Abstract
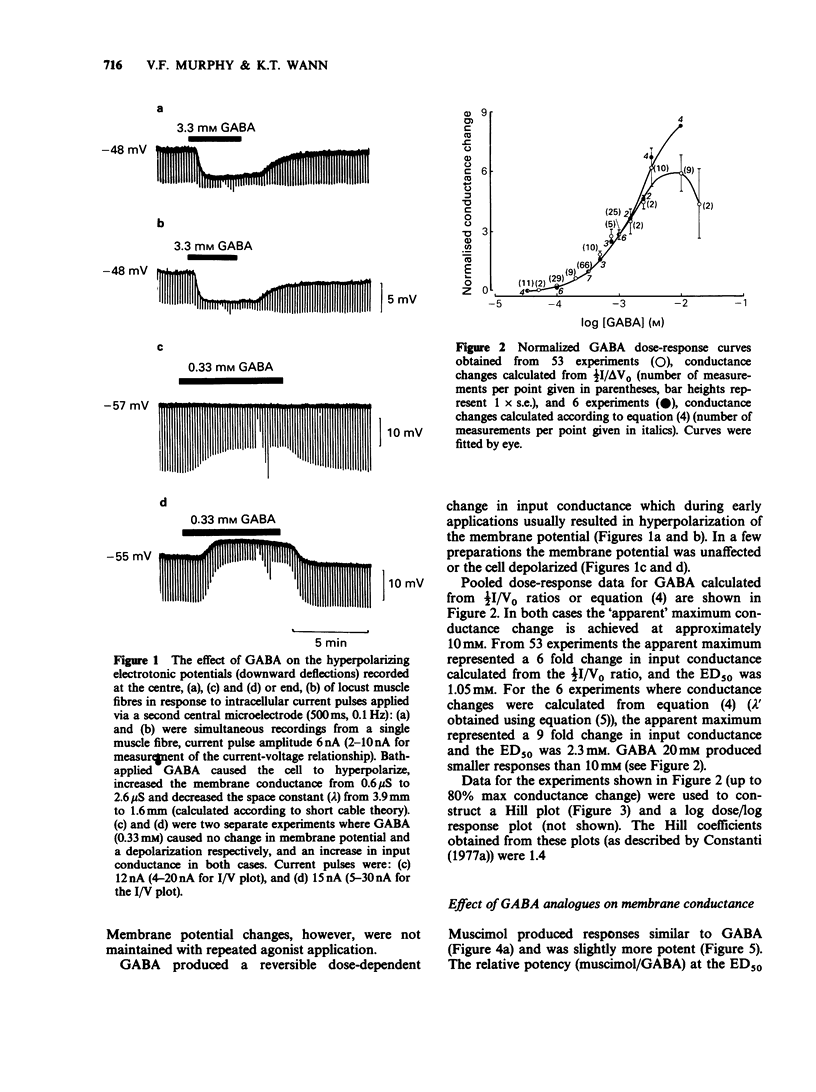
1. The properties of postsynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the extensor tibiae muscle of Schistocerca gregaria were studied by conventional electrophysiological recording techniques. 2. GABA and other active GABA receptor agonists produced rapid, dose-dependent, reversible increases in membrane conductance. 3. In two microelectrode experiments the ED50 for GABA was approximately 1 mM. In three microelectrode experiments (assuming short cable theory conditions) the ED50 for GABA was 2.3 mM. The Hill coefficient for GABA estimated from the latter experiments was 1.4. 4. The relative potency of muscimol/GABA at the ED50 for GABA was 1.36. 3-Aminopropane sulphonic acid (3-APS) and isonipecotic acid were weakly active, baclofen and piperidine-4-sulphonic acid (P4S) were inactive. Isoguvacine produced depolarizations and increases in conductance in preparations which hyperpolarized in response to GABA. These depolarizations were enhanced by both picrotoxin and pitrazepin although the increases in input conductance were depressed. 5. Picrotoxin (20 microM), (+)-bicuculline (20-100 microM) and pitrazepin (1-10 microM) all reversibly antagonized GABA-induced responses. Such antagonism was not competitive in the case of picrotoxin and (+)-bicuculline but was competitive for pitrazepin. Schild plot analysis gave an average pA2 value of 5.5 for pitrazepin. 6. The significance of these results is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF


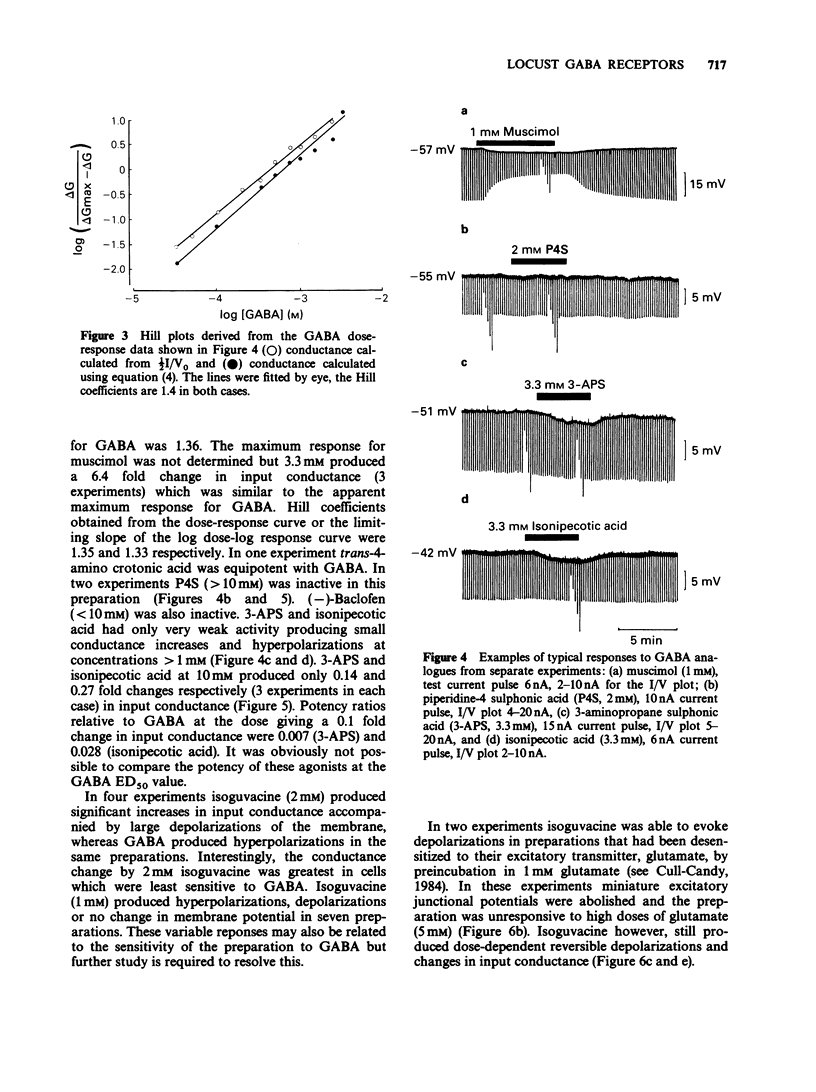
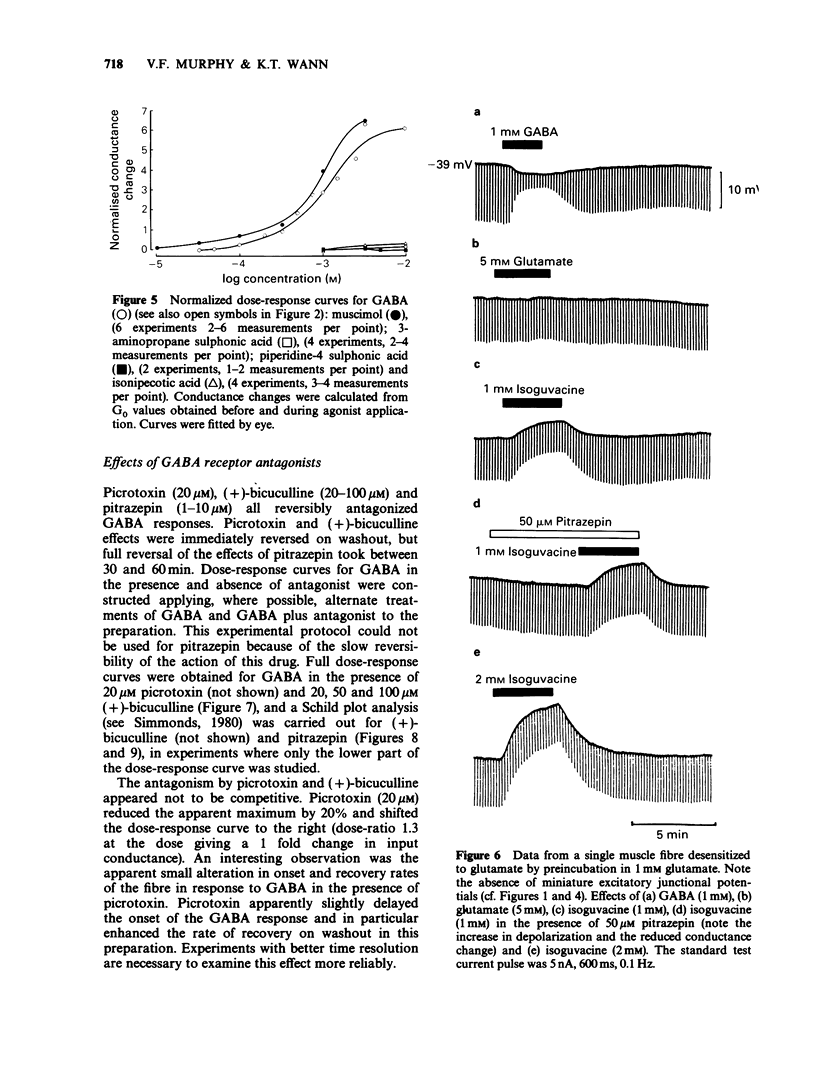



Selected References
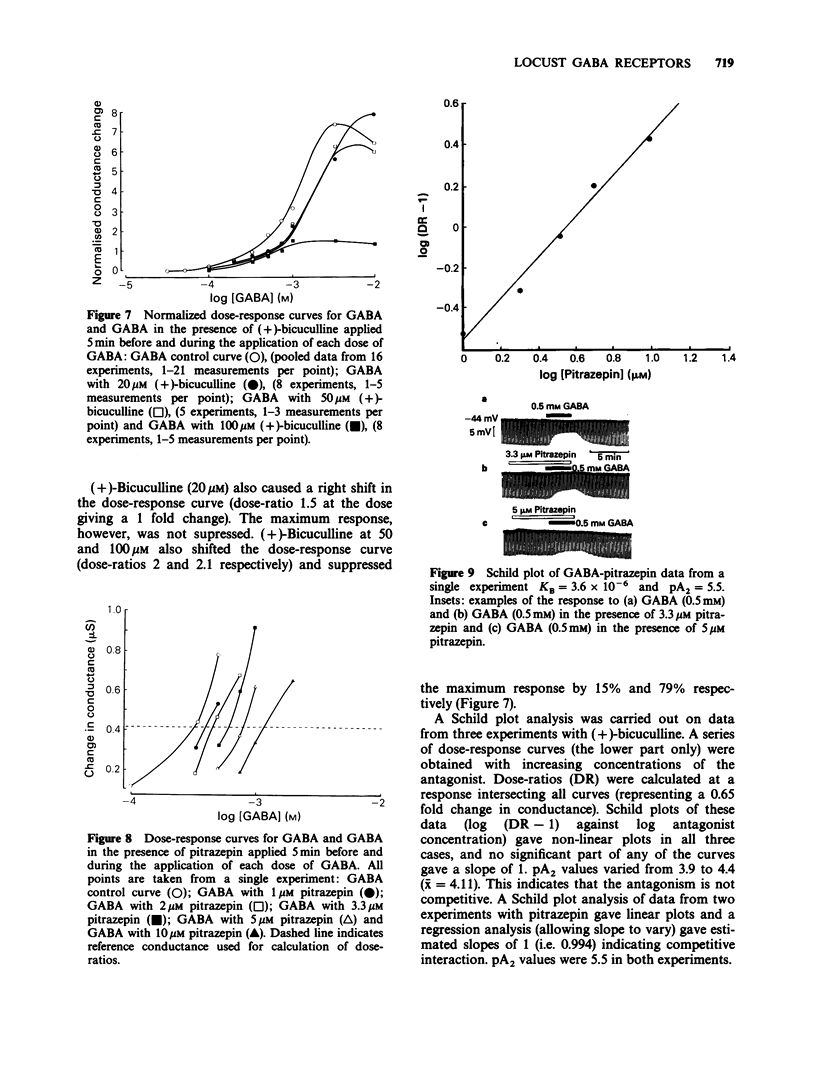
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Banks F. W. Voltage clamp analysis of inhibitory synaptic action in crayfish stretch receptor neurons. Fed Proc. 1981 Sep;40(11):2637–2641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge R. J., Nicholson S. H., Nicol A. J., Suckling C. J., Leigh B., Iversen L. Inhibition of [3H]GABA binding to postsynaptic receptors in human cerebellar synaptic membranes by carboxyl and amino derivatives of GABA. J Neurochem. 