Abstract
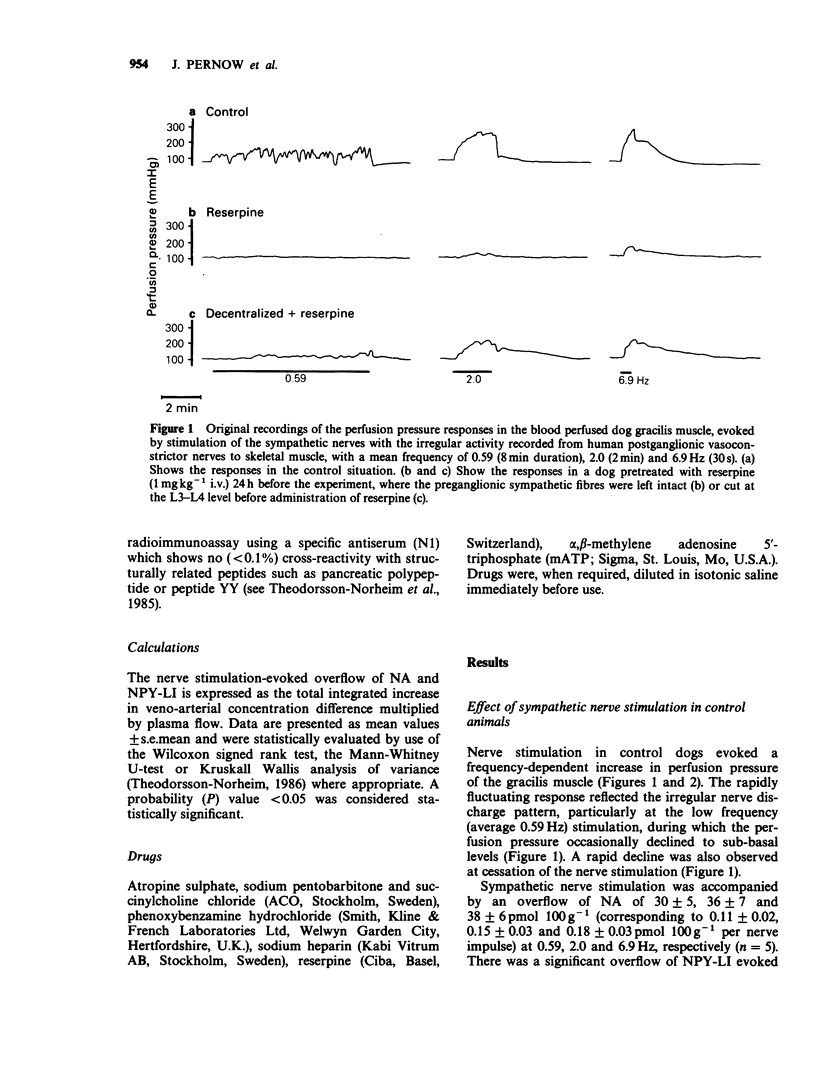
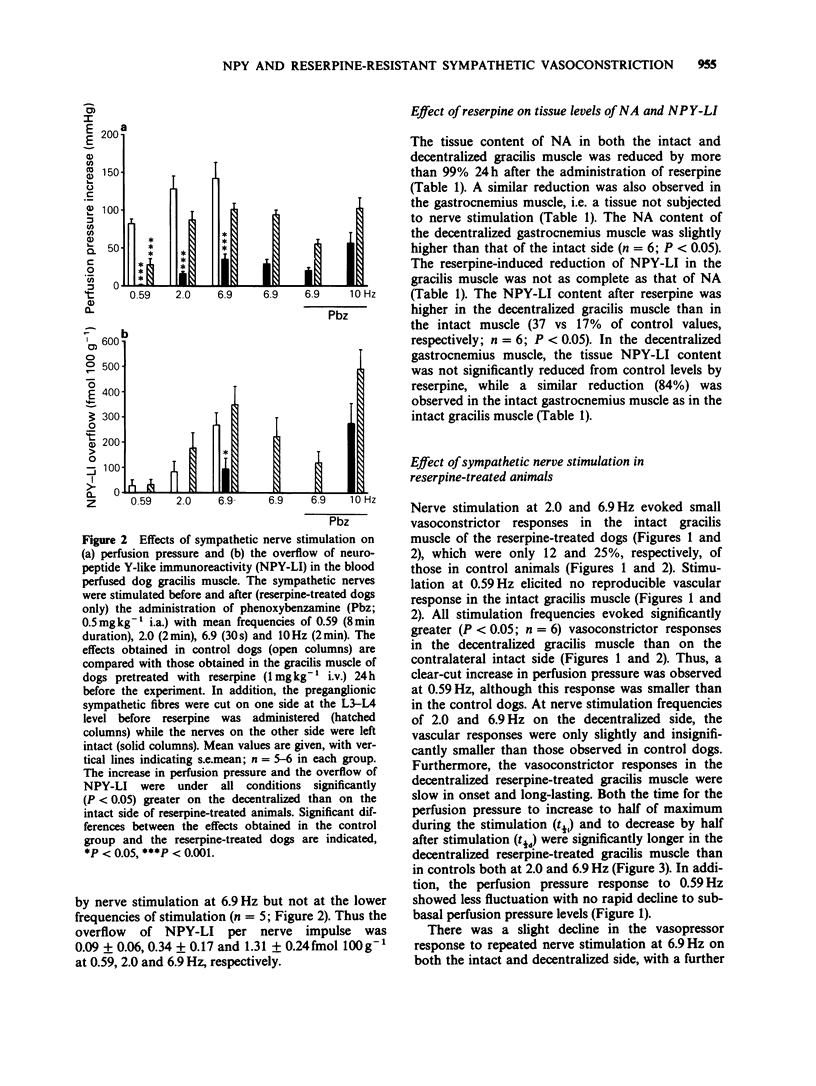
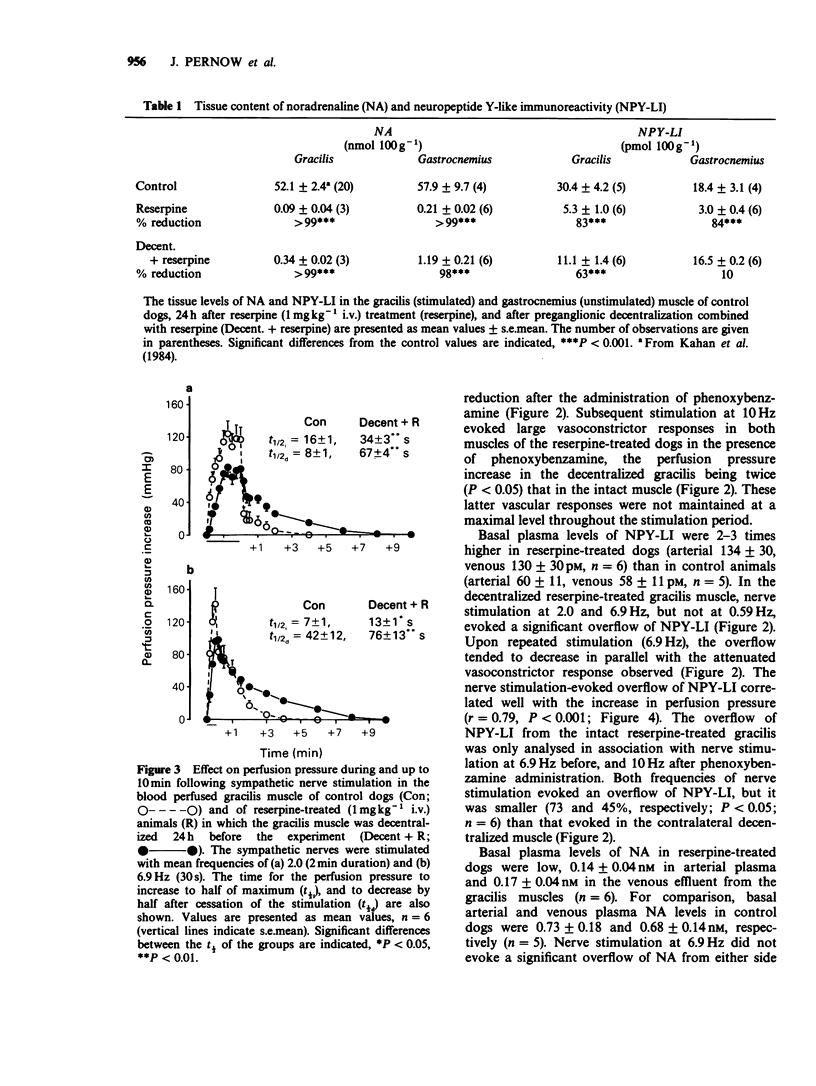
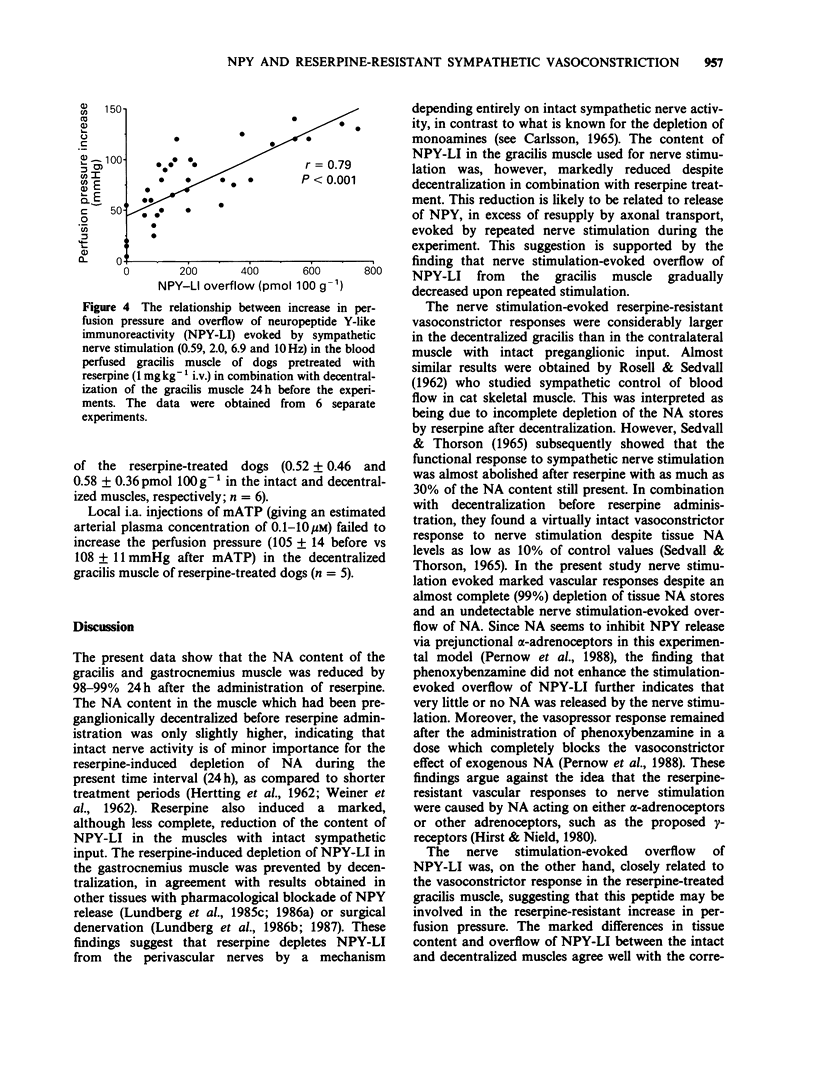
1. The effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation (evoked by recordings of authentic irregular vasoconstrictor nerve fibre discharge with average frequencies of 0.59, 2.0 and 6.9 Hz) on the perfusion pressure and the overflow of noradrenaline (NA) and neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity (NPY-LI) were investigated in the blood-perfused gracilis muscle of the dog in situ. 2. Nerve stimulation in the untreated control group evoked a frequency-dependent increase in perfusion pressure and overflow of NA. A significant overflow of NPY-LI was found at the highest frequency only. 3. In a separate group of animals, the sympathetic supply was unilaterally interrupted by preganglionic decentralization before the administration of reserpine (1 mgkg-1 i.v.) 24 h before the experiment. Reserpine reduced the NA content of the intact and decentralized gracilis and gastrocnemius muscle by 98-99%. Reserpine also induced a marked (80%) reduction of the muscular content of NPY-LI. The depletion of NPY-LI was, in contrast to that of NA, prevented by the decentralization, suggesting that nerve impulse activity was of primary importance for the reserpine-induced depletion of NPY-LI. 4. A slowly developing and long-lasting perfusion pressure increase was evoked by nerve stimulation, at 2.0 and 6.9 Hz after reserpine treatment. These responses were larger in the decentralized, as compared to the intact gracilis muscle and correlated with the nerve stimulation evoked overflow of NPY-LI (r = 0.79, P less than 0.001). Stimulation at 0.59 Hz caused vasoconstriction in the decentralized but not in the intact gracilis.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Schon F., Yeats J. C., Kelly J. S., Bloom S. R. Effect of reserpine, phenoxybenzamine and cold stress on the neuropeptide Y content of the rat peripheral nervous system. Neuroscience. 1986 Dec;19(4):1251–1254. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Warland J. J. A pharmacological study of the rabbit saphenous artery in vitro: a vessel with a large purinergic contractile response to sympathetic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlöf C., Kahan T., Ablad B. Prejunctional beta 2-adrenoreceptor blockade reduces nerve stimulation evoked release of endogenous noradrenaline in skeletal muscle in situ. