Abstract
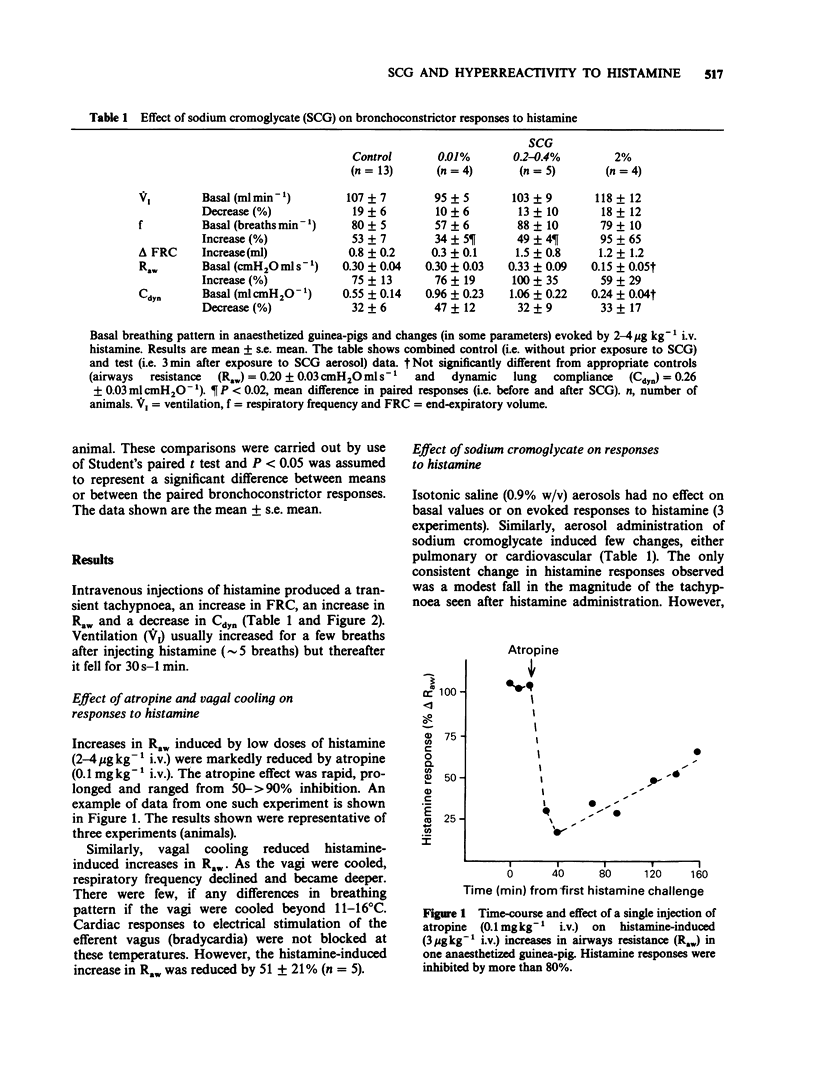
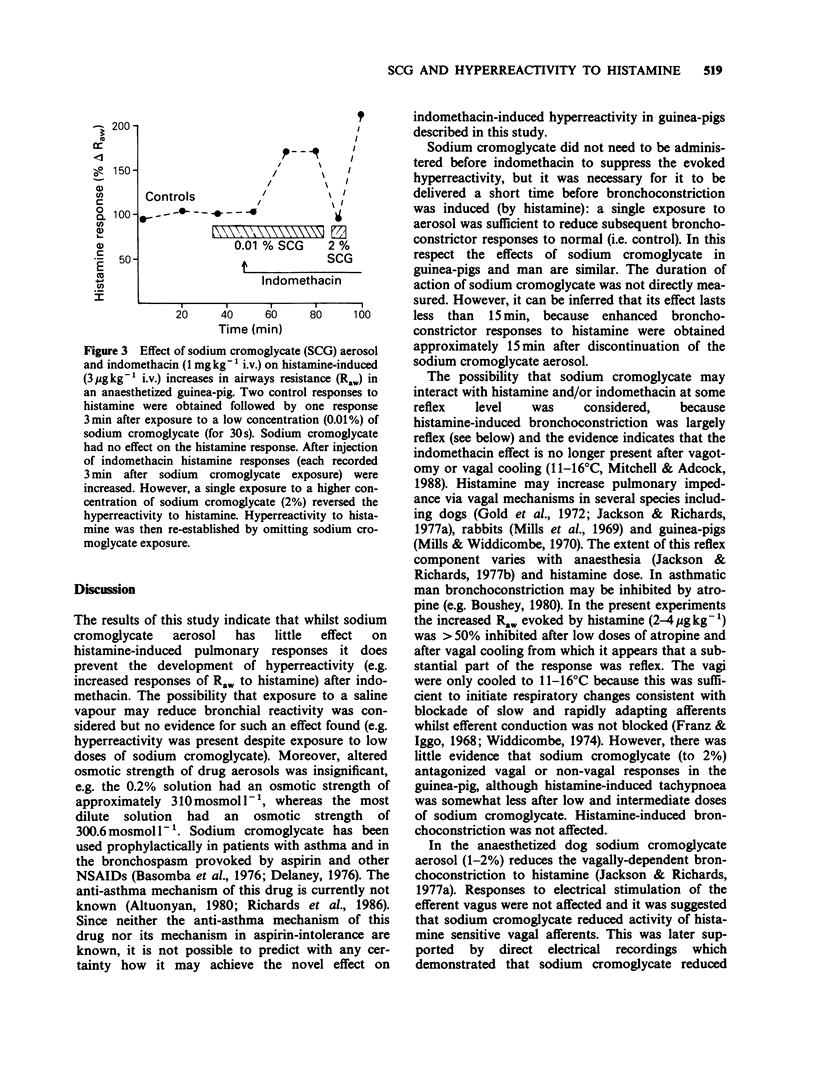
1. Histamine (2-4 micrograms kg-1 i.v.) increased airways resistance (Raw) and decreased dynamic lung compliance (Cdyn) in urethane-anaesthetized guinea-pigs. The effects on Raw were almost abolished by atropine (0.1 mg kg-1 i.v.) and reduced by vagal cooling (11-16 degrees C). 2. Histamine-induced changes in Raw and Cdyn were significantly (P less than 0.05) enhanced by indomethacin (1 mg kg-1 i.v.). 3. In animals not treated with indomethacin, exposure to an aerosol containing sodium cromoglycate (0.01-2% for 30 s) failed to affect subsequent (3 min) histamine-induced bronchoconstriction. 4. Administration of an aerosol containing low (0.01-0.2%) concentrations of sodium cromoglycate had no effect on the enhanced responses (i.e. hyperreactivity) seen after indomethacin. However, more concentrated sodium cromoglycate aerosols (greater than 0.2%) reduced or abolished the hyperreactivity to histamine seen after indomethacin. 5. It was concluded that sodium cromoglycate can prevent the development of hyperreactivity to histamine, possibly by interacting with some mechanism utilized by both histamine and indomethacin in this model.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altounyan R. E. Review of clinical activity and mode of action of sodium cromoglycate. Clin Allergy. 1980 Jul;10 (Suppl):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1980.tb02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basomba A., Romar A., Peláez A., Villalmanzo I. G., Campos A. The effect of sodium cromoglycate in preventing aspirin induced bronchospasm. Clin Allergy. 1976 May;6(3):269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basran G. S., Page C. P., Paul W., Morley J. Cromoglycate (DSCG) inhibits responses to platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) in man: an alternative mode of action for DSCG in asthma? Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 17;86(1):143–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. G., Fuller R. W. Evidence for an effect of sodium cromoglycate on sensory nerves in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;16(6):639–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl R. Oral and inhaled sodium cromoglycate in challenge test with food allergens or acetylsalicylic acid. Allergy. 1981 Apr;36(3):161–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1981.tb01831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney J. C. The effect of sodium cromoglycate on analgesic-induced asthmatic reactions. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jul;6(4):365–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M., Jackson D. M., Richards I. M. The action of sodium cromoglycate on 'C' fibre endings in the dog lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;70(1):11–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish J. E., Ankin M. G., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Peterman V. I. Indomethacin modification of immediate-type immunologic airway responses in allergic asthmatic and non-asthmatic subjects: evidence for altered arachidonic acid metabolism in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):609–614. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz D. N., Iggo A. Conduction failure in myelinated and non-myelinated axons at low temperatures. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):319–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold W. M., Kessler G. F., Yu D. Y., Frick O. L. Pulmonary physiologic abnormalities in experimental asthma in dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Oct;33(4):496–501. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.4.