Abstract
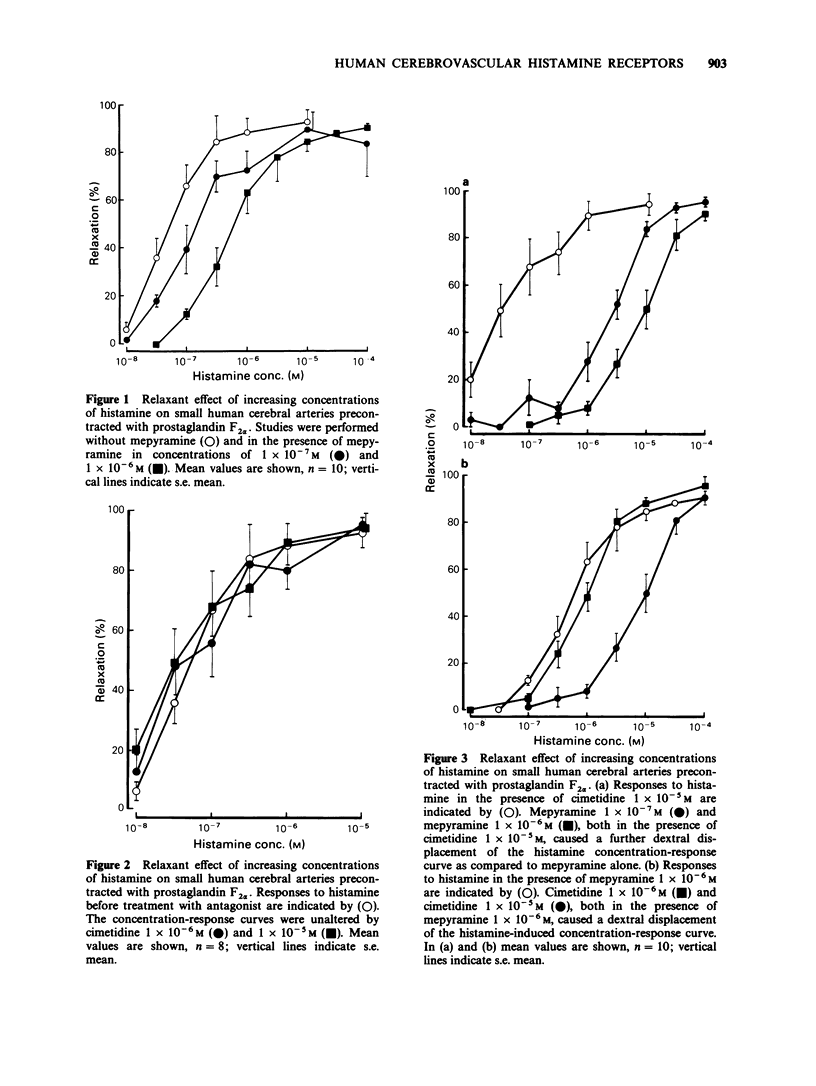
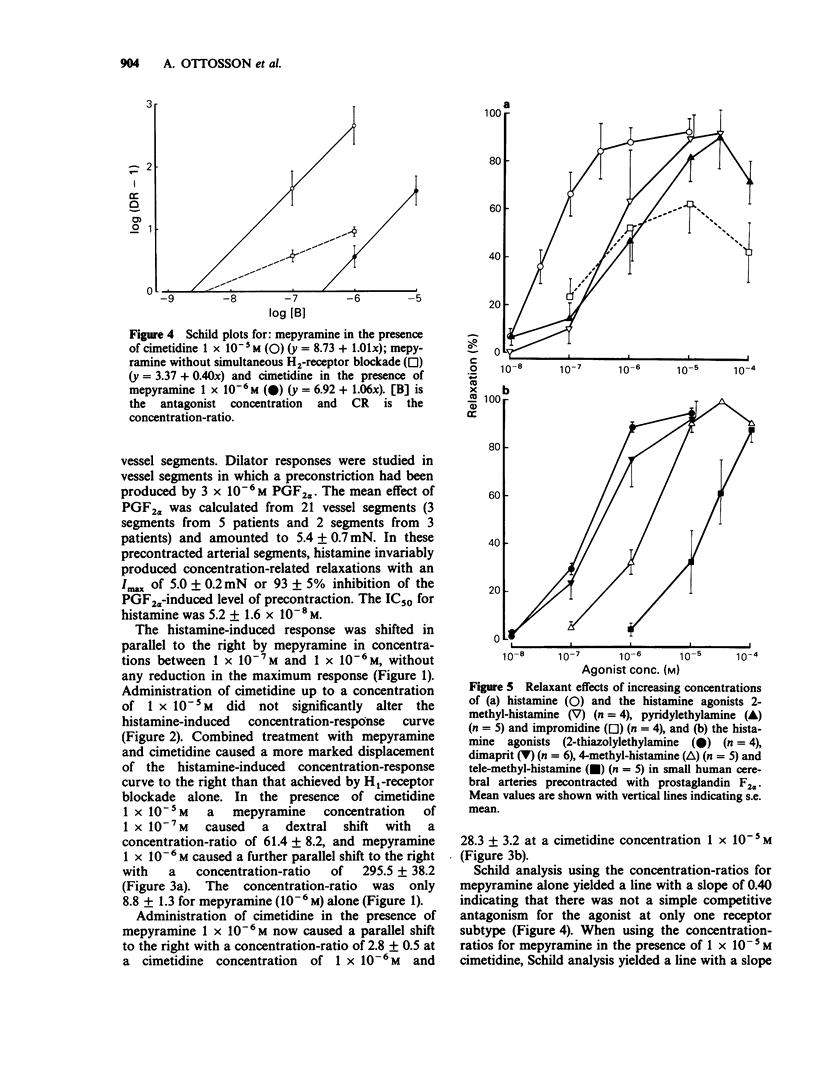
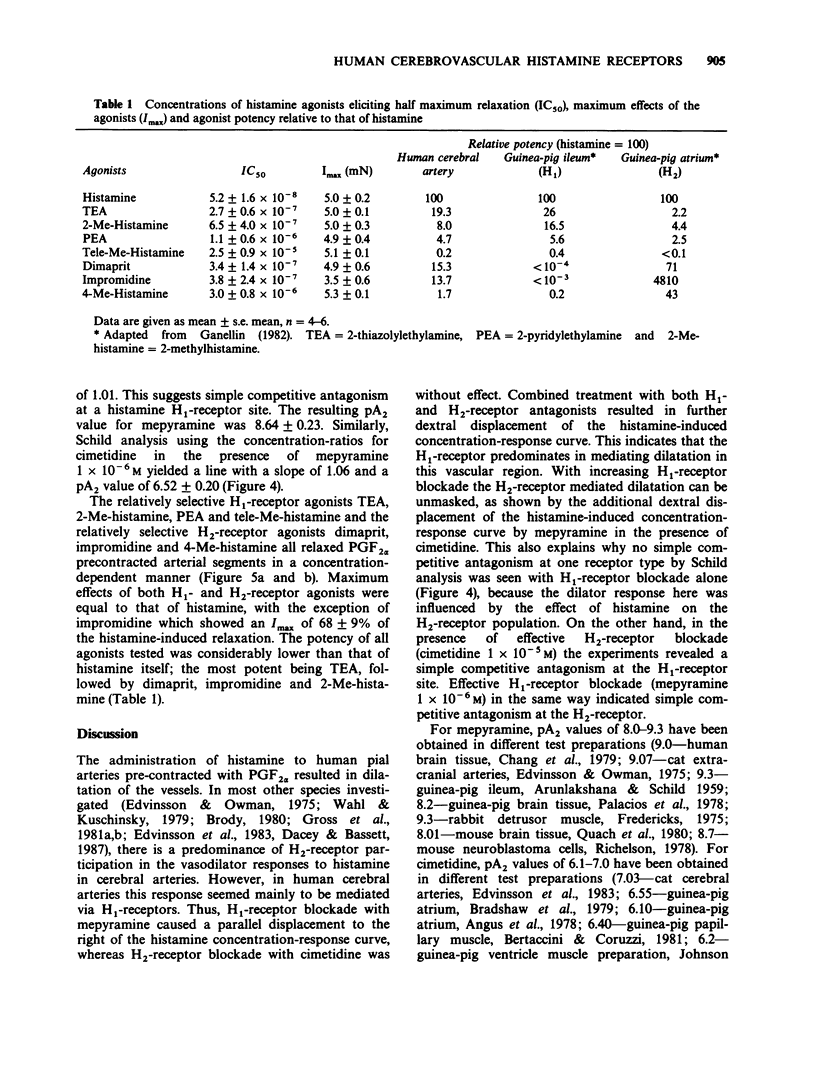
1. The subtypes of histamine-receptors which mediate dilatation of small human cerebral arteries have been characterized in vitro using 'selective' agonists and antagonists. 2. Dilator responses were studied after preconstriction with prostaglandin F2 alpha, since contraction was not seen with histamine concentrations up to 10(-4) M. Histamine caused a concentration-related relaxation of cerebral vessels with an IC50 value of 5.2 +/- 1.6 x 10(-8) M. 3. Mepyramine caused a parallel shift to the right of the histamine concentration-response curve whereas cimetidine was without observable effect. This suggests the presence of histamine H1-receptors only. However, combined treatment with mepyramine and cimetidine caused a more marked displacement of the concentration-response curve to the right. Schild analysis indicated that in situations of near complete blockade of either of the histamine receptor subtypes, simple competitive antagonism both at H1- and H2-receptors can be revealed with a pA2 value of 8.64 for mepyramine and a pA2 value of 6.52 for cimetidine. 4. The 'selective' H1-receptor agonists pyridylethylamine, 2-methylhistamine (2-Me-histamine) and thiazolylethylamine, and the H2-receptor agonists dimaprit, impromidine and 4-methylhistamine (4-Me-histamine) all mimicked the histamine response, but were less potent than histamine. The order of potency was thiazolylethylamine greater than dimaprit greater than impromidine greater than 2-Me-histamine greater than pyridylethylamine greater than 4-Me-histamine. 5. These results indicate that the histamine-induced dilatation in small human cerebral arteries is mediated by both H1- and H2-receptors and that the former subtype of histamine receptor predominates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARIENS E. J., SIMONIS A. M., VAN ROSSUM J. M. A theoretical basis of molecular pharmacology. III. Interaction of one or two compounds with two independent receptor systems. Arzneimittelforschung. 1956 Dec;6(12):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini G., Coruzzi G. Effect of impromidine (SK&F 92676) on the isolated papillary muscle of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):197–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Owen D. A., Parsons M. E. An analysis of the depressor responses to histamine in the cat and dog: involvement of both H1- and H2-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;54(3):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw J., Brittain R. T., Clitherow J. W., Daly M. J., Jack D., Price B. J., Stables R. Ranitidine (AH 19065): a new potent, selective histamine H2-receptor antagonist [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;66(3):464P–464P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneity of histamine H1-receptors: species variations in [3H]mepyramine binding of brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1979 Jun;32(6):1653–1663. