Abstract
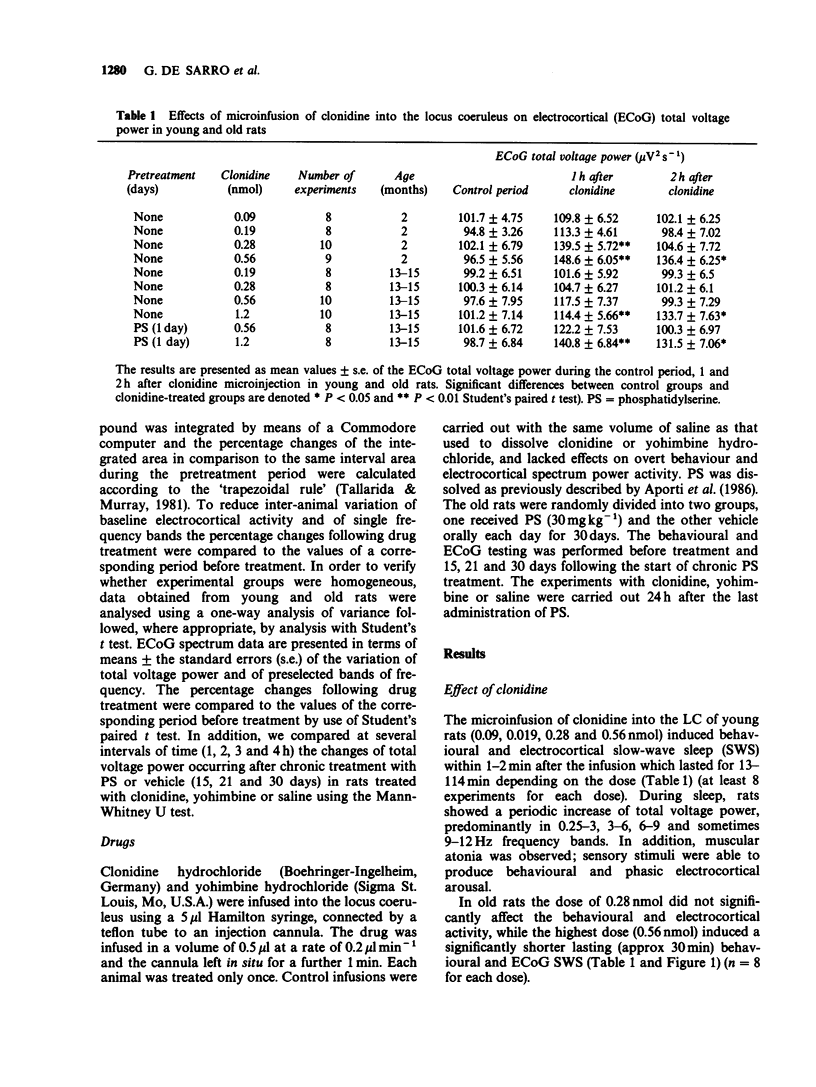
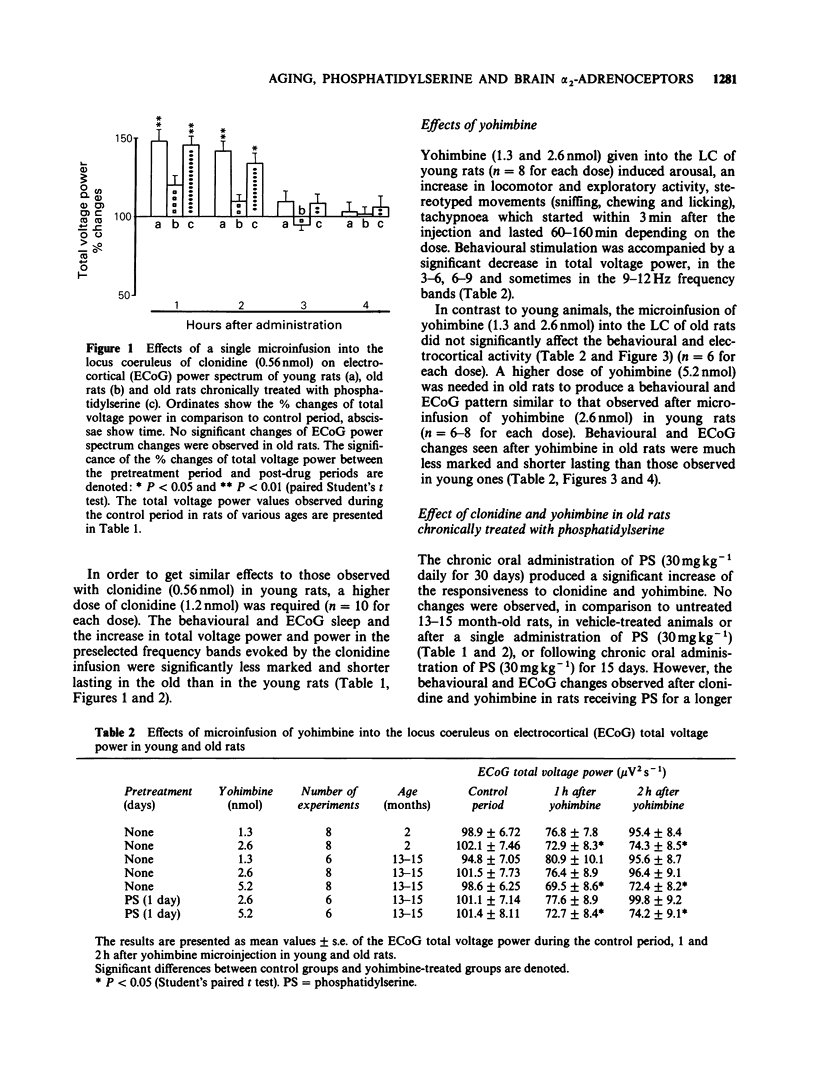
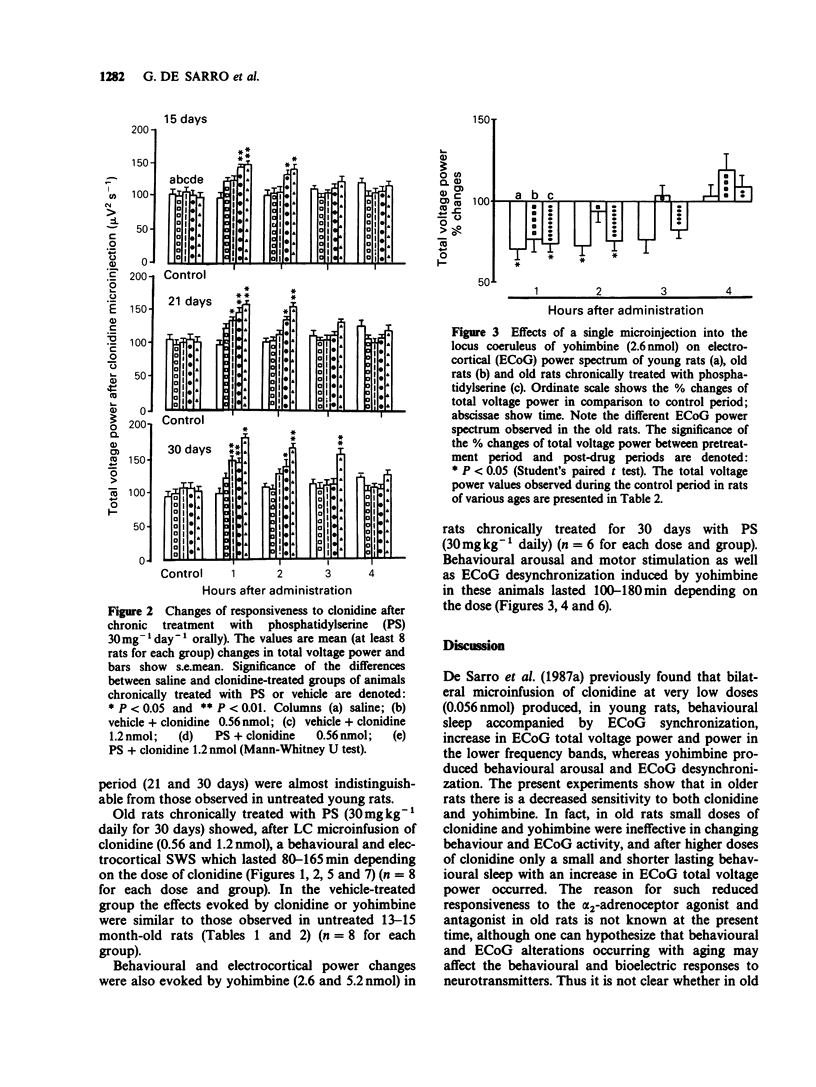
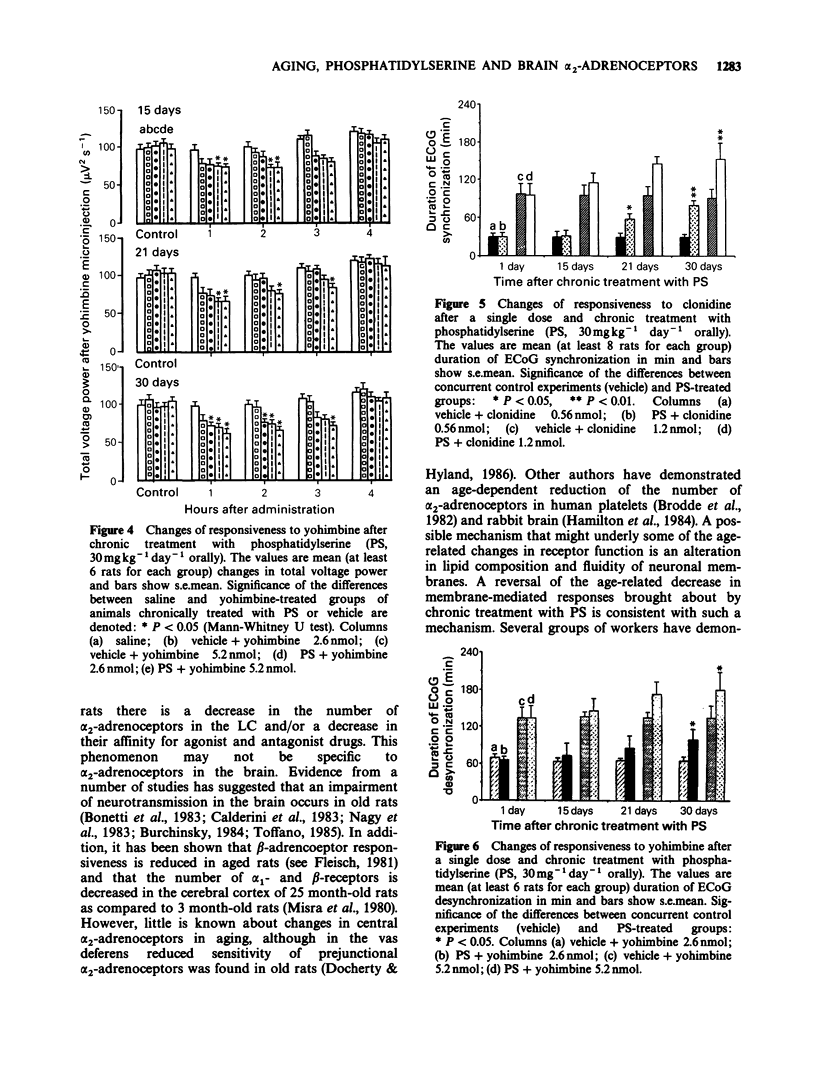
1. The behavioural and electrocortical (ECoG) power spectrum effects of clonidine, and yohimbine, an agonist and an antagonist at alpha 2-adrenoceptors, after their unilateral microinfusion into the rat locus coeruleus (LC) in young (50-70 days old) and old (13-15 months old) rats were studied. 2. Clonidine (0.09, 0.19, 0.28 and 0.56 nmol) microinfused into the LC of young rats induced dose-dependent behavioural and ECoG slow wave sleep (SWS) with a significant increase in total voltage power and power in the lower frequency bands. In contrast, yohimbine (1.3 and 2.6 nmol) infused into the LC of young rats produced ECoG desynchronization and a significant decrease in total voltage power. 3. In contrast to young rats, clonidine (0.19 and 0.28 nmol) given into the LC did not affect behaviour and the ECoG power spectrum in old rats. However, after higher doses of clonidine (0.56 and 1.2 nmol) a small and short-lasting period of behavioural and ECoG SWS was still evident. Similarly, in old rats yohimbine, at a dose (1.3 nmol) which was stimulative in young animals, did not significantly affect behaviour and ECoG power spectrum. Higher doses of yohimbine (2.6 and 5.2 nmol) were required to induce behavioural and ECoG changes similar to those observed with lower doses of yohimbine in young rats. 4. Chronic treatment with phosphatidylserine (30 mg kg-1, orally, daily for 21 and 30 days), was able gradually to restore in old rats, in comparison with a vehicle-treated group, the responsiveness of alpha 2-adrenoceptors to clonidine and yohimbine given into the LC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaral D. G., Sinnamon H. M. The locus coeruleus: neurobiology of a central noradrenergic nucleus. Prog Neurobiol. 1977;9(3):147–196. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(77)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Bloom F. E. Activity of norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats anticipates fluctuations in the sleep-waking cycle. J Neurosci. 