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Apr;129(4):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. Impulse frequency in sympathetic vasomotor fibres correlated to the release and elimination of the transmitter. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;25(1):49–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTTING G., POTTER L. T., AXELROD J. Effect of decentralization and ganglionic blocking agents on the spontaneous release of H3-norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Jun;136:289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Evidence for two populations of excitatory receptors for noradrenaline on arteriolar smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):767–768. doi: 10.1038/283767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjemdahl P. Catecholamine measurements in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:521–534. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjemdahl P., Daleskog M., Kahan T. Determination of plasma catecholamines by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: comparison with a radioenzymatic method. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 9;25(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan T., Hjemdahl P., Dahlöf C. Relationship between the overflow of endogenous and radiolabelled noradrenaline from canine blood perfused gracilis muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Dec;122(4):571–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Al-Saffar A., Saria A., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Reserpine-induced depletion of neuropeptide Y from cardiovascular nerves and adrenal gland due to enhanced release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;332(2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00511407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Pernow J., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide Y-, substance P- and VIP-immunoreactive nerves in cat spleen in relation to autonomic vascular and volume control. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(1):9–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00214896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Pernow J. Guanethidine-sensitive release of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the cat spleen by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Fried G., Pernow J., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Anggård A. NPY--a mediator of reserpine-resistant, non-adrenergic vasoconstriction in cat spleen after preganglionic denervation? Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Jan;126(1):151–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Pernow J., Fried G., Anggärd A. Neuropeptide Y and noradrenaline mechanisms in relation to reserpine induced impairment of sympathetic neurotransmission in the cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Sep;131(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hamberger B. Frequency- and reserpine-dependent chemical coding of sympathetic transmission: differential release of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y from pig spleen. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 2;63(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Franco-Cereceda A., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Goldstein M. Differential effects of reserpine and 6-hydroxydopamine on neuropeptide Y (NPY) and noradrenaline in peripheral neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;328(3):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00515563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Franco-Cereceda A., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Mechanisms underlying changes in the contents of neuropeptide Y in cardiovascular nerves and adrenal gland induced by sympatholytic drugs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Aug;124(4):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. High levels of neuropeptide Y in peripheral noradrenergic neurons in various mammals including man. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I. The effect of reserpine on sympathetic, purinergic neurotransmission in the isolated mesenteric artery of the dog: a pharmacological study. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):467–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neild T. O., Zelcer E. Noradrenergic neuromuscular transmission with special reference to arterial smooth muscle. Prog Neurobiol. 1982;19(3):141–158. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(82)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Kahan T., Hjemdahl P., Lundberg J. M. Possible involvement of neuropeptide Y in sympathetic vascular control of canine skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jan;132(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Lundberg J. M., Kaijser L. Vasoconstrictor effects in vivo and plasma disappearance rate of neuropeptide Y in man. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 5;40(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKIN E. M., ROSELL S. The influence of sympathetic adrenergic vasoconstrictor nerves on transport of diffusible solutes from blood to tissues in skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Mar-Apr;54:223–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSELL S., SEDVALL G. The rate of disappearance of vasoconstrictor responses to sympathetic chain stimulation after reserpine treatment. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:306–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedvall G., Thorson J. Adrenergic transmission at vasoconstrictor nerve terminals partially depleted of noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jul;64(3):251–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. ATP as a co-transmitter in rat tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollevi A., Fredholm B. B. Influence of adenosine on the vascular responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the canine subcutaneous adipose tissue. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Sep;119(1):15–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundlöf G., Wallin B. G. The variability of muscle nerve sympathetic activity in resting recumbent man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):383–397. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hemsén A., Lundberg J. M. Radioimmunoassay for neuropeptide Y (NPY): chromatographic characterization of immunoreactivity in plasma and tissue extracts. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;45(4):355–365. doi: 10.3109/00365518509161019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E. Kruskal-Wallis test: BASIC computer program to perform nonparametric one-way analysis of variance and multiple comparisons on ranks of several independent samples. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1986 Aug;23(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER N., PERKINS M., SIDMAN R. L. Effect of reserpine on noradrenaline content of innervated and denervated brown adipose tissue of the rat. Nature. 1962 Jan 13;193:137–138. doi: 10.1038/193137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


