Abstract
1. CGS 19755 (cis-4-phosphonomethyl-2-piperidine carboxylic acid), a rigid analogue of 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP5), is one of the most potent competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists described. Using Triton-treated crude synaptic membranes from rat brain, binding studies indicated that [3H]-CGS 19755 bound with high affinity and selectivity to the NMDA-type excitatory amino acid receptor. 2. [3H]-CGS 19755 binding was saturable, reversible, heat-labile, pH-dependent and linear with protein concentration. Specific binding represented 80-85% of the total amount bound. 3. Using a centrifugation assay, saturation experiments revealed two distinct binding components with Kd values of 9 and 200 nM, and corresponding Bmax values of 0.55 and 1.00 pmol mg-1 protein. In contrast, a single binding component with a Kd value of 24 nM and an apparent Bmax value of 0.74 pmol mg-1 protein was observed with a filtration assay. 4. Competition experiments in which both assay techniques were used, showed that [3H]-CGS 19755 selectively labels the NMDA receptor. The most active inhibitors of [3H]-CGS 19755 binding were L-glutamate and CGS 19755 (IC50 values = 100 nM). 5. In the centrifugation assay, a number of excitatory amino acids were found to generate shallow inhibition curves, and computer analysis indicated the presence of two binding components. The quisqualate receptor ligand AMPA (D,L-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate), kainic acid and the non-competitive NMDA antagonists, such as phencyclidine, tiletamine and MK-801, were without activity.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
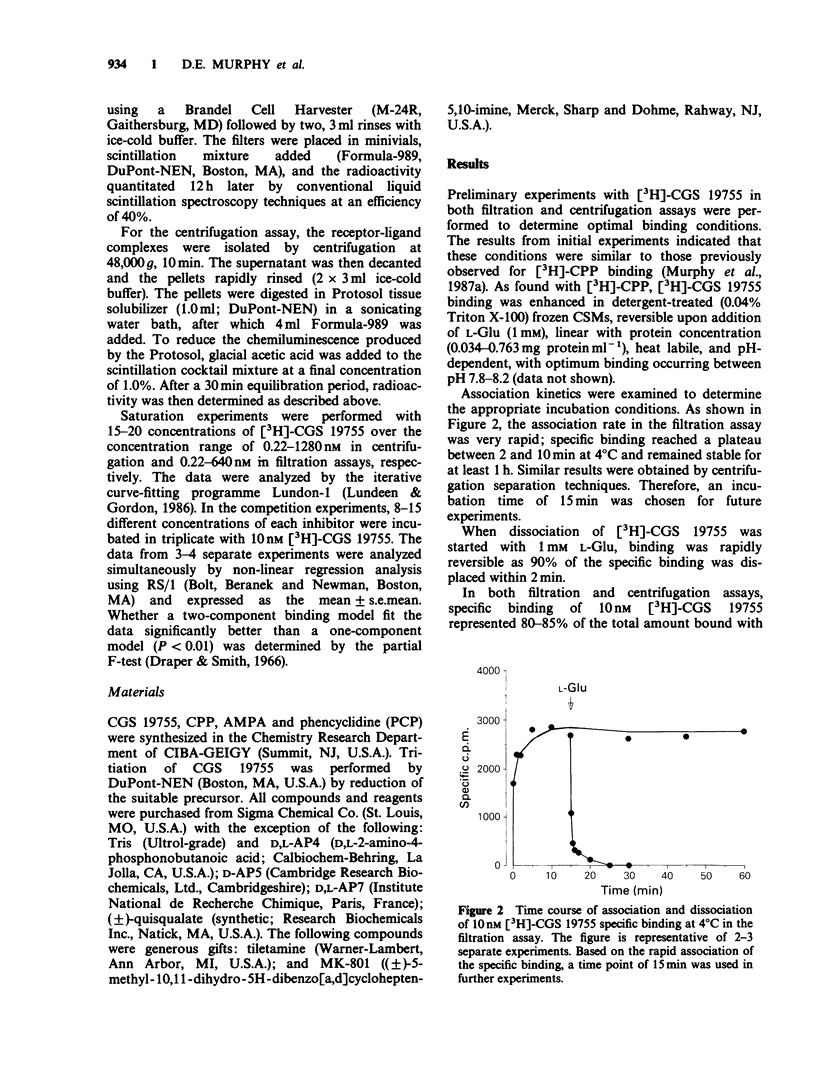
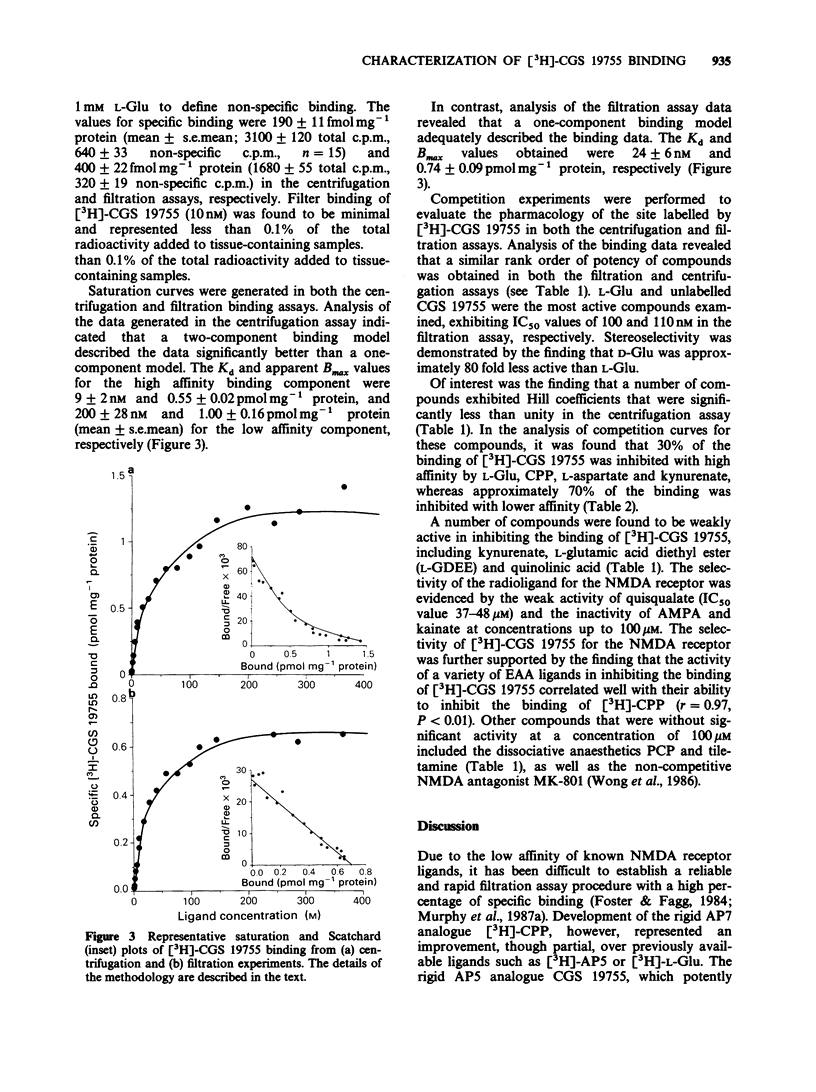
PDF
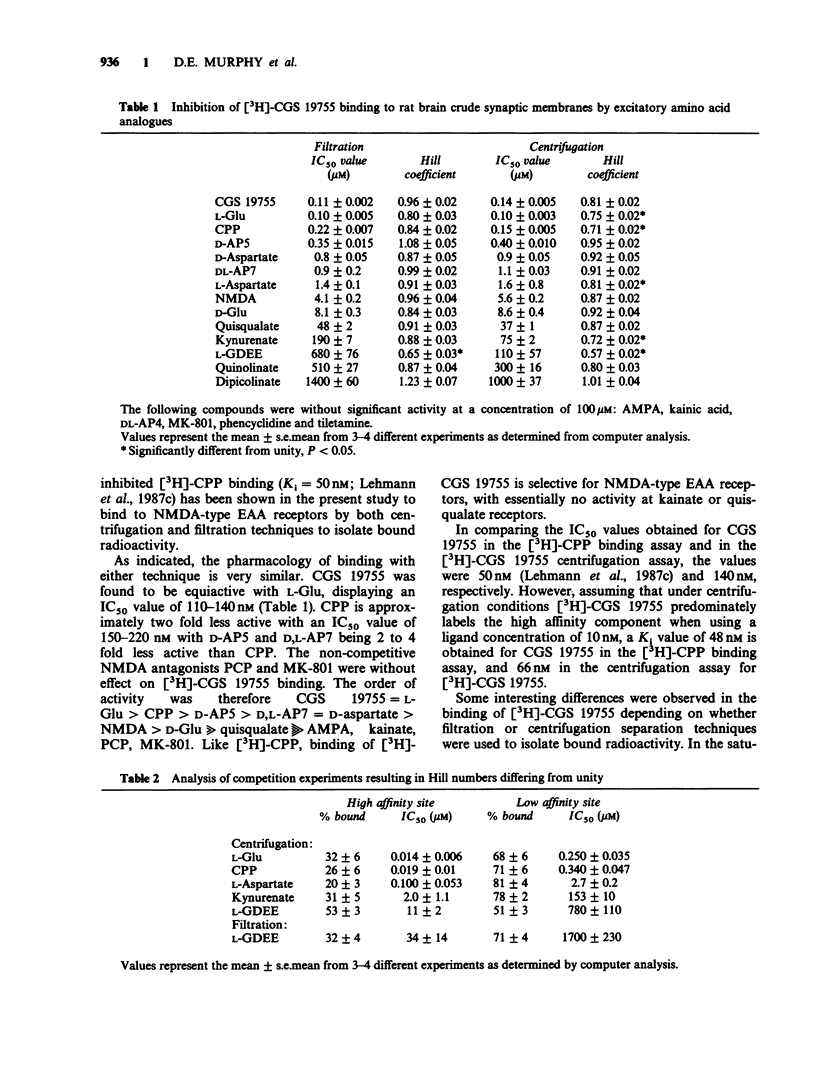


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boast C. A., Gerhardt S. C., Pastor G., Lehmann J., Etienne P. E., Liebman J. M. The N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists CGS 19755 and CPP reduce ischemic brain damage in gerbils. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher T. E., Tuchek J. M., Johnson D. D. A comparison of methods for removal of endogenous GABA from brain membranes prepared for binding assays. Neurochem Res. 1986 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00965160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Acidic amino acid binding sites in mammalian neuronal membranes: their characteristics and relationship to synaptic receptors. Brain Res. 1984 May;319(2):103–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Comparison of L-[3H]glutamate, D-[3H]aspartate, DL-[3H]AP5 and [3H]NMDA as ligands for NMDA receptors in crude postsynaptic densities from rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 20;133(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Schneider J., McPherson S., Murphy D. E., Bernard P., Tsai C., Bennett D. A., Pastor G., Steel D. J., Boehm C. CPP, a selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type receptor antagonist: characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Schneider J., Boehm C., Lehmann J., Williams M. Binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid to rat brain membranes: a selective, high-affinity ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):778–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Snowhill E. W., Williams M. Characterization of quisqualate recognition sites in rat brain tissue using DL-[3H]alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) and a filtration assay. Neurochem Res. 1987 Sep;12(9):775–781. doi: 10.1007/BF00971514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


