Abstract
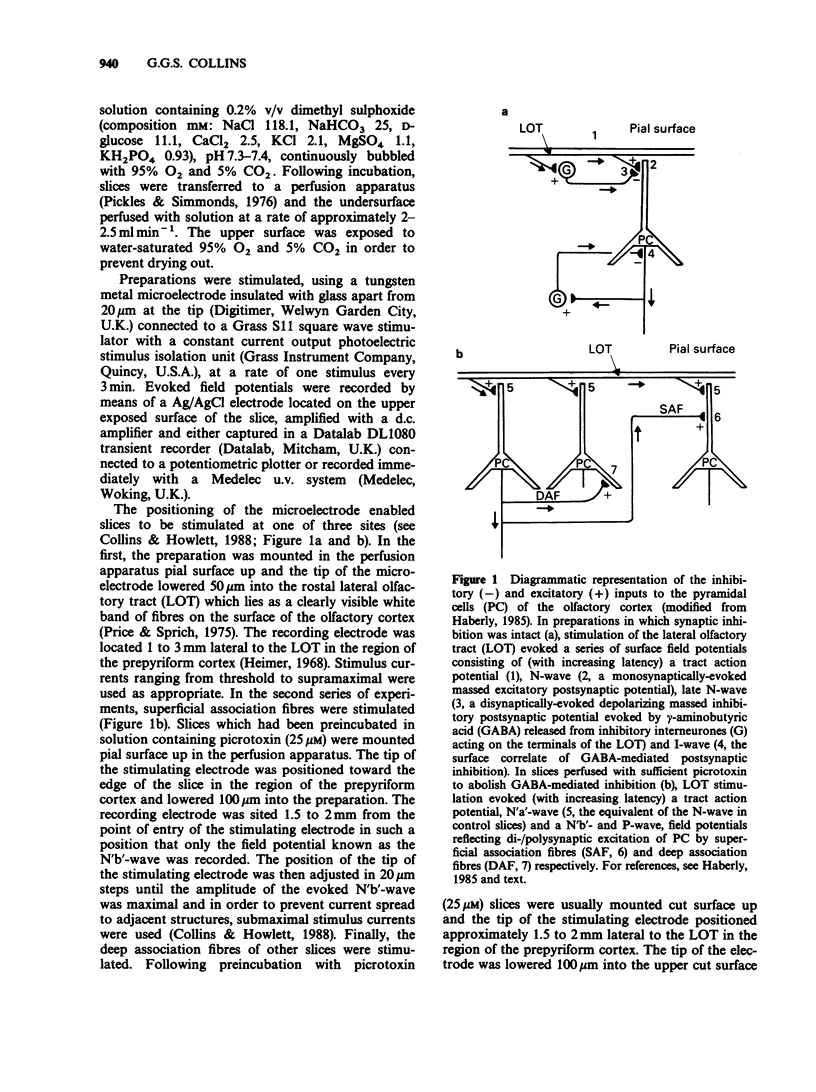
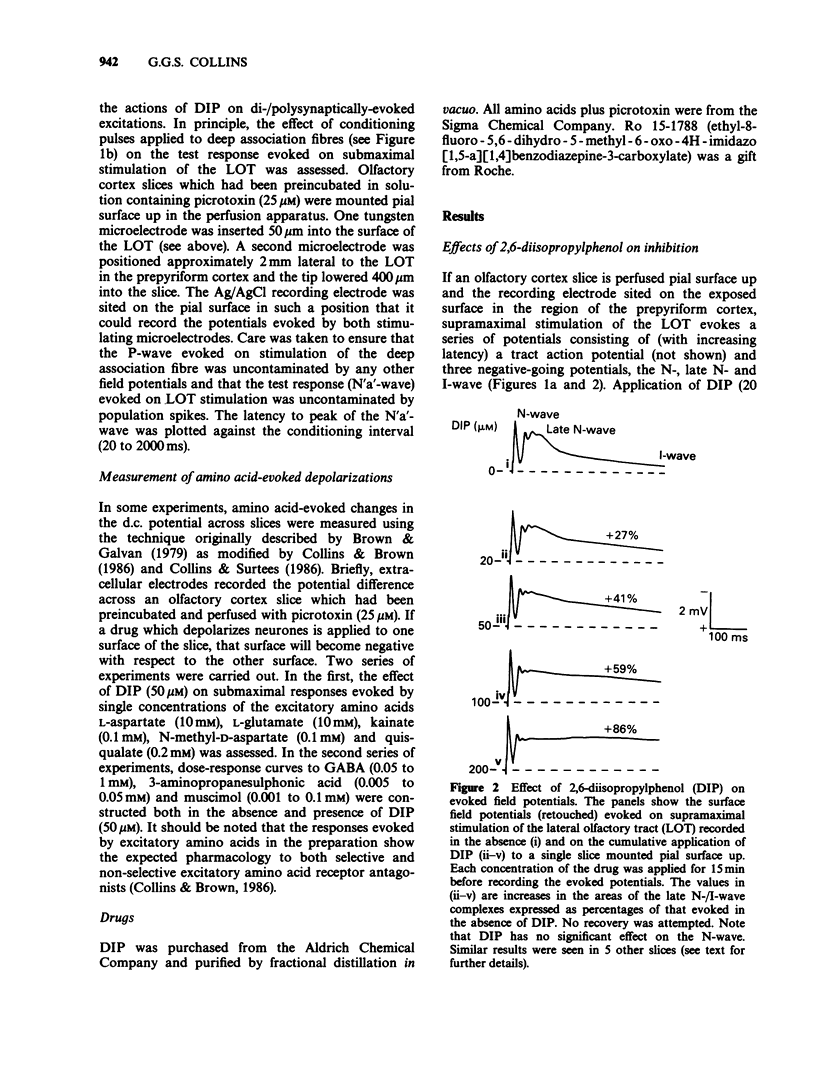
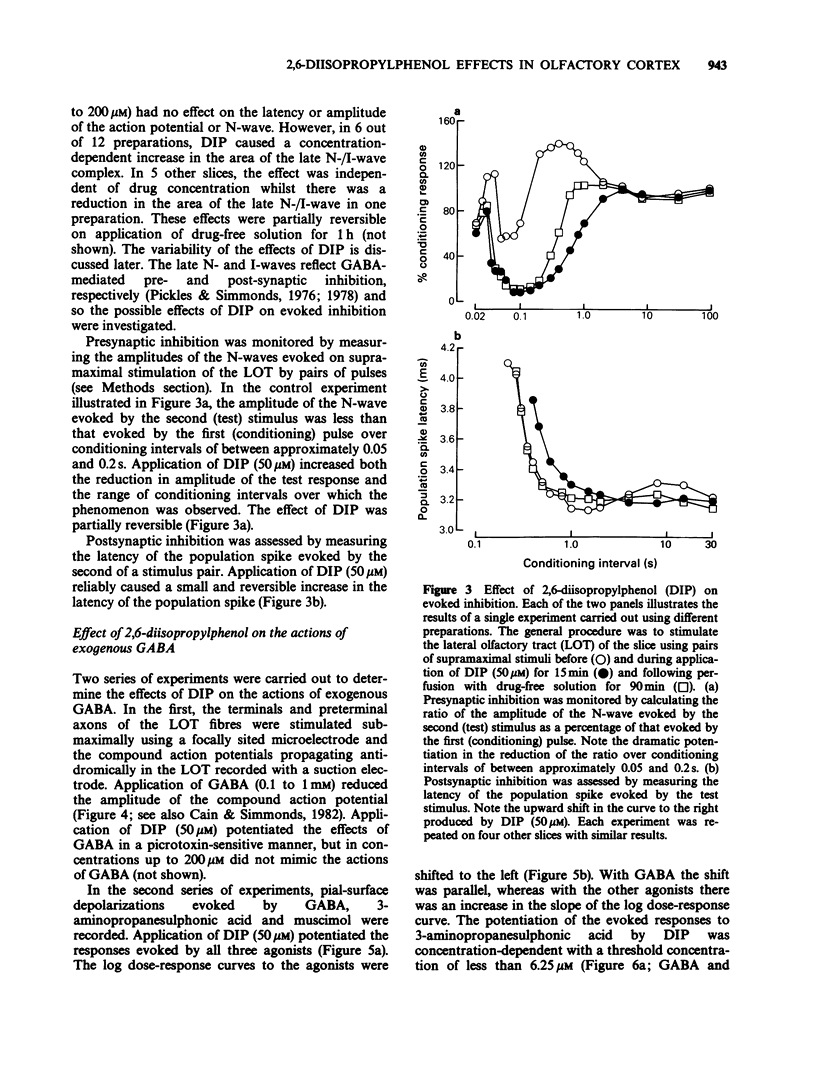
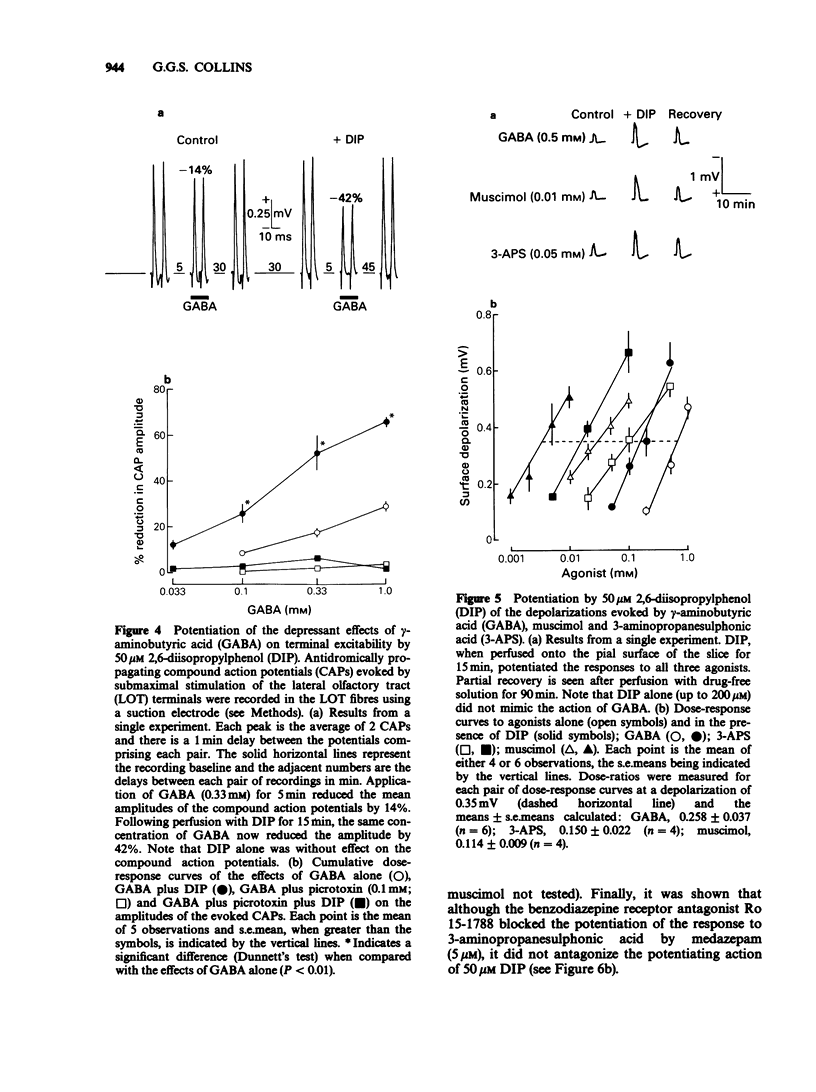
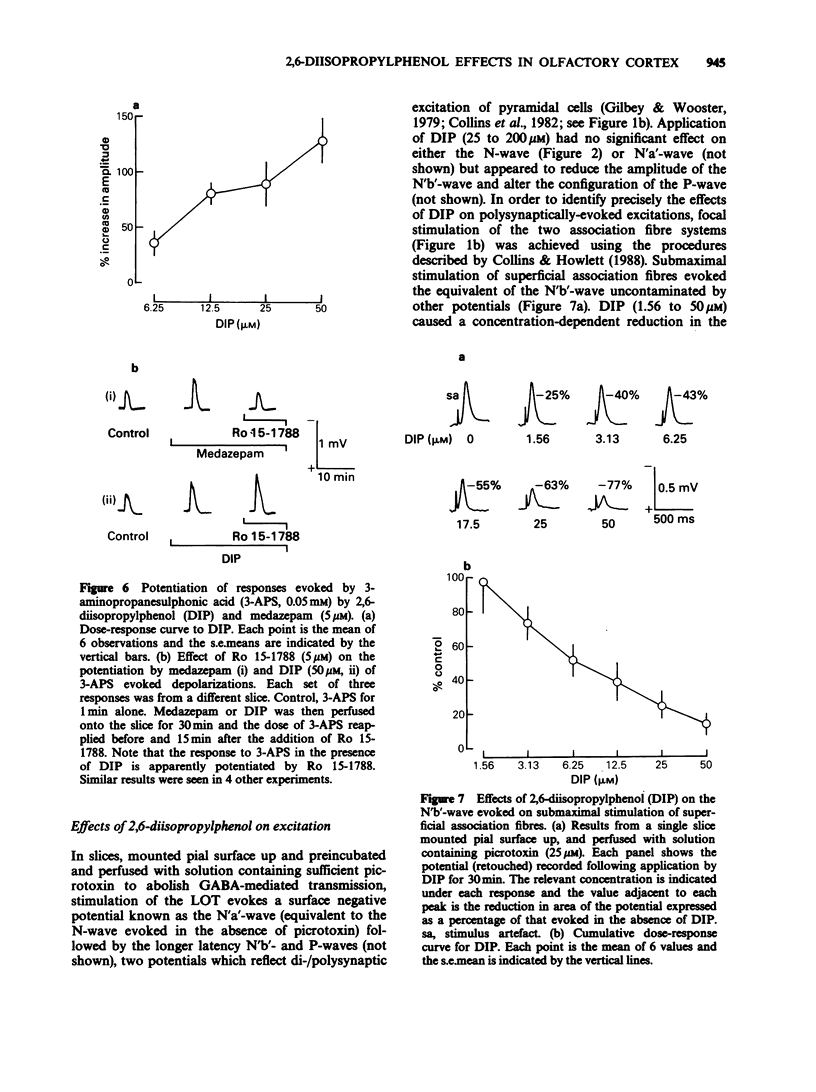
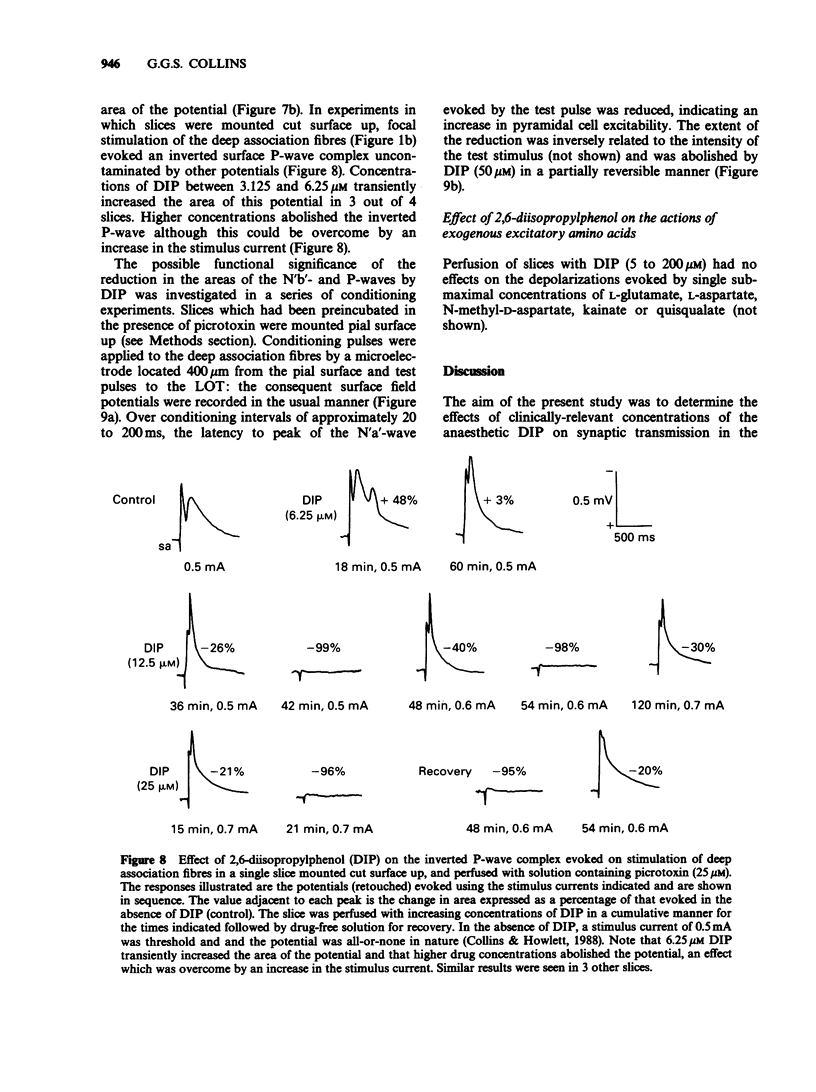
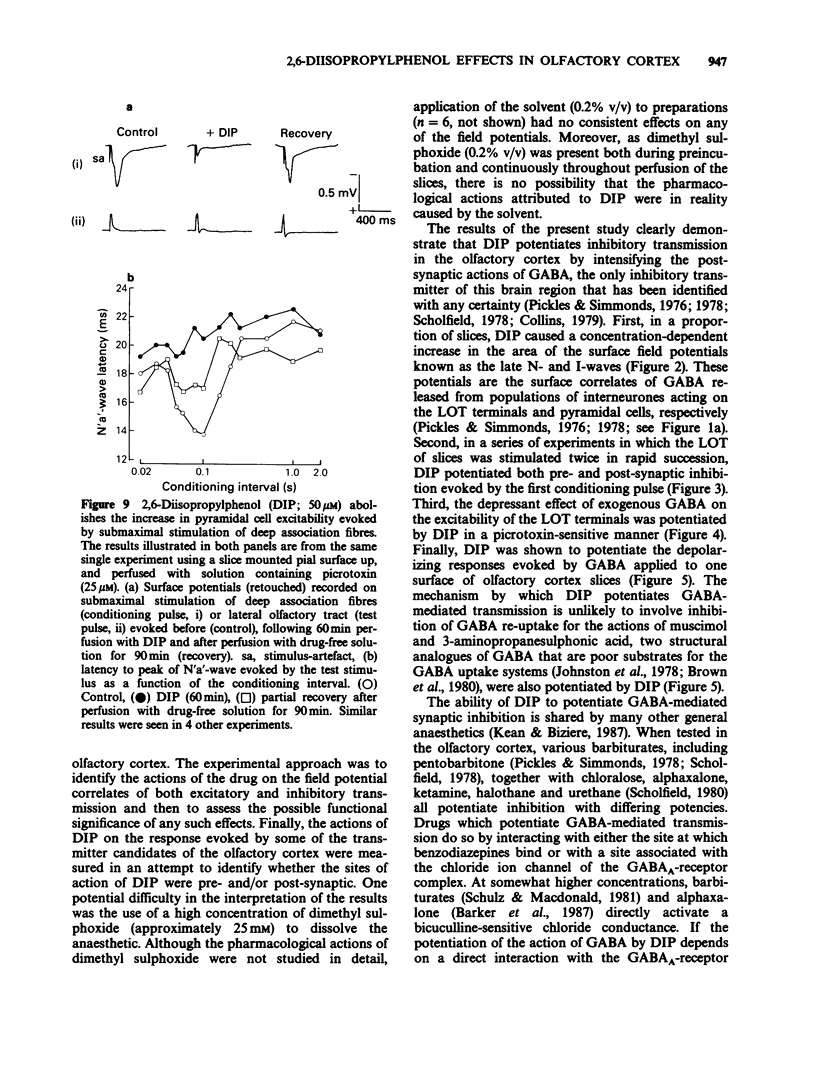
1. The effects of the general anaesthetic 2,6-diisopropylphenol (DIP) on synaptic transmission and the actions of amino acid transmitter candidates have been investigated in rat olfactory cortex slices. 2. On electrical stimulation of the lateral olfactory tract (LOT), DIP (20 to 200 microM) increased the area of those surface field potentials which reflect gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated transmission in a concentration-dependent manner in 6 out of 12 slices. In a series of conditioning experiments, DIP (50 microM) also potentiated GABA-mediated pre- and post-synaptic inhibition. 3. Perfusion of slices with DIP (50 microM) potentiated the reduction in the excitability of the terminals of the LOT produced by exogenous GABA in a picrotoxin-sensitive manner. 4. DIP (50 microM) markedly potentiated the surface depolarizations evoked by GABA, muscimol and 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid. The effect on the response to 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid was observed over a concentration range of DIP of 6.25 to 50 microM and was not blocked by the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15-1788. 