Abstract
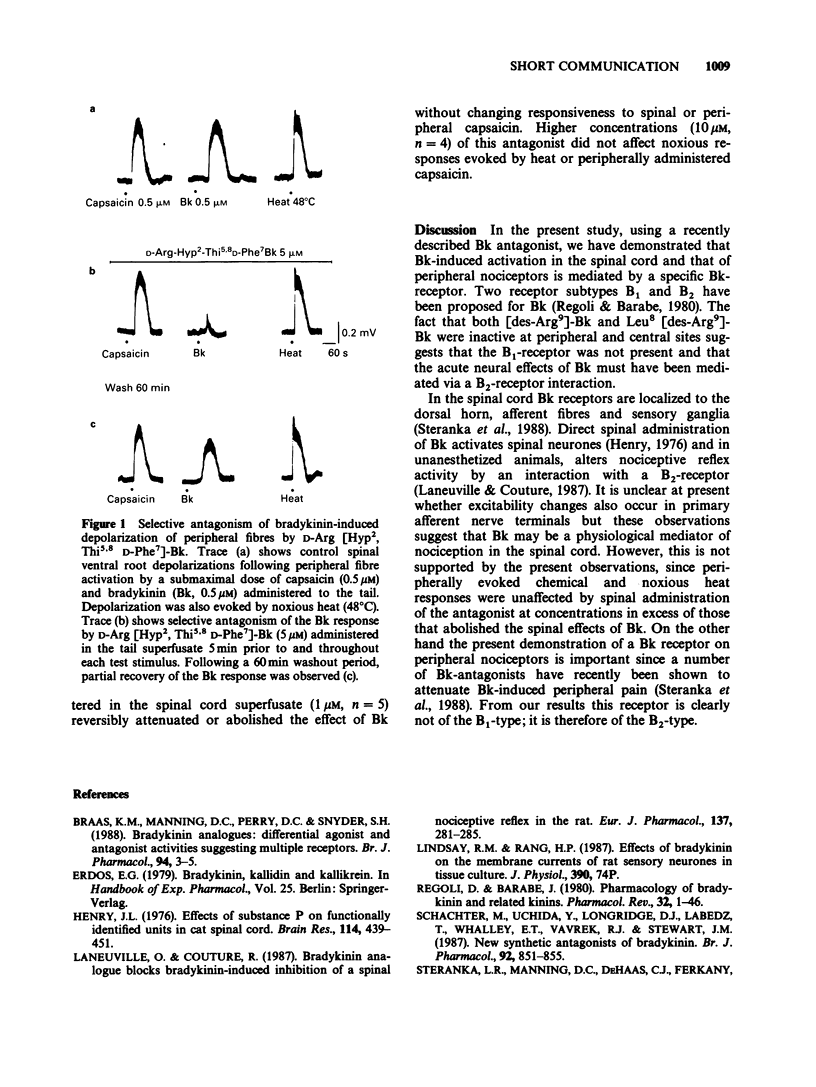
In an in vitro preparation of the neonatal rat spinal cord with attached tail, administration of bradykinin (Bk) to the spinal cord or to the tail produced depolarization of a ventral root (L3-L5). The effect of Bk at each site was selectively and reversibly antagonized by D-Arg [Hyp2, Thi5,8 D-Phe7]-Bk but could not be mimicked or antagonized by the B1-receptor ligands [des-Arg9]-Bk or Leu8[des-Arg9]-Bk, respectively. Peripherally evoked noxious responses produced by capsaicin or heat, were unaffected by either antagonist administered to the spinal cord. These data suggest that Bk-evoked responses in the spinal cord and at peripheral nociceptors were mediated via a receptor which by definition is of the B2-type. Additionally Bk is unlikely to be a physiological mediator of acute nociception in the spinal cord.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braas K. M., Manning D. C., Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin analogues: differential agonist and antagonist activities suggesting multiple receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Effects of substance P on functionally identified units in cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):439–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laneuville O., Couture R. Bradykinin analogue blocks bradykinin-induced inhibition of a spinal nociceptive reflex in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 4;137(2-3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M., Uchida Y., Longridge D. J., Labedz T., Whalley E. T., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. New synthetic antagonists of bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;92(4):851–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Manning D. C., DeHaas C. J., Ferkany J. W., Borosky S. A., Connor J. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3245–3249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


