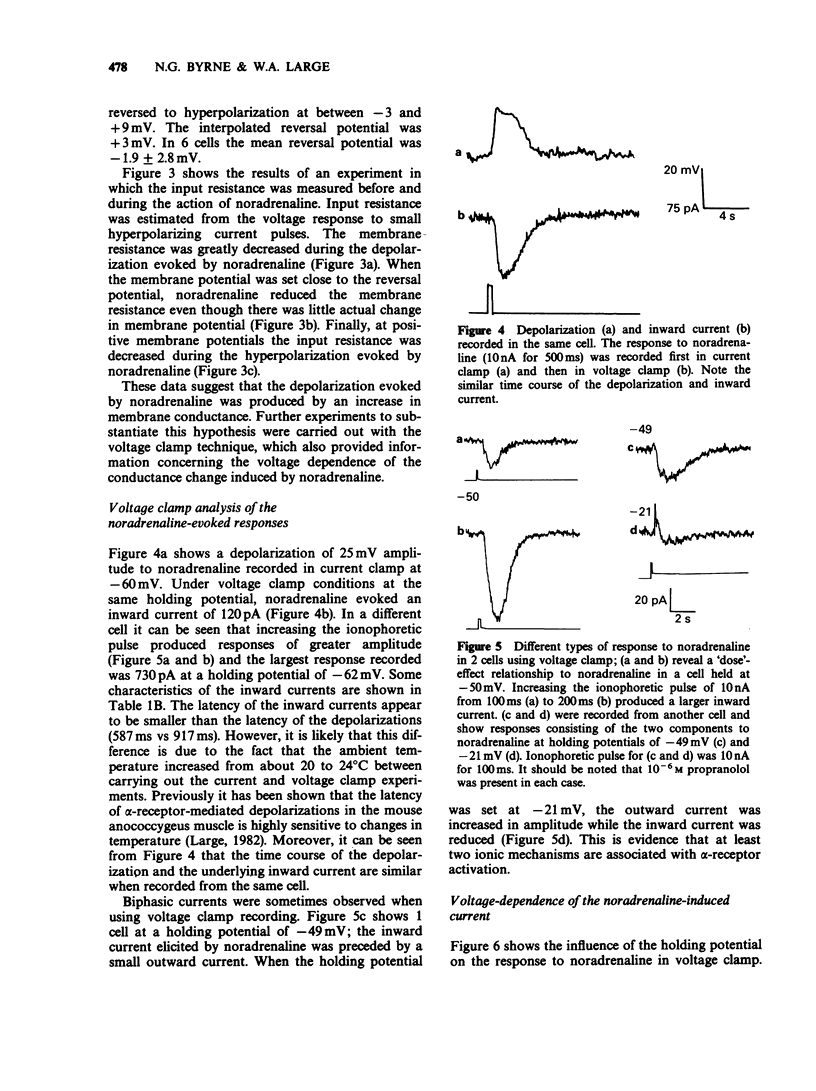
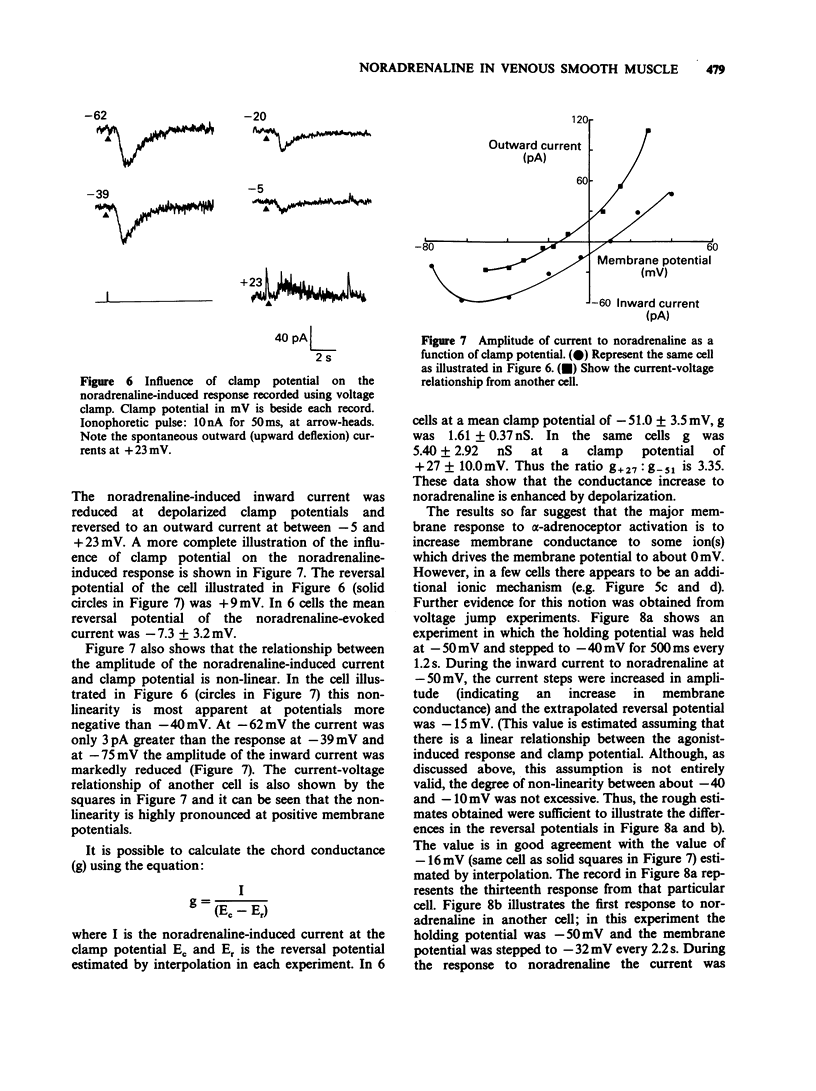
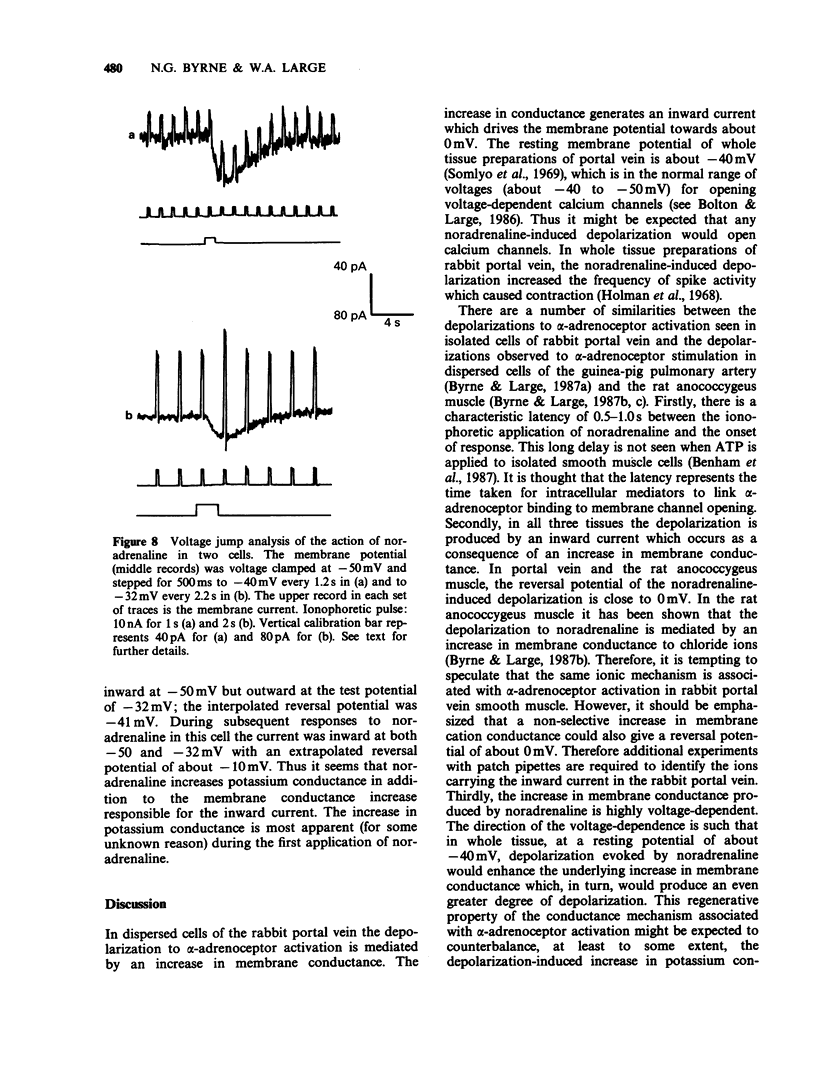
1. The action of noradrenaline was studied in freshly dispersed cells of the rabbit portal vein using microelectrode techniques. 2. In normal physiological salt solution, the ionophoretic application of noradrenaline evoked an alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated depolarization and sometimes a beta-adrenoceptor-mediated hyperpolarization. Experiments were carried out in the presence of propranolol to study the membrane mechanism associated with alpha-adrenoceptor activation. 3. In the current clamp mode of recording, the equilibrium potential of the noradrenaline-evoked depolarization was -1.9 mV. The depolarization was brought about by an increase in membrane conductance. 4. Under voltage clamp conditions, noradrenaline produced an inward current with a reversal potential of -7 +/- 3 mV (mean +/- s.e. mean). 5. The relationship between the noradrenaline-induced inward current and clamp potential was non-linear. Depolarization enhanced the conductance elicited by noradrenaline. 6. Evidence is presented which suggests that an additional conductance mechanism (probably an increase in potassium conductance) is also evoked by alpha-adrenoceptor stimulation in dispersed cells of rabbit portal vein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Action of externally applied adenosine triphosphate on single smooth muscle cells dispersed from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:473–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Large W. A. Are junction potentials essential? Dual mechanism of smooth muscle cell activation by transmitter released from autonomic nerves. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jan;71(1):1–28. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Action of noradrenaline on single smooth muscle cells freshly dispersed from the rat anococcygeus muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:513–525. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Evidence for two mechanisms of depolarization associated with alpha 1-adrenoceptor activation in the rat anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):711–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Membrane mechanism associated with muscarinic receptor activation in single cells freshly dispersed from the rat anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):371–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11333.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. The action of noradrenaline on single smooth muscle cells freshly dispersed from the guinea-pig pulmonary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung D. W. An electrophysiological study of alpha-adrenoceptor mediated excitation-contraction coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rat saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):265–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenhofen K., Hermstein N., Lammel E. Membrane potential and contraction of vascular smooth muscle (portal vein) during application of noradrenaline and high potassium, and selective inhibitory effects of iproveratril (verapamil). Microvasc Res. 1973 Jan;5(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/s0026-2862(73)80007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Kasby C. B., Suthers M. B., Wilson J. A. Some properties of the smooth muscle of rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):111–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large W. A. Membrane potential responses of the mouse anococcygeus muscle to ionophoretically applied noradrenaline. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:385–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. D., McCafferty G. P., Grous M. Characterization of alpha adrenoceptors on vascular smooth muscle: electrophysiological differentiation in canine saphenous vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Vinall P., Somlyo A. P. Excitation-contraction coupling and electrical events in two types of vascular smooth muscle. Microvasc Res. 1969 Oct;1(4):354–373. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(69)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. Adrenergic transmission in the dog mesenteric vein and its modulation by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;81(3):479–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. Effects of endogenous and exogenous noradrenaline on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig mesenteric vein. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:495–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. Increase in membrane resistance during noradrenaline-induced depolarization in arterial smooth muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1986;36(3):433–440. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.36.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström B. A. A study on the action of noradrenaline on ionic content and sodium, potassium and chloride effluxes in the rat portal vein. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Dec;89(4):522–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