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacey R. G., Jr, Bassett J. E. Histaminergic vasodilation of intracerebral arterioles in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Jun;7(3):327–331. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Cervós-Navarro J., Larsson L. I., Owman C., Rönnberg A. L. Regional distribution of mast cells containing histamine, dopamine, or 5-hydroxytryptamine in the mammalian brain. Neurology. 1977 Sep;27(9):878–883. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.9.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Gross P. M., Mohamed A. Characterization of histamine receptors in cat cerebral arteries in vitro and in situ. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Apr;225(1):168–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Owman C. A pharmacologic comparison of histamine receptors in isolated extracranial and intracranial arteries in vitro. Neurology. 1975 Mar;25(3):271–276. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Owman C., Sjöberg N. O. Autonomic nerves, mast cells, and amine receptors in human brain vessels. A histochemical and pharmacological study. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):377–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn S. B., Owen D. A. Histamine receptors in peripheral vascular beds in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredericks C. M. Characterization of the rabbit detrusor response to histamine through pharmacologic antagonism. Pharmacology. 1975;13(1):5–11. doi: 10.1159/000136879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. M. Cerebral histamine: indications for neuronal and vascular regulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1982;2(1):3–23. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1982.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. M., Harper A. M., Teasdale G. M. Cerebral circulation and histamine: 1. Participation of vascular H1- and H2-receptors in vasodilatory responses to carotid arterial infusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):97–108. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. M., Harper A. M., Teasdale G. M. Cerebral circulation and histamine: 2. Responses of pial veins and arterioles to receptor agonists. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(2):219–225. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. M. Histaminergic dilatation of resistance vessels in the brain. Bibl Cardiol. 