5. In slices in which GABA-mediated transmission was abolished by picrotoxin (25 microM), DIP (50 microM) had no significant effect on monosynaptically-evoked excitatory transmission but depressed the areas of those field potentials which reflect di-/polysynaptic excitations in a concentration-dependent manner (from between 1.6 and 6.25 to 50 microM). 6. In a series of conditioning experiments DIP (50 microM) abolished the increase in the excitability of the pyramidal cells evoked on stimulation of deep association fibres. 7. DIP (50 microM) had no significant effect on surface depolarizations evoked by N-methyl-D-aspartate, quisqualate and kainate or by the transmitter candidates L-glutamate and L-aspartate. 8. It is concluded that, at clinically relevant concentrations, DIP potentiates GABA-mediated transmission probably by an interaction with the GABA receptor complex and inhibits di-/polysynaptic excitations, possibly by inhibiting the release of excitatory transmitters.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. L., Harrison N. L., Lange G. D., Owen D. G. Potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-activated chloride conductance by a steroid anaesthetic in cultured rat spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:485–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Collins G. G., Galvan M. Influence of cellular transport on the interaction of amino acids with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-receptors in the isolated olfactory cortex of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):251–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Galvan M. Responses of the guinea-pig isolated olfactory cortex slice to gamma-aminobutyric acid recorded with extracellular electrodes. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):347–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. R., Simmonds M. A. GABA-mediated changes in excitability of the rat lateral olfactory tract in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:487–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockshott I. D. Propofol ('Diprivan') pharmacokinetics and metabolism--an overview. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 3):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Anson J., Kelly E. P. Baclofen: effects on evoked field potentials and amino acid neurotransmitter release in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 29;238(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Brown G. A quantitative estimate of the contribution made by various receptor categories to the depolarizations evoked by some excitatory amino acids in the olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 16;371(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90804-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G. Evidence of a neurotransmitter role for aspartate and gamma-aminobutyric acid in the rat olfactory cortex. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:51–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Howlett S. J. The pharmacology of excitatory transmission in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Jul;27(7):697–705. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G. Some effects of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists on synaptic transmission in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 29;244(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Surtees L. "Desensitization" of excitatory amino acid responses in the rat olfactory cortex. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Mar;25(3):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts E., Claeys A. M., Camu F. Pharmacokinetics of propofol ('Diprivan') administered by continuous intravenous infusion in man. A preliminary report. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 3):51–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Wooster M. J. Mono-and multi-synaptic origin of the early surface-negative wave recorded from guinea-pig olfactory cortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:153–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer L. Synaptic distribution of centripetal and centrifugal nerve fibres in the olfactory system of the rat. An experimental anatomical study. J Anat. 1968 Nov;103(Pt 3):413–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Kennedy S. M., Lodge D. Muscimol uptake, release and binding in rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1519–1523. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane P. E., Biziere K. The effects of general anaesthetics on GABAergic synaptic transmission. Life Sci. 1987 Sep 21;41(12):1437–1448. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90708-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Anis N. A. Effects of ketamine and three other anaesthetics on spinal reflexes and inhibitions in the cat. Br J Anaesth. 1984 Oct;56(10):1143–1151. doi: 10.1093/bja/56.10.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles H. G., Simmonds M. A. Field potentials, inhibition and the effect of pentobarbitone in the rat olfactory cortex slice. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:135–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles H. G., Simmonds M. A. Possible presynaptic inhibition in rat olfactory cortex. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):475–486. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polc P., Laurent J. P., Scherschlicht R., Haefely W. Electrophysiological studies on the specific benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;316(4):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00501364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. L., Sprich W. W. Observations on the lateral olfactory tract of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Aug 1;162(3):321–336. doi: 10.1002/cne.901620304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Russell W. J., Smaje J. C. The action of ether and methoxyflurane on synaptic transmission in isolated preparations of the mammalian cortex. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):121–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Sercombe R. Electrical activity observed in guinea-pig olfactory cortex maintained in vitro. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):667–683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Smaje J. C. Anaesthetics depress the sensitivity of cortical neurones to L-glutamate. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):347–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. A barbiturate induced intensification of the inhibitory potential in slices of guinea-pig olfactory cortex. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:559–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. Potentiation of inhibition by general anaesthetics in neurones of the olfactory cortex in vitro. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Feb;383(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00587527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


