Abstract
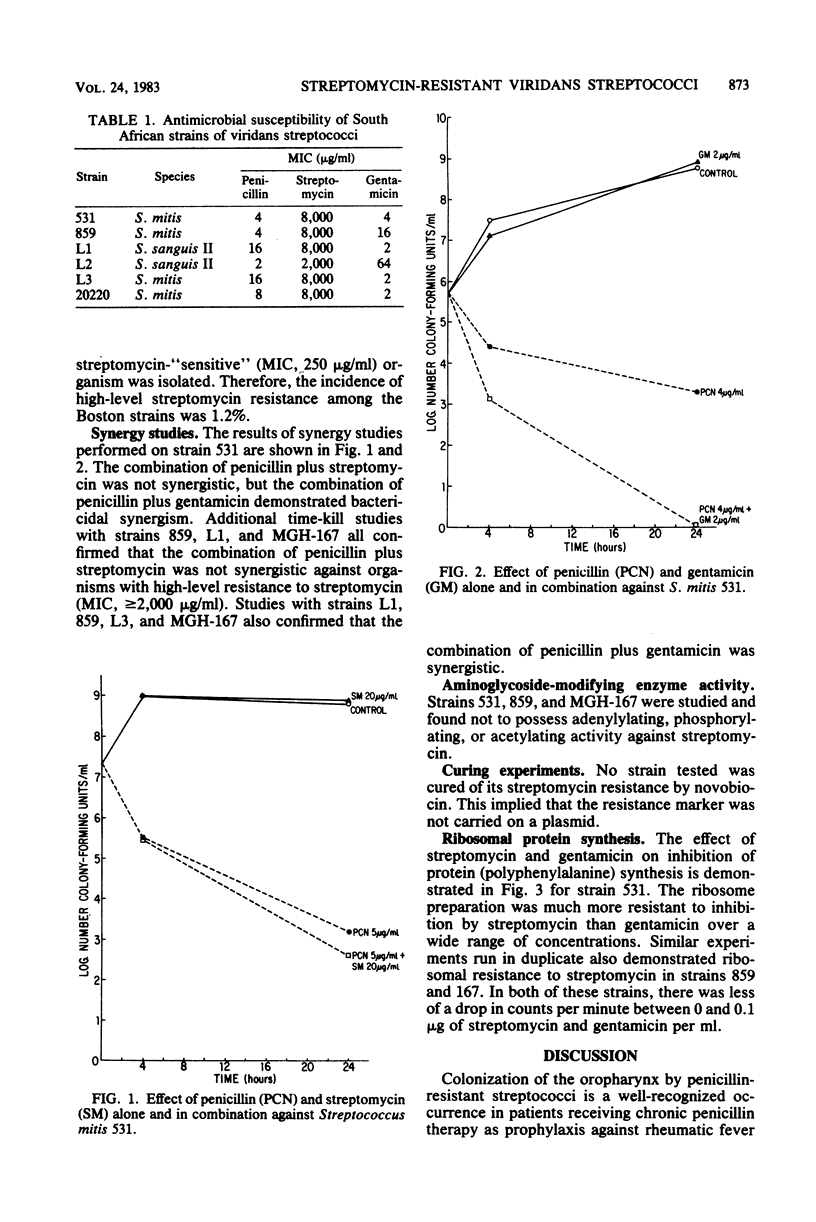
Viridans streptococci are thought to be highly susceptible to penicillin and streptomycin. We recently encountered a unique group of 15 isolates from South Africa epidemiologically related to the isolation of penicillin-resistant pneumococci. These organisms were highly resistant to penicillin (PCN) (minimal inhibitory concentration, 1 to 32 micrograms/ml) and streptomycin (SM) (minimal inhibitory concentration, greater than or equal to 2,000 micrograms/ml). Two additional organisms with high-level streptomycin resistance were identified when 168 clinical isolates from Boston were screened. Time-kill studies with four organisms resistant to high levels of SM demonstrated lack of synergy between PCN and SM but marked synergy between PCN and gentamicin. Adenylylating, acetylating, and phosphorylating activity could not be detected in three organisms studied, and novobiocin failed to cure the SM resistance. Protein synthesis by ribosomes isolated from these organisms was dramatically reduced in the presence of gentamicin but was relatively resistant to inhibition by SM.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L., Dismukes W. E., Durack D. T., Kaplan E. L., Karchmer A. W., Kaye D., Sande M. A., Sanford J. P., Wilson W. R. Treatment of infective endocarditis due to viridans streptococci, This statement was prepared by the ad hoc subcommittee on Treatment of Bacterial endocarditis of the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Circulation. 1981 Mar;63(3):730A–733A. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber B. F., Eliopoulos G. M., Ward J. I., Ruoff K. L., Syriopoulou V., Moellering R. C., Jr Multiply resistant viridans streptococci: susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics and comparison of penicillin-binding protein patterns. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):702–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey G. J., Neu H. C. Infective endocarditis--an evolving disease. A review of endocarditis at the Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center, 1968-1973. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Mar;57(2):105–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Tarpay M., Tomasz A. Multiple changes of penicillin-binding proteins in penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):364–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Buu-Hoï A., Delbos F., Bieth G. High-level aminoglycoside resistance in group A, B, G, D (Streptococcus bovis), and viridans streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):176–179. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Stevenson C. M., Vermaak Z. A., Freiman I., Miller G. B., Witcomb M. A., Isaäcson M., Ward J. I. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A. Properties of R plasmids determining gentamicin resistance by acetylation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):239–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Dismukes W. E., Buckley M. J., Austen W. G. Late prosthetic valve endocarditis: clinical features influencing therapy. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Korfhagen T. R., Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Swartz M. N. Plasmid-mediated resistance to antibiotic synergism in enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1645–1653. doi: 10.1172/JCI109085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Wennersten C. B. Species-specific resistance to antimocrobial synergism in Streptococcus faecium and Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci. I. Bacteriologic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Borst G. C., Mazur M. H., Iannini P., Klempner M. S., Moellering R. C., Jr, Anderson S. E. Endocarditis due to resistant viridans streptococci during oral penicillin chemoprophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 8;300(6):296–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902083000608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C., Harrison J. M., Sharples P., Ball L. C., Parker M. T. Antibiotic susceptibilities of streptococci from the mouth and blood of patients treated with penicillin or lincomycin and clindamycin. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):393–404. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kunz L. J. Identification of viridans streptococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):920–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.920-925.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K., Phillips I. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides in clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Feb;9(2):91–102. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Okanishi M., Kondo S., Hamana K., Utahara R., Maeda K., Mitsuhashi S. Phosphorylative inactivation of aminoglycosidic antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying R factor. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1559–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of pneumococci to 14 beta-lactam agents: comparison of strains resistant, intermediate-resistant, and susceptible to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):204–207. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. C., Johnson W. D. Penicillin-sensitive streptococcal endocarditis. In-vitro and clinical observations on penicillin-streptomycin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Aug;81(2):178–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-2-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


