Abstract
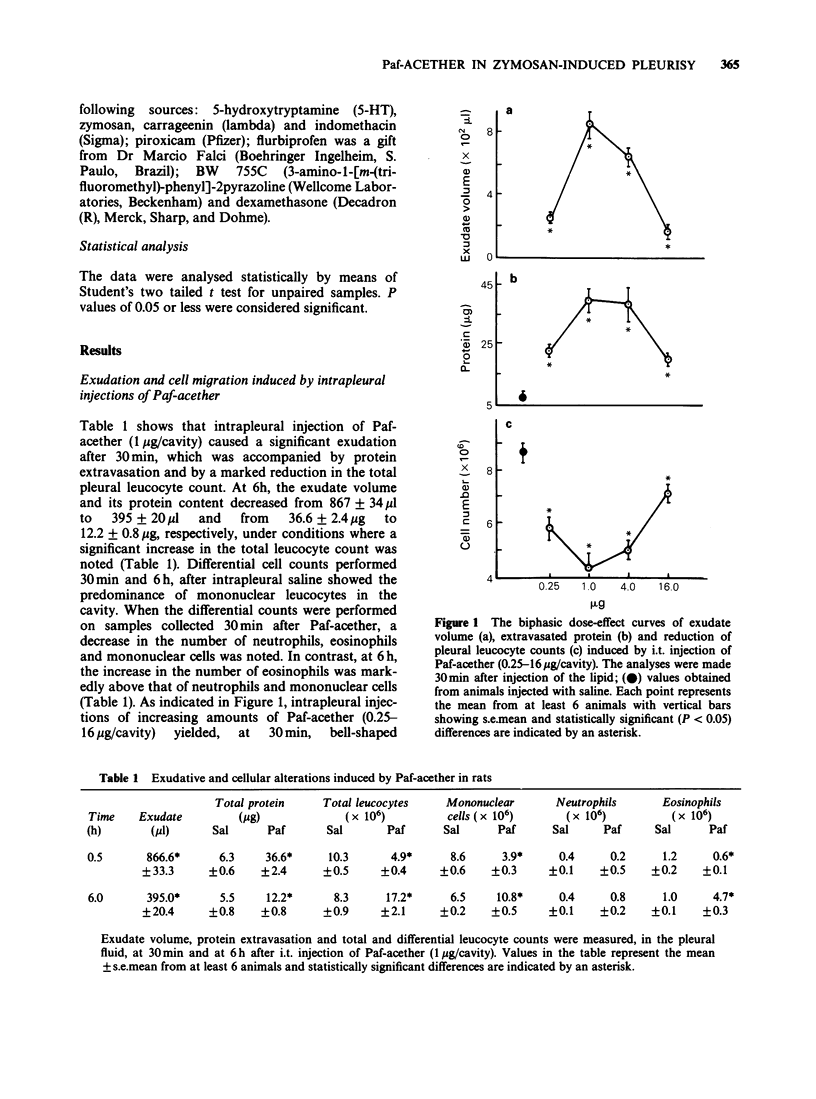
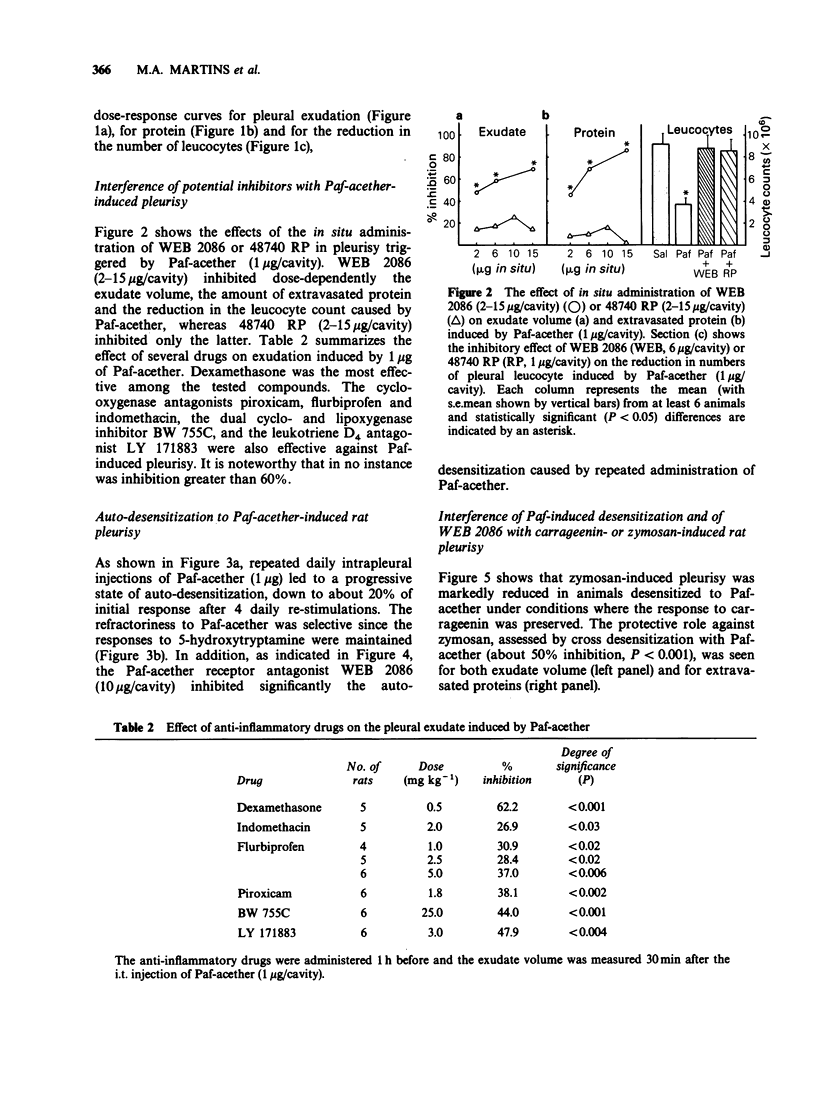
