Abstract
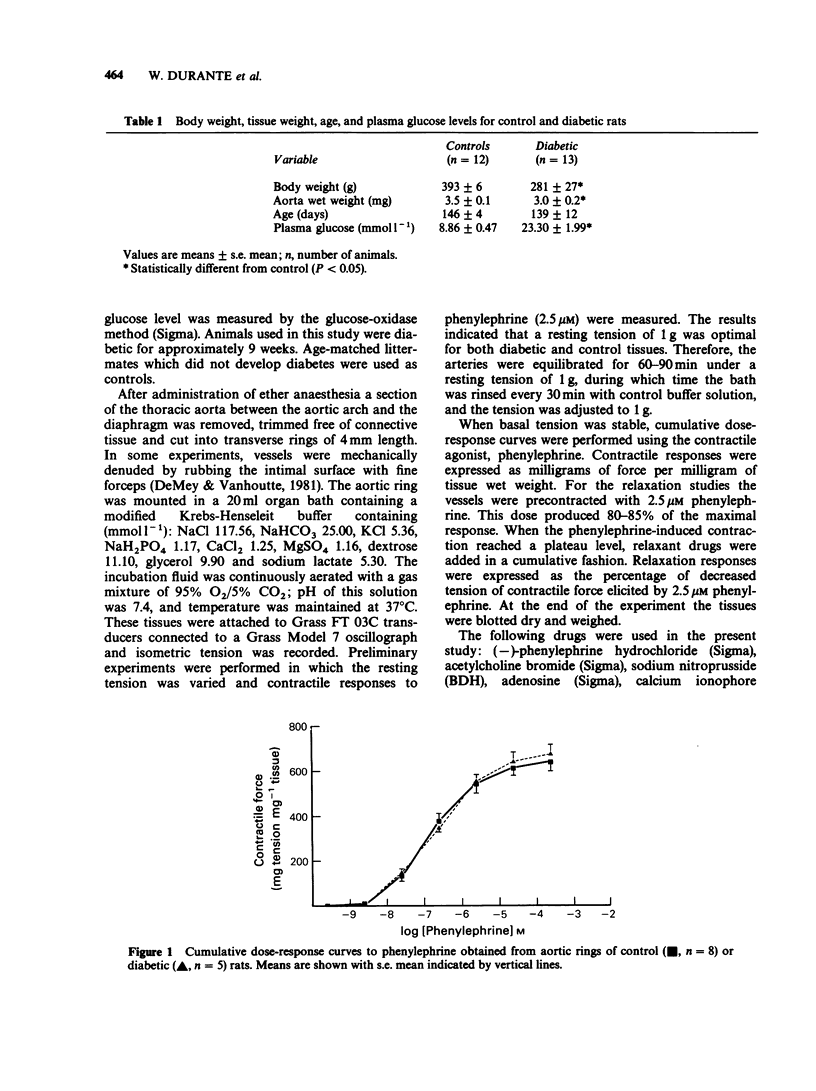
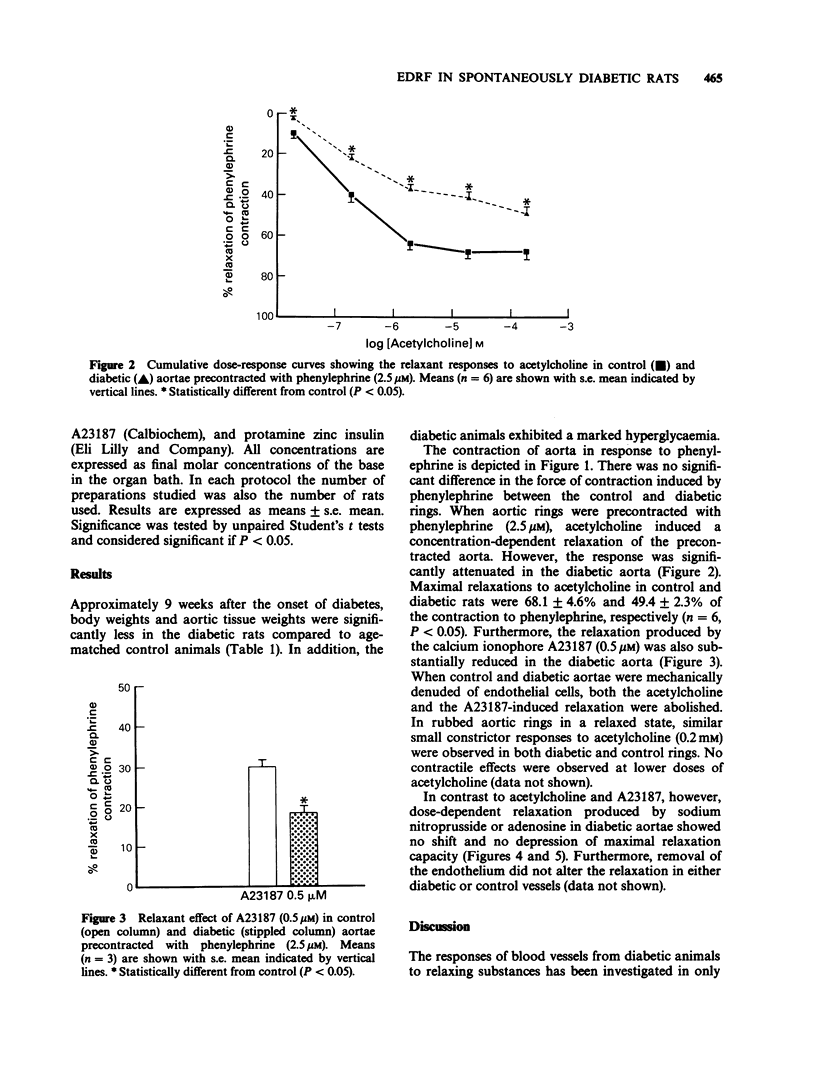
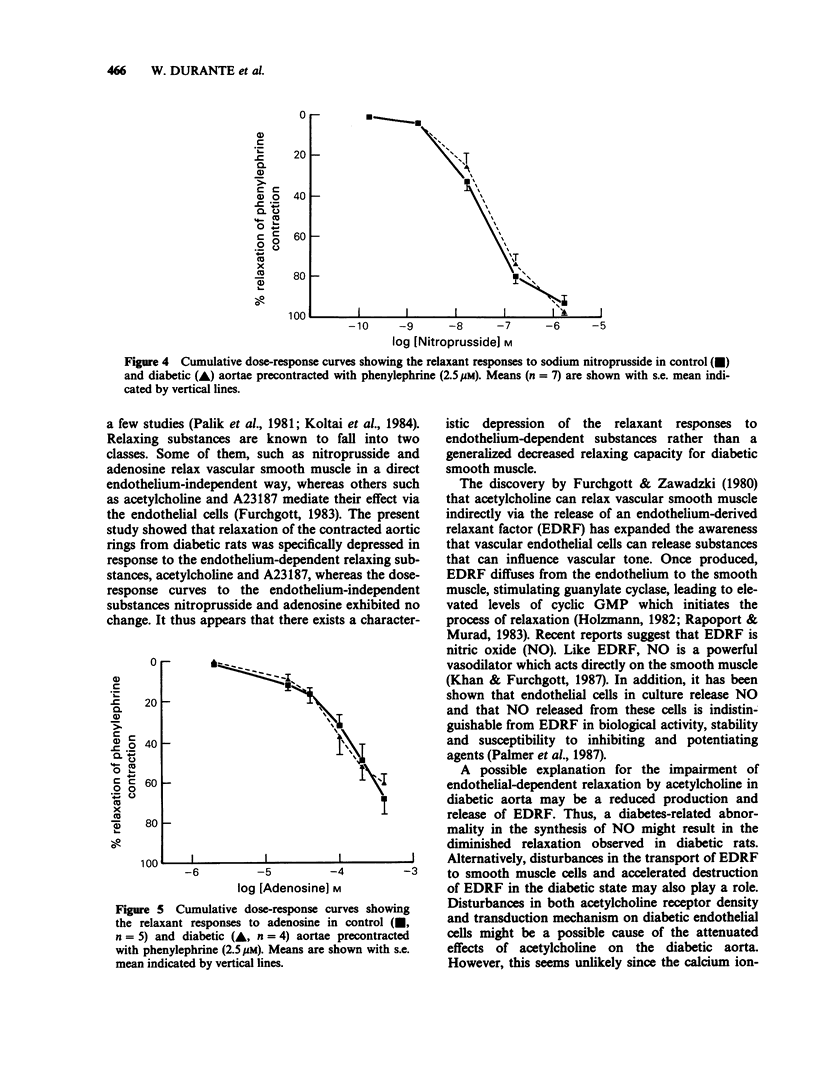
1. Diabetes mellitus is known to produce alterations in vascular reactivity. The present study examined the effects of endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent relaxing substances on thoracic aorta from control and spontaneously diabetic rats. 2. Endothelium-dependent relaxation produced by acetylcholine or the calcium ionophore, A23187, in aortic rings precontracted with phenylephrine was significantly attenuated in diabetic vessels. 3. Relaxations produced by sodium nitroprusside or adenosine in diabetic preparations were comparable to those in control vessels. 4. The results show that diabetes leads to a specific impairment of endothelial-dependent relaxation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODY M. J., DIXON R. L. VASCULAR REACTIVITY IN EXPERIMENTAL DIABETES MELLITUS. Circ Res. 1964 Jun;14:494–501. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.6.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christlieb A. R., Janka H. U., Kraus B., Gleason R. E., Icasas-Cabral E. A., Aiello L. M., Cabral B. V., Solano A. Vascular reactivity to angiotensin II and to norepinephrine in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1976 Apr;25(4):268–274. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.4.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Role of the intima in cholinergic and purinergic relaxation of isolated canine femoral arteries. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:347–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURCHGOTT R. F. The pharmacology of vascular smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1955 Jun;7(2):183–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. J., McNamara P. M., Gordon T., Kannel W. B. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann S. Endothelium-induced relaxation by acetylcholine associated with larger rises in cyclic GMP in coronary arterial strips. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(6):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakody R. L., Senaratne M. P., Thomson A. B., Kappagoda C. T. Cholesterol feeding impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit aorta. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;63(9):1206–1209. doi: 10.1139/y85-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M. Z., Jermendy G., Kiss V., Wagner M., Pogátsa G. The effects of sympathetic stimulation and adenosine on coronary circulation and heart function in diabetes mellitus. Acta Physiol Hung. 1984;63(2):119–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod K. M., McNeill J. H. The influence of chronic experimental diabetes on contractile responses of rat isolated blood vessels. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;63(1):52–57. doi: 10.1139/y85-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. P., Carrier G. O. Calcium dependence of norepinephrine-induced vascular contraction in experimental diabetes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Feb;212(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama Y., Kawasaki H., Hattori Y., Kanno M. Attenuation of endothelium-dependent relaxation in aorta from diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 2;132(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palik I., Hadházy P., Magyar K., Malomvölgyi B., Wagner M., Pogátsa G. Effects on prostaglandins F2 alpha, I2, and indomethacin on isolated coronary arteries from healthy and alloxan-diabetic dogs. Experientia. 1981;37(8):863–864. doi: 10.1007/BF01985683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffman M. A., Ball C. R., Darby A., Hilman R. Insulin reversal of diabetes-induced inhibition of vascular contractility in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):H490–H495. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.242.4.H490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough N. L., Carrier G. O. Increased alpha 2-adrenoreceptor mediated vascular contraction in diabetic rats. J Auton Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;3(3):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1983.tb00533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S., Sparks H. V. Diminished contractile response of aortas from diabetic rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):H301–H306. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.2.H301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi I., Hatake K., Kimura N., Kakishita E., Nagai K. Modulation of vascular tonus by the endothelium in experimental diabetes. Life Sci. 1987 Feb 16;40(7):643–648. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann P., Beretta-Piccoli C., Keusch G., Glück Z., Mujagic M., Grimm M., Meier A., Ziegler W. H. Sodium-volume factor, cardiovascular reactivity and hypotensive mechanism of diuretic therapy in mild hypertension associated with diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1979 Nov;67(5):779–784. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90734-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. E., Carrier G. O. Supersensitivity and endothelium dependency of histamine-induced relaxation in mesenteric arteries isolated from diabetic rats. Pharmacology. 1986;33(1):34–38. doi: 10.1159/000138197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Bunting P. B., Baskin E. P., Wallace A. A. Decreased endothelium-dependent relaxation in New Zealand genetic hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1984 Oct;2(5):541–545. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198410000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