1984;(38):138–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardebo J. E., Krabbe A. A., Gjerris F. Enhanced dilatory response to histamine in large extracranial vessels in chronic cluster headache. Headache. 1980 Nov;20(6):316–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1980.hed2006316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högestätt E. D., Andersson K. E., Edvinsson L. Mechanical properties of rat cerebral arteries as studied by a sensitive device for recording of mechanical activity in isolated small blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jan;117(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Harvey C. A., Gristwood R. W. Cardiovascular studies with impromidine (SK&F 92676), a new very potent and specific histamine H2-receptor agonist. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;31(9):577–582. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Harvey C. A., Quinn E. H. Vascular studies with histamine in vitro. Agents Actions. 1981 Apr;11(1-2):116–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01991477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A. Histamine receptors in the cardiovascular. Gen Pharmacol. 1977;8(3):141–156. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(77)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Garbarg M., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological characterization of histamine receptors mediating the stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in slices from guinea-pig hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):971–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Moskowitz M. A., Reinhard J. F., Jr, Snyder S. H. Neurotransmitter receptor binding in bovine cerebral microvessels. Science. 1980 May 9;208(4444):610–612. doi: 10.1126/science.6102801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polanin A., Longhurst P. A., McNeill J. H. Comparison of histamine receptors in left and right rabbit atria. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1980;23:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Duchemin A. M., Rose C., Schwartz J. C. 3H-Glycogen hydrolysis elicited by histamine in mouse brain slices: selective involvement of H1 receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 May;17(3):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Tricyclic antidepressants block histamine H1 receptors of mouse neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):176–177. doi: 10.1038/274176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Kuschinsky W. The dilating effect of histamine on pial arteries of cats and its mediation by H2 receptors. Circ Res. 1979 Feb;44(2):161–165. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


