Abstract
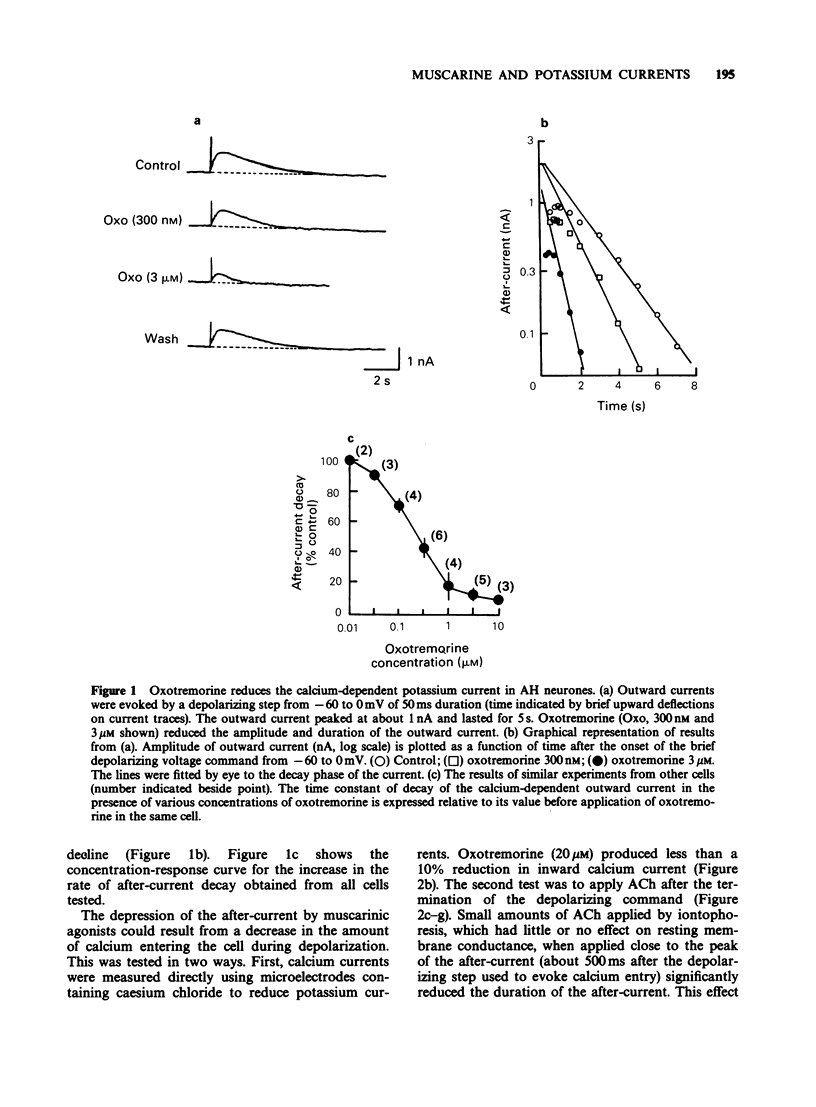
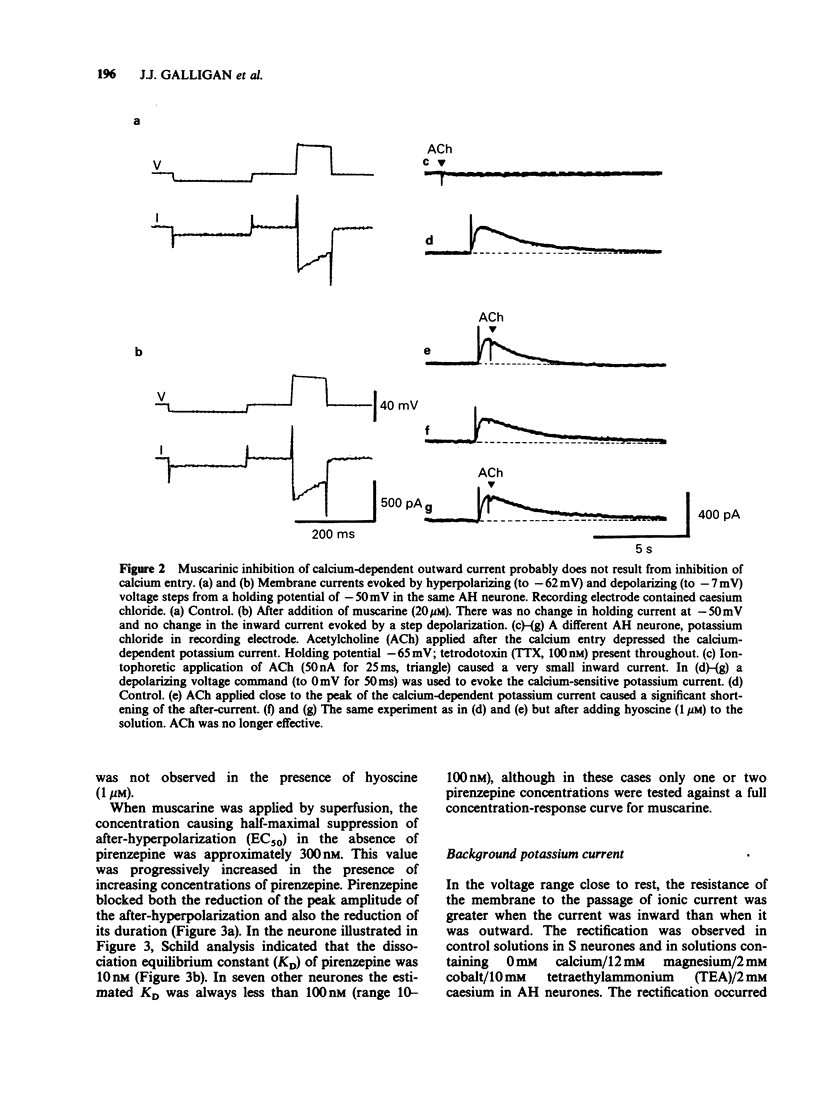
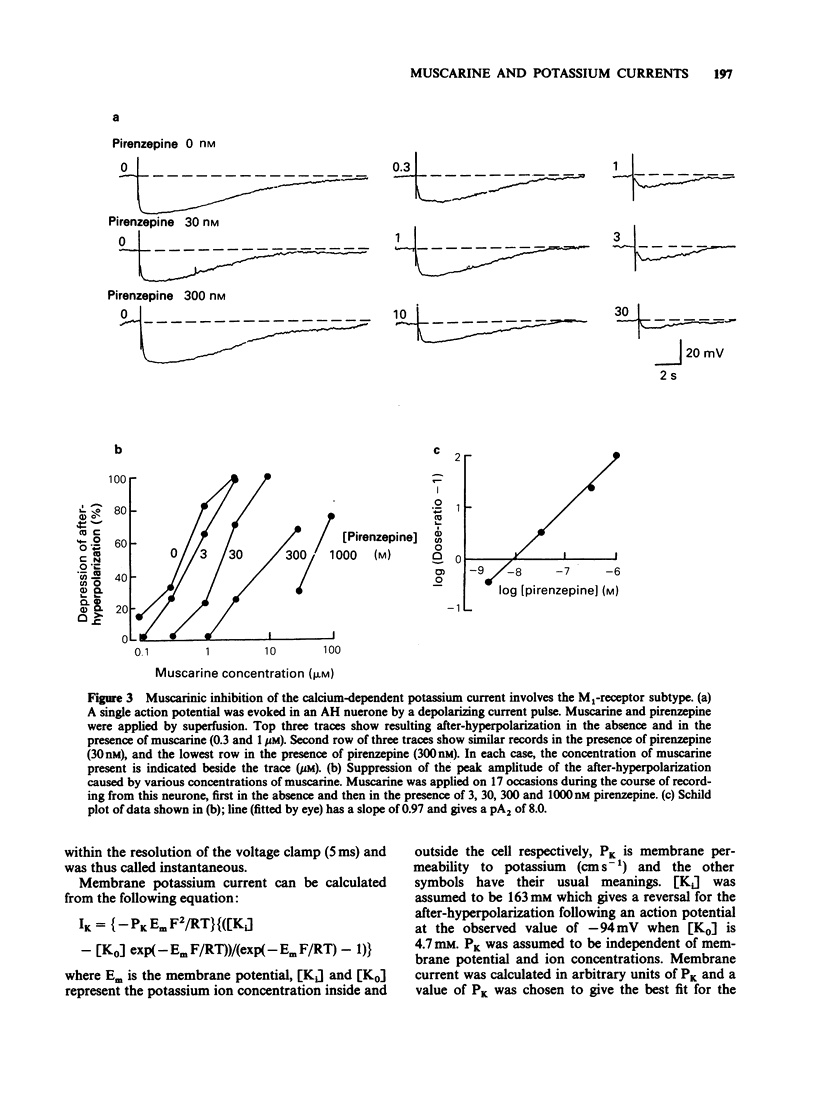
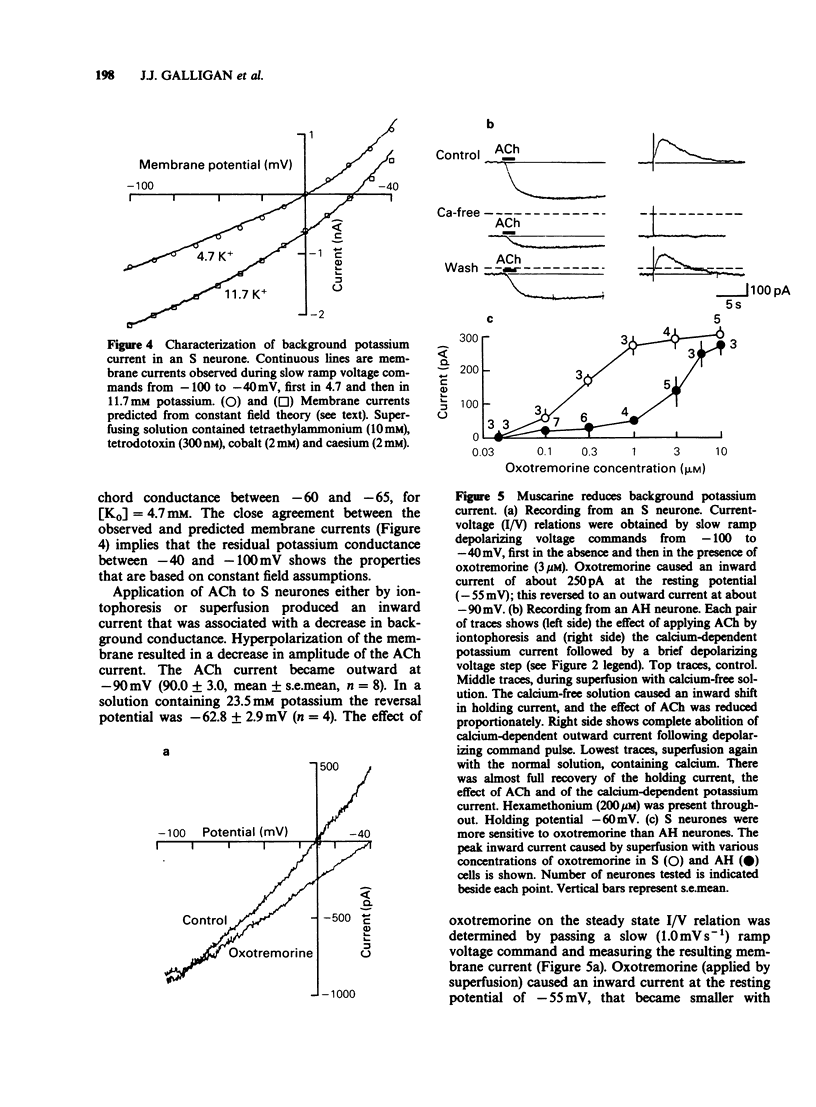
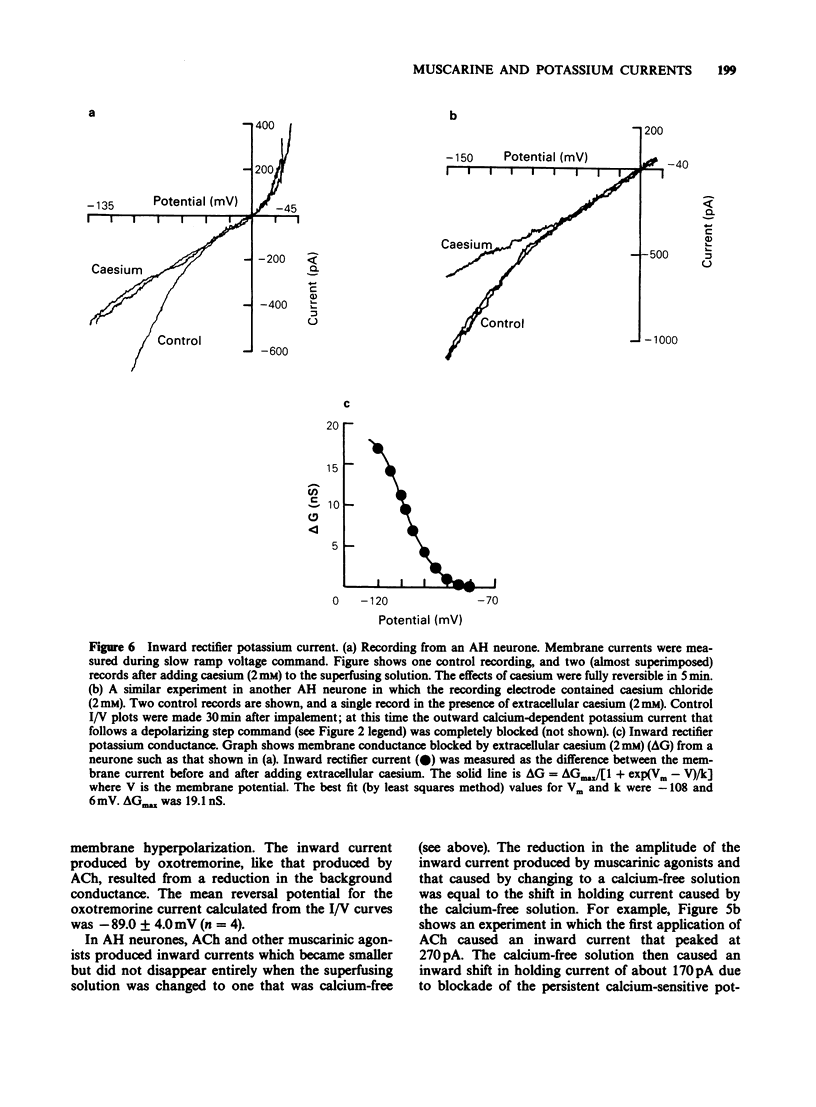
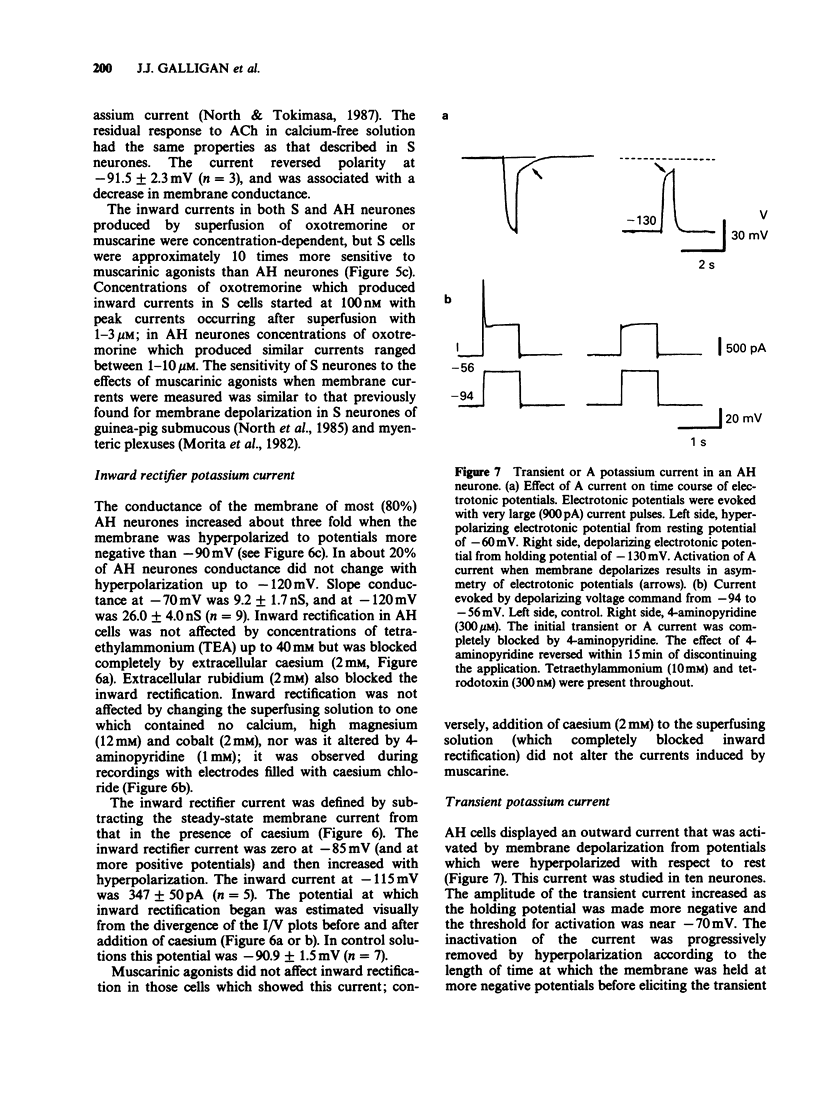
1. Intracellular electrophysiological recordings were obtained from single neurones of the guinea-pig myenteric plexus in vitro. Using single electrode voltage clamp techniques, four distinct potassium currents were described and the effects of muscarinic agonists on these currents were studied. 2. A calcium-dependent potassium current (gKCa) was present in AH neurones at rest, and was much increased following a brief depolarization (50 ms, to 0 mV). Muscarinic agonists reduced both the resting current and the current evoked by depolarization. Pirenzepine competitively antagonized the suppression by muscarine of the calcium-dependent potassium current (or after-hyperpolarization) following an action potential. The dissociation equilibrium constant for pirenzepine was about 10 nM. 3. The conductance of AH neurones increased two to three fold when they were hyperpolarized negative to -90 mV. This inward rectification was blocked by extracellular caesium (2 mM) or rubidium (2 mM), but not by tetraethylammonium (TEA, 40 mM), 4-aminopyridine (100 microM) or cobalt (2 mM). The inward rectification was unaffected by muscarinic agonists. 