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goose J., Blair A. M. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in the rat, induced with two homologous reagin-like antibodies and its specific inhibition with disodium cromoglycate. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):749–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Tajima K. Spontaneous activity in the trachea of dogs treated with indomethacin: an experimental model for aspirin-related asthma. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;73(2):563–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. M., Richards I. M. The effects of pentobarbitone and chloralose anaesthesia on the vagal component of bronchoconstriction produced by histamine aerosol in the anaesthetized dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;61(2):251–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. M., Richards I. M. The effects of sodium cromoglycate on histamine aerosol-induced reflex bronchoconstriction in the anaesthetized dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;61(2):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. E., Sellick H., Widdicombe J. G. Activity of lung irritant receptors in pulmonary microembolism, anaphylaxis and drug-induced bronchoconstrictions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):337–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. E., Widdicombe J. G. Role of the vagus nerves in anaphylaxis and histamine-induced bronchoconstrictions in guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Aug;39(4):724–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. W., Adcock J. Potency of several non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs on airways responses to histamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90566-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. W., Adcock J. Vagal mechanisms and the effect of indomethacin on bronchoconstrictor stimuli in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):522–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. W. Indomethacin enhances the effect of histamine on airways resistance in the anaesthetized guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):287–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murlas C., Lee H. K., Roum J. H. Indomethacin increases bronchial reactivity after exposure to subthreshold ozone levels. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1986 Mar;21(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(86)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler R. A., Mitchell H. W. Airways hyperreactivity and bronchoconstriction induced by vanadate in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):173–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne P. M., Jones G. L. The effect of indomethacin on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction and refractoriness after exercise. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):69–72. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards I. M., Dixon M., Jackson D. M., Vendy K. Alternative modes of action of sodium cromoglycate. Agents Actions. 1986 Jun;18(3-4):294–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01964987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczeklik A., Gryglewski R. J., Czerniawska-Mysik G. Clinical patterns of hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Nov;60(5):276–284. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woenne R., Kattan M., Levison H. Sodium cromoglycate-induced changes in the dose-response curve of inhaled methacholine and histamine in asthmatic children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):927–932. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



