Abstract
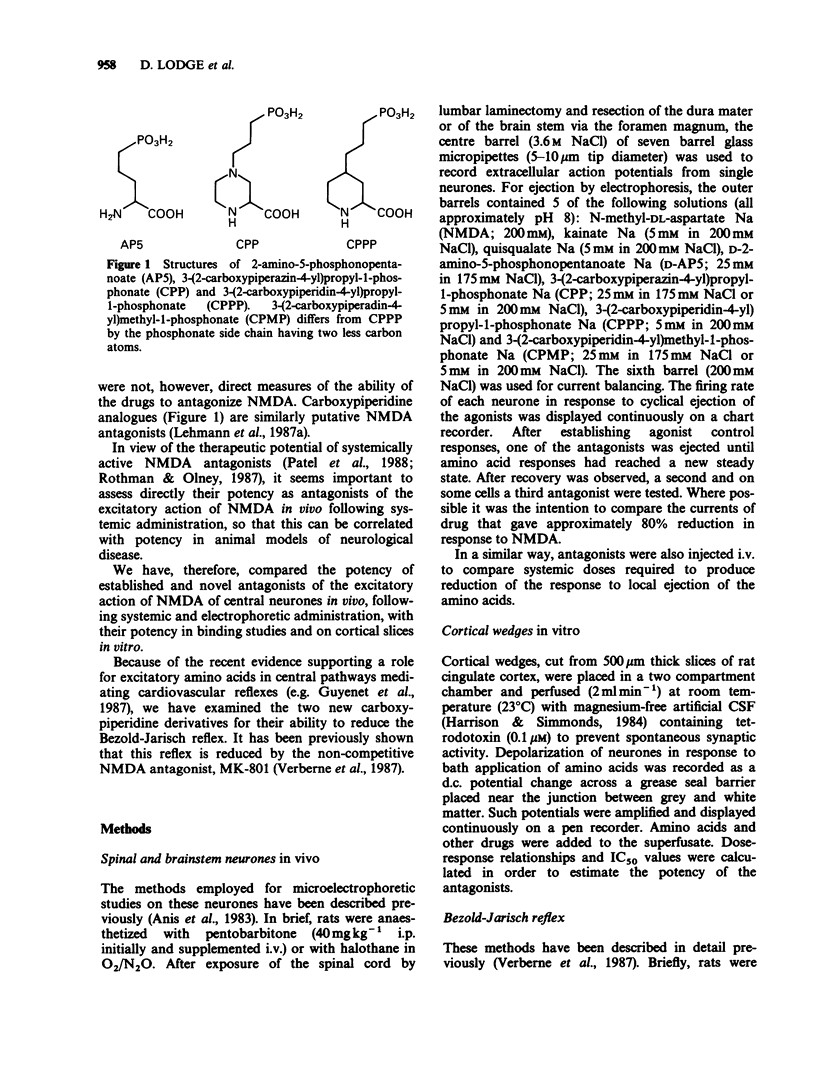
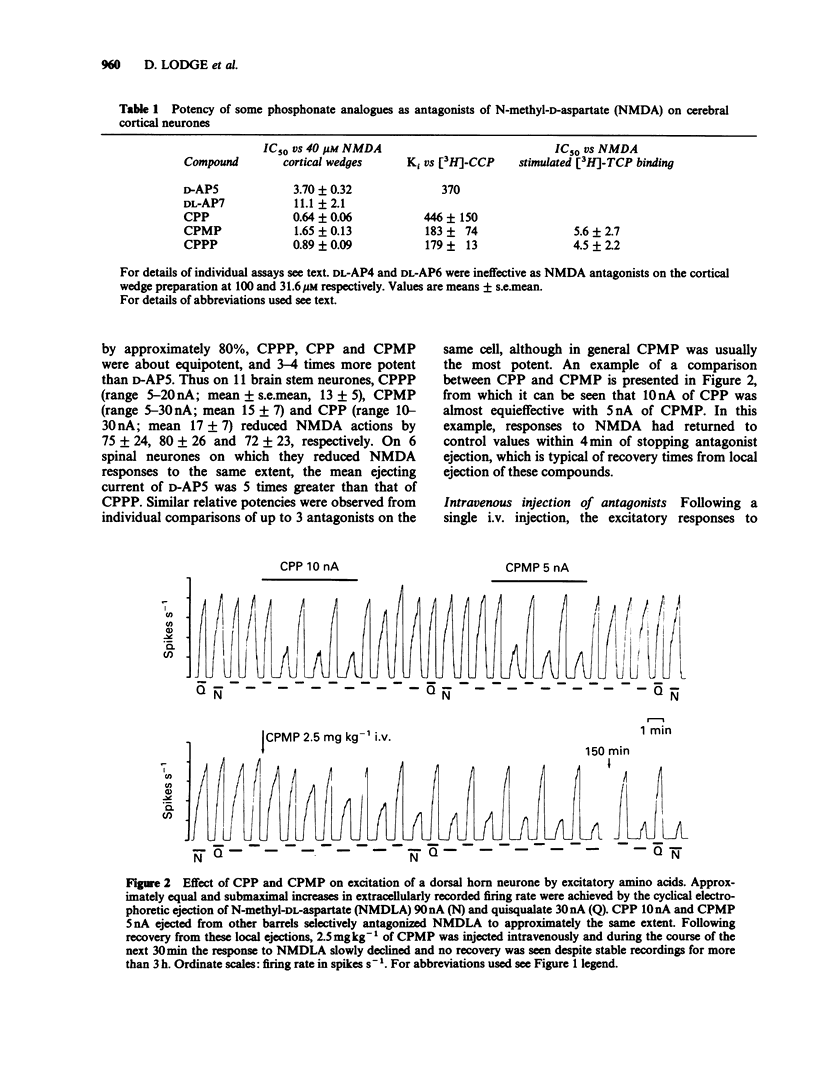
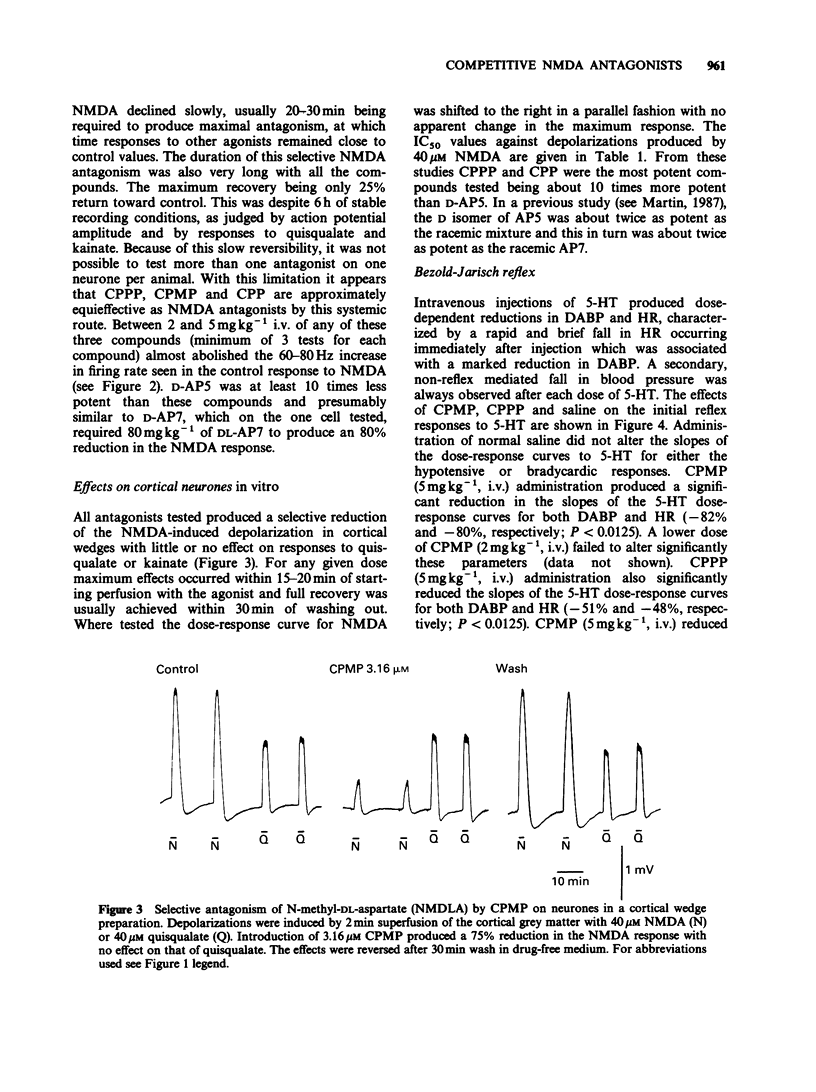
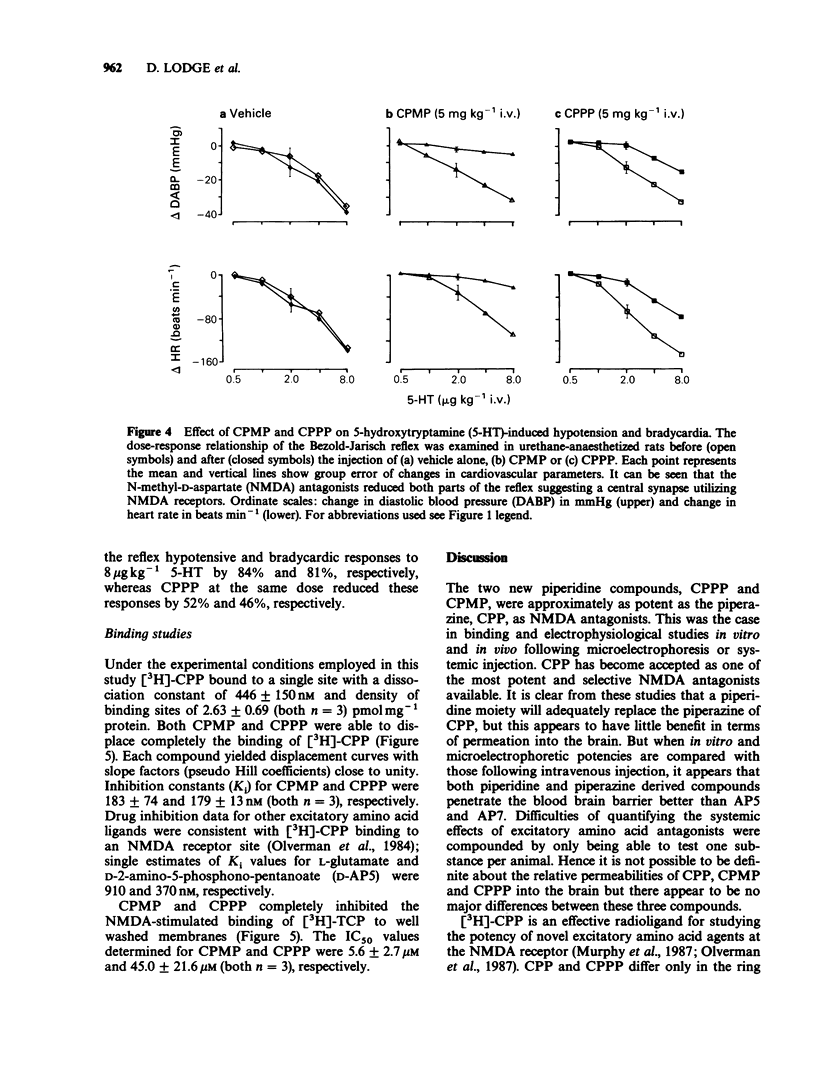
1. Phosphonate analogues of glutamate have been tested and compared as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists in electrophysiological and binding experiments. The compounds tested were three established NMDA antagonists: D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate (D-AP5), DL-2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate (DL-AP7), 3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonate (CPP), and two novel putative NMDA antagonists: 3-(2-carboxypiperidin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonate (CPPP) and 3-(2-carboxy-piperidin-4-yl)methyl-1-phosphonate (CPMP). 2. When administered electrophoretically to rat spinal neurones in vivo, these compounds were found to be selective NMDA antagonists with little effect on excitations evoked by quisqualate and kainate. CPMP and CPPP were approximately equipotent with CPP and about 5 times more potent than D-AP5. 3. Following systemic administration, 2-5 mg kg-1 i.v. of CPP, CPMP and CPPP reduced NMDA-evoked excitations by 70-100% whereas 50-100 mg kg-1 of D-AP5 and DL-AP7 produced a similar effect. The onset of the effects required 20-30 min and lasted more than six hours. 4. On bath application to cortical wedges, the IC50 values (microM) for antagonism of 40 microM NMDA were: CPP, 0.64 +/- 0.06 (mean +/- s.e.mean; n greater than 4); CPMP, 1.65 +/- 0.13; CPPP 0.89 +/- 0.09; D-AP5, 3.7 +/- 0.32; DL-AP7, 11.1 +/- 2.1; and DL-AP4 and DL-AP6 were inactive at 100 microM.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
