Abstract
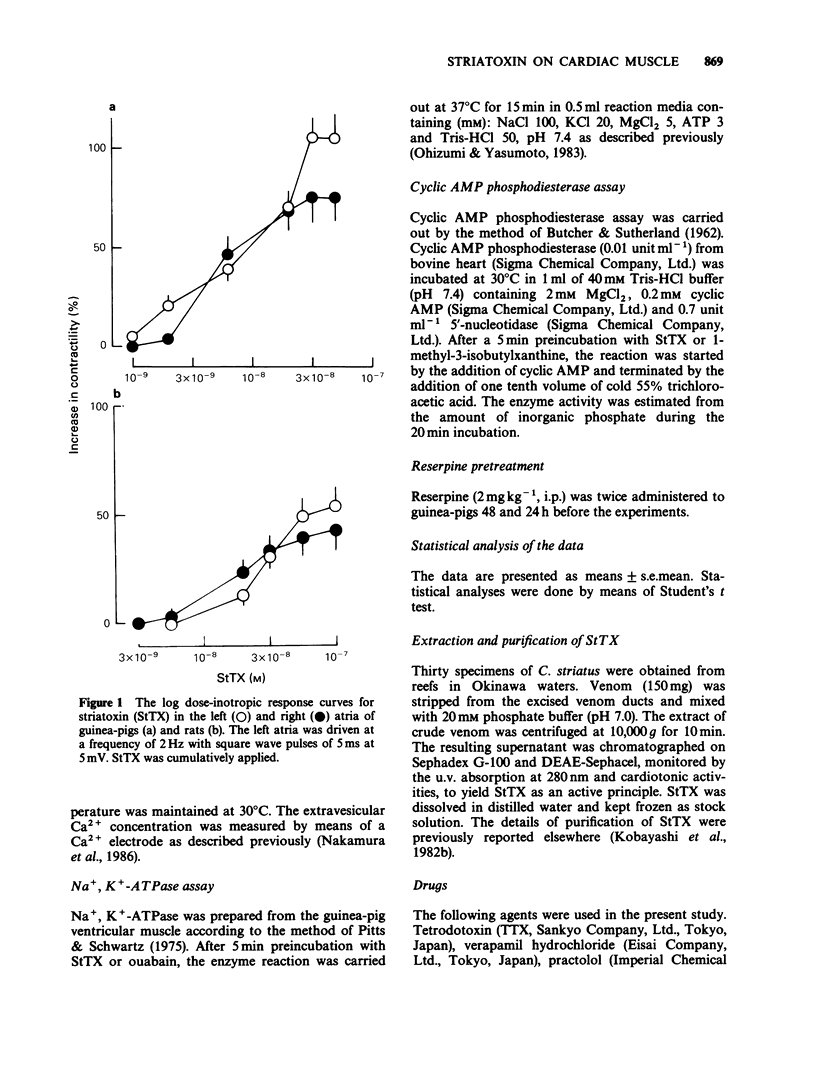
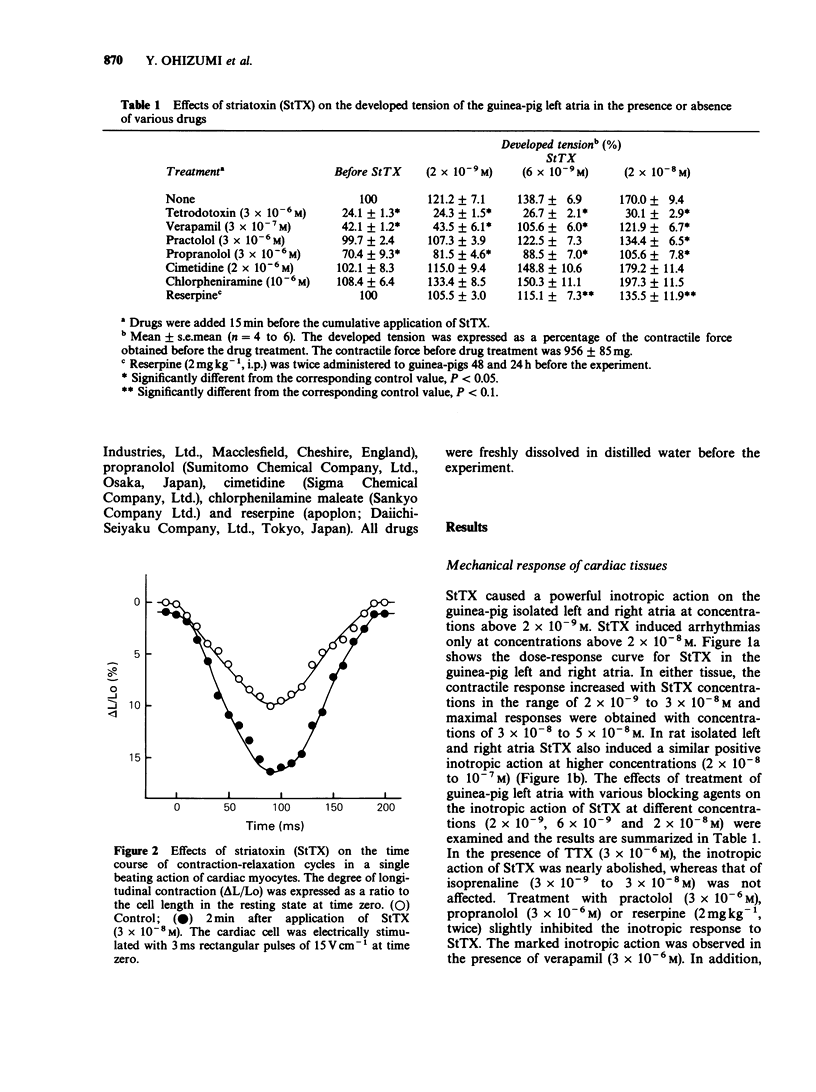
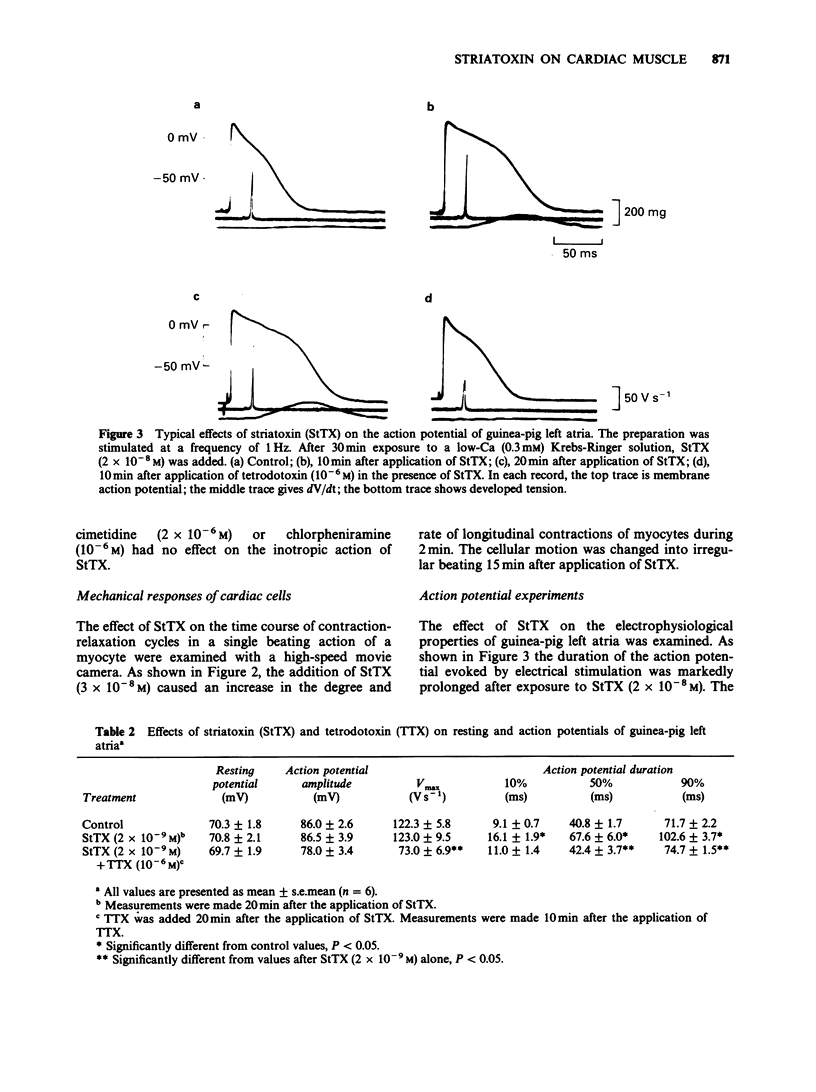
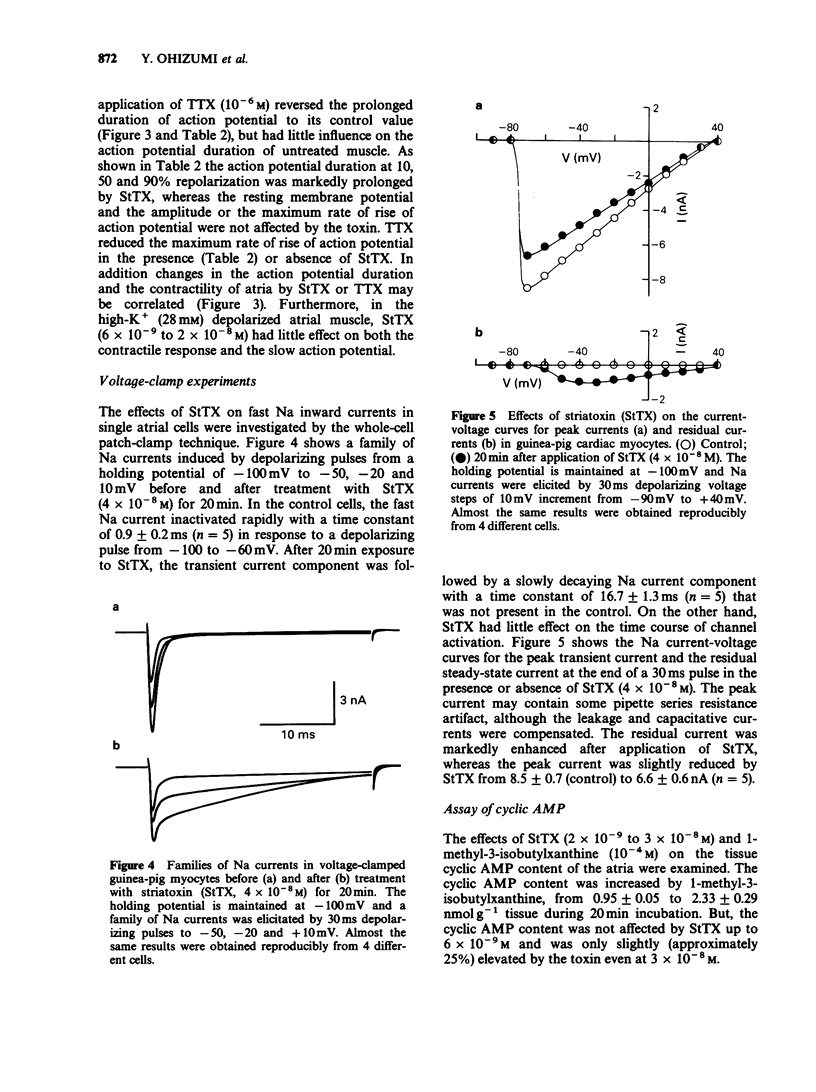
1. Striatoxin (StTX), a novel polypeptide from a marine snail, caused a dose-dependent increase in contractility in the isolated atria of guinea-pig and rat in the concentration-range of 2 x 10(-9) to 3 x 10(-8)M and 3 x 10(-6)M, respectively. 2. In guinea-pig atria, the StTX-induced inotropic effect was inhibited by tetrodotoxin but not by cimetidine or chlorpheniramine. Practolol, propranolol or reserpine caused only partial block of this inotropic action. 3. In isolated single cells from rat hearts, StTX caused an increase in the degree and the rate of contraction. 4. In guinea-pig atria, StTX provoked action potentials with a plateau phase of long duration without affecting the maximum rate of rise, the amplitude of action potential and the resting membrane potential. This prolongation was also reversed by tetrodotoxin. 5. In guinea-pig cardiac myocytes, whole-cell patch-clamp experiments showed that StTX slowed Na channel inactivation without affecting the time course of channel activation. The voltage dependence of Na currents was not altered by StTX. 6. The residual currents, but not peak currents were markedly enhanced by StTX. 7. These results suggest that StTX causes prolongation of the action potential duration probably due to slowed inactivation of Na inward currents and enhanced residual currents and that this may result in an increase in Ca2+ availability in cardiac muscle cells. This could explain the cardiotonic action of StTX.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T., Brody T. M. The role of Na+,K+-ATPase in the inotropic action of digitalis. Pharmacol Rev. 1977 Sep;29(3):187–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., De Peyer J. E., Kokubun S., Reuter H. Sodium channels in cultured cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:389–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Gyr P., Surridge J. The effects of crude venoms of Conus magus and Conus striatus on the contractile response and electrical activity of guinea-pig cardiac musculature. Toxicon. 1979;17(4):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Gyr P., Surridge J. The pharmacological actions on guinea-pig ileum of crude venoms from the marine gastropods Conus striatus and Conus magus. Toxicon. 