4. When AH neurones were depolarized from very negative holding potentials (less than -80 mV) a brief outward current was recorded with a duration of about 200 ms. This transient or A current was completely blocked by 4-aminopyridine (100 microM) but was not affected by tetrodotoxin (300 nM), TEA (40 mM) or cobalt (2 mM). Muscarinic agonists did not affect the A current. 5. In S neurones, and in AH neurones in calcium-free solutions, the potassium conductance (in TEA and caesium) behaved according to constant field assumptions. This background conductance was suppressed by muscarinic agonists. 6. It is concluded that the depolarization by muscarinic agonists of myenteric AH neurones is due to a suppression of both a calcium-dependent potassium conductance and a background potassium conductance. Muscarinic depolarization of S neurones results only from suppression of the background potassium conductance. Effects on both conductances result from M1-receptor activation. Inward rectifying and transient outward (A) potassium currents are unaffected.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. THE RUBIDIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY OF FROG MUSCLE MEMBRANE. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:134–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Synaptic inhibition of the M-current: slow excitatory post-synaptic potential mechanism in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:263–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., McLachlan E. M. Muscarinic agonists block five different potassium conductances in guinea-pig sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):259–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):31–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Galvan M. Fast inward-rectifying current accounts for anomalous rectification in olfactory cortex neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:153–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:173–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepel F., Penit-Soria J. Inward rectification and low threshold calcium conductance in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. An in vitro study. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LIBET B. Origin and blockade of the synaptic responses of curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Krasne S., Ciani S. Anomalous permeabilities of the egg cell membrane of a starfish in K+-Tl+ mixtures. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):269–281. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(1):61–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Synaptic events in sympathetic ganglia. Prog Neurobiol. 1978;11(2):77–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech C. A., Stanfield P. R. Inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres and its dependence on membrane potential and external potassium. J Physiol. 1981;319:295–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists inactivate potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:125–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Misgeld U. Slow cholinergic excitation of guinea pig hippocampal neurons is mediated by two muscarinic receptor subtypes. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 18;67(2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Slack B. E., Surprenant A. Muscarinic M1 and M2 receptors mediate depolarization and presynaptic inhibition in guinea-pig enteric nervous system. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:435–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic synaptic potentials in guinea-pig myenteric plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:151–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Persistent calcium-sensitive potassium current and the resting properties of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:333–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Rubidium block and rubidium permeability of the inward rectifier of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:415–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists depress calcium-dependent gK in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Apr;10(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T. Spontaneous muscarinic suppression of the Ca-activated K-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 30;344(1):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Votava J. Slow synaptic excitation in sympathetic ganglion cells: evidence for synaptic inactivation of potassium conductance. Science. 1970 Nov 13;170(3959):755–758. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3959.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