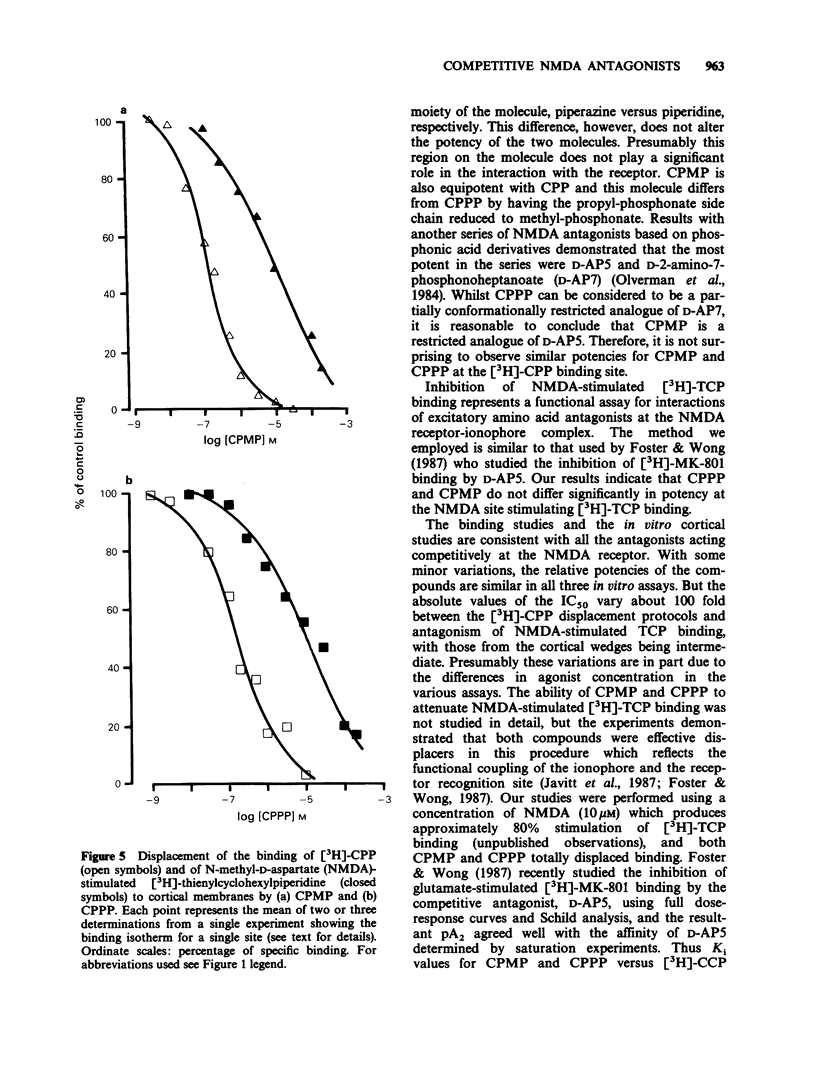
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C., Davies J., Dray A. D-alpha-Aminoadipate as a selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of mammalian spinal neurones. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):743–745. doi: 10.1038/270743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs A. M., Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. The pharmacological selectivity of three NMDA antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 5;145(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90352-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Herrling P. L., Jones A. W., Olverman H. J., Pook P., Watkins J. C. CPP, a new potent and selective NMDA antagonist. Depression of central neuron responses, affinity for [3H]D-AP5 binding sites on brain membranes and anticonvulsant activity. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. N., Martin D., Millar J. D., Aram J. A., Church J., Lodge D. Differences in results from in vivo and in vitro studies on the use-dependency of N-methylaspartate antagonism by MK-801 and other phencyclidine receptor ligands. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 12;145(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Neurobiology. Taking apart NMDA receptors. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):395–396. doi: 10.1038/329395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Wong E. H. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801 binds to the activated state of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon F. J. Aortic baroreceptor reflexes are mediated by NMDA receptors in caudal ventrolateral medulla. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):R628–R633. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.252.3.R628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granata A. R., Reis D. J. Blockade by glutamic acid diethyl ester of excitation of nucleus tractus solitarii neurons and vasodepressor responses reflexly elicited by vagal stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G., Filtz T. M., Donaldson S. R. Role of excitatory amino acids in rat vagal and sympathetic baroreflexes. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 31;407(2):272–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks T. P., Hall J. G., McLennan H. Ranking of excitatory amino acids by the antagonists glutamic acid diethylester and D-alpha-aminoadipic acid. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;56(6):901–907. doi: 10.1139/y78-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt D. C., Jotkowitz A., Sircar R., Zukin S. R. Non-competitive regulation of phencyclidine/sigma-receptors by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist D-(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jul 22;78(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Gundlach A. L., Snyder S. H. Pharmacological and autoradiographic discrimination of sigma and phencyclidine receptor binding sites in brain with (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047, (+)-[3H]-3-[3-hydroxyphenyl]-N-(1-propyl)piperidine and [3H]-1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Schneider J., McPherson S., Murphy D. E., Bernard P., Tsai C., Bennett D. A., Pastor G., Steel D. J., Boehm C. CPP, a selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type receptor antagonist: characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. J., Cincotta M., Verberne A. J., Jarrott B., Lodge D., Beart P. M. Receptor autoradiography with [3H]L-glutamate reveals the presence and axonal transport of glutamate receptors in vagal afferent neurones of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCUBBIN J. W., PAGE I. H., SALMOIRAGHI G. C. Cardiovascular and respiratory response to intravenous serotonin in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Dec;118(4):477–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Lodge D. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitation of spinal neurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Schneider J., Boehm C., Lehmann J., Williams M. Binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid to rat brain membranes: a selective, high-affinity ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):778–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Watkins J. C. [3H]CPP, a new competitive ligand for NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 12;131(1):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verberne A. J., Costa M., Lewis S. J., Louis W. J., Beart P. M. The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist MK-801, attenuates the Bezold-Jarisch reflex in the anaesthetized rat. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Aug;26(8):1243–1246. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