1977;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Surridge J., Gyr P. Some effects of crude venom from the cones Conus striatus and Conus magus on isolated guinea-pig atria. Toxicon. 1977;15(5):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Williams H., Gyr P., Surridge J. Some effects on muscle and nerve of crude venom from the gastropod Conus striatus. Toxicon. 1976;14(4):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(76)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Yamashita S., Taira N. Positive inotropic effect of amrinone in relation to cyclic nucleotide metabolism in the canine ventricular muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jun;221(3):775–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. E., Turner R. J., Silva S. R. The venom and venom apparatus of the marine gastropod Conus striatus Linne. Toxicon. 1974 Dec;12(6):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M., Muramatsu I., Hidaka H., Ikushima S., Ashida K. Effects of Goniopora toxin, a polypeptide isolated from coral, on electromechanical properties of rabbit myocardium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Aug;210(2):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Ohizumi Y., Kobayashi J., Nakamura H., Catterall W. A. Actions of a polypeptide toxin from the marine snail Conus striatus on voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):691–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harigaya S., Schwartz A. Rate of calcium binding and uptake in normal animal and failing human cardiac muscle. Membrane vesicles (relaxing system) and mitochondria. Circ Res. 1969 Dec;25(6):781–794. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Ochi R., Hashimoto K., Inui J., Miura Y. The ionic mechanism of prolongation of action potential duration of cardiac ventricular muscle by anthopleurin-A and its relationship to the inotropic effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Nov;215(2):479–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Patlak J., Stevens C. F. Sodium channels need not open before they inactivate. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):426–427. doi: 10.1038/291426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Ohnishi S. T., Ikemoto N. Kinetic studies of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9662–9668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi J., Nakamura H., Hirata Y., Ohizumi Y. Effect of venoms from Conidae on skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles. Toxicon. 