1981 Aug;1(8):876–886. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-08-00876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Bloom F. E. Norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats exhibit pronounced responses to non-noxious environmental stimuli. J Neurosci. 1981 Aug;1(8):887–900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-08-00887.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonetti A. C., Bellini F., Calderini G., Galbiati E., Toffano G. Age-dependent changes in the mechanisms controlling prolactin secretion and phosphatidylinositol turnover in male rats: effect of phosphatidylserine. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Feb;45(2):123–129. doi: 10.1159/000124714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricolo A., Turazzi S., Faccioli F., Odorizzi F., Sciaretta G., Erculiani P. Clinical application of compressed spectral array in long-term EEG monitoring of comatose patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):211–225. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(78)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E., Anlauf M., Graben N., Bock K. D. Age-dependent decrease of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor number in human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchinsky S. G. Neurotransmitter receptors in the central nervous system and aging: pharmacological aspect (review). Exp Gerontol. 1984;19(4):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(84)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderini G., Bonetti A. C., Battistella A., Crews F. T., Toffano G. Biochemical changes of rat brain membranes with aging. Neurochem Res. 1983 Apr;8(4):483–492. doi: 10.1007/BF00965104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casamenti F., Mantovani P., Amaducci L., Pepeu G. Effect of phosphatidylserine on acetylcholine output from the cerebral cortex of the rat. J Neurochem. 