1981 Oct;37(4):837–844. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N., Blank M., Werman R. The kinetics of the conductance increase produced by -aminobutyric acid at the membrane of locust muscle fibers. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):580–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A. Comparison of dose/conductance curves for GABA and some structurally related compounds at the lobster inhibitory neuromuscular junction. Neuropharmacology. 1977 May;16(5):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A. The "mixed" effect of picrotoxin on the GABA dose/conductance relation recorded from lobster muscle. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Mar;17(3):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G. Inhibitory synaptic currents in voltage-clamped locust muscle fibres desensitized to their excitatory transmitter. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):375–383. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Junctional and extrajunctional membrane channels activated by GABA in locust muscle fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 27;211(1185):527–535. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duce I. R., Scott R. H. Actions of dihydroavermectin B1a on insect muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):395–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Hatt H. Four types of GABA receptors in crayfish leg muscles characterized by desensitization and specific antagonist. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Aug 24;364(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00581758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R., Grundfest H. Desensitization of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in muscle fibers of the crab Cancer borealis. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):33–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Maurer R., Wüthrich H. J. Pitrazepin, a novel GABAA antagonist. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Apr 6;45(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori N., Ikeda K., Roberts E. Muscimol, GABA and picrotoxin: effects on membrane conductance of a crustacean neuron. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 10;141(2):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. N., Ikeda K., Roberts E. Dose-conductance relationships for GABA agonists and the effect of uptake inhibitors in crayfish stretch receptor neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 30;225(2):319–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Falch E., Schousboe A., Curtis D. R., Lodge D. Piperidine-4-sulphonic acid, a new specific GABA agonist. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):756–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A., Lodge D., Curtis D. R. A new class of GABA agonist. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):53–55. doi: 10.1038/268053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A. Structure-activity studies on the inhibition of GABA binding to rat brain membranes by muscimol and related compounds. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1377–1382. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A., Constanti A. Pharmacological characterization of different types of GABA and glutamate receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(2):117–235. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Ban M., Miller T. Studies on the neuropharmacological activity of bicuculline and related compounds. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 6;102(2):283–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Inhibitory postsynaptic current in voltage-clamped crayfish muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):153–154. doi: 10.1038/263153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Evidence that bicuculline and picrotoxin act at separate sites to antagonize gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat cuneate nucleus. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jan;19(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Resting potential and electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. Effect of different external solutions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):383–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Onodera K. Effect of bicuculline on the GABA receptor of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):55–56. doi: 10.1038/newbio236055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. Anion permeability of the inhibitory post-synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):575–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. The structure-activity relationship for GABA and related compounds in the crayfish muscle. Neuropharmacology. 1975 Sep;14(9):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(75)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USHERWOOD P. N., GRUNDFEST H. PERIPHERAL INHIBITION IN SKELETAL MUSCLE OF INSECTS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:497–518. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. The electrical constants of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):348–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. J., Woodruff G. N., Kerkut G. A. The effect of ibotenic acid and muscimol on single neurons of the snail, Helix aspersa. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;2(6):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(71)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. The elasticity of relaxed insect fibrillar flight muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:31–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