1982;20(5):823–830. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi J., Nakamura H., Hirata Y., Ohizumi Y. Isolation of a cardiotonic glycoprotein, striatoxin, from the venom of the marine snail Conus Striatus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 29;105(4):1389–1395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90941-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi J., Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y. Biphasic mechanical responses of the guinea-pig isolated ileum to the venom of the marine snail Conus striatus. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):583–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Miyakoda G., Nakamura T., Ohizumi Y. Ca-dependent arrhythmogenic effects of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, on isolated rat cardiac muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ochi R., Ohizumi Y. Maitotoxin-activated single calcium channels in guinea-pig cardiac cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):665–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. The mechanism of action of maitotoxin in relation to Ca2+ movements in guinea-pig and rat cardiac muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama I., Shibata S., Toyama J., Yamada K. Electromechanical effects of anthopleurin-A (AP-A) on rabbit ventricular muscle: influence of driving frequency, calcium antagonists, tetrodotoxin, lidocaine and ryanodine. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;74(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Kobayashi J., Gilmore J., Mascal M., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y. Bromo-eudistomin D, a novel inducer of calcium release from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum that causes contractions of skinned muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4139–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Muramatsu I., Fujiwara M. Effects of Goniopora toxin on the membrane currents of bullfrog atrial muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Aug;327(1):75–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00504995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi R., Trautwein W. The dependence of cardiac contraction on depolarization and slow inward current. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(3):187–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00586383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Minoshima S., Takahashi M., Kajiwara A., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J. Geographutoxin II, a novel peptide inhibitor of Na channels of skeletal muscles and autonomic nerves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Oct;239(1):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Catterall W. A. Specific inhibition of [3H] saxitoxin binding to skeletal muscle sodium channels by geographutoxin II, a polypeptide channel blocker. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6149–6152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Contractile response of the rabbit aorta to maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:711–721. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Gray W. R., Zeikus R., McIntosh J. M., Varga J., Rivier J., de Santos V., Cruz L. J. Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.4071055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opie L. H. Role of cyclic nucleotides in heart metabolism. Cardiovasc Res. 1982 Sep;16(9):483–507. doi: 10.1093/cvr/16.9.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J., Schwartz A. Improved purification and partial characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase from cardiac muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 20;401(2):184–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravens U. Electromechanical studies of an Anemonia sulcata toxin in mammalian cardiac muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;296(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00498842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Renaud J. F., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Pharmacological properties of the interaction of a sea anemone polypeptide toxin with cardiac cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):607–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Iwamura N., Toyama J., Yamada K., Shibata S. Effect of cardiotonic polypeptide anthopleurin-A on canine Purkinje and ventricular muscle fibers. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;56(1-2):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90426-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