1979 Feb;32(2):529–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb00380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Catecholamine receptors on locus coeruleus neurons: pharmacological characterization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug 15;44(4):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cespuglio R., Gomez M. E., Faradji H., Jouvet M. Alterations in the sleep-waking cycle induced by cooling of the locus coeruleus area. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982 Nov;54(5):570–578. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(82)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T. K. The locus coeruleus in behavior regulation: evidence for behavior-specific versus general involvement. Behav Neural Biol. 1979 Mar;25(3):271–300. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(79)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews F. T., Calderini G., Battistella A., Toffano G. Age dependent changes in the methylation of rat brain phospholipids. Brain Res. 1981 Dec 14;229(1):256–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sarro G. B., Ascioti C., Froio F., Libri V., Nisticò G. Evidence that locus coeruleus is the site where clonidine and drugs acting at alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors affect sleep and arousal mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;90(4):675–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaiti A., Brunetti M., Gatti C., Porcellati G. Turnover of ethanolamine phosphoglycerides in different brain areas of adult and aged rats. Neurochem Res. 1984 Nov;9(11):1549–1558. doi: 10.1007/BF00964590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaiti A., Sitkievicz D., Brunetti M., Porcellati G. Phospholipid metabolism in neuronal and glial cells during aging. Neurochem Res. 1981 Jan;6(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00963901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti C., Cantelmi M. G., Brunetti M., Gaiti A., Calderini G., Teolato S. Effect of chronic treatment with phosphatidyl serine on phospholipase A1 and A2 activities in different brain areas of 4 month and 24 month old rats. Farmaco Sci. 1985 Jul;40(7):493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Howe C. A., Reid J. L. Changes in brain alpha-adrenoceptors with increasing age in rabbits. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 19;322(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon A., Benvegnù D., Toffano G., Orlando P., Massari P. Effect of brain cortex phospholipids on adenylate-cyclase activity of mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):23–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra C. H., Shelat H. S., Smith R. C. Effect of age on adrenergic and dopaminergic receptor binding in rat brain. Life Sci. 1980 Aug 11;27(6):521–526. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy K., Simon P., Zs-Nagy I. Spin label studies on synaptosomal membranes of rat brain cortex during aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):688–694. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91652-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm P. The locus coeruleus, catecholamines, and REM sleep: a critical review. Behav Neural Biol. 1979 Apr;25(4):415–448. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(79)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder F. Role of membrane lipid asymmetry in aging. Neurobiol Aging. 1984 Winter;5(4):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(84)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Hobson J. Neuronal activity during the sleep-waking cycle. Prog Neurobiol. 1976;6(3-4):155–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Hartman B. K. The central adrenergic system. An immunofluorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine-beta-hydroxylase as a marker. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Oct 15;163(4):467–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.901630406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffano G., Bruni A. Pharmacological properties of phospholipid liposomes. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1980 Oct;12(9):829–845. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(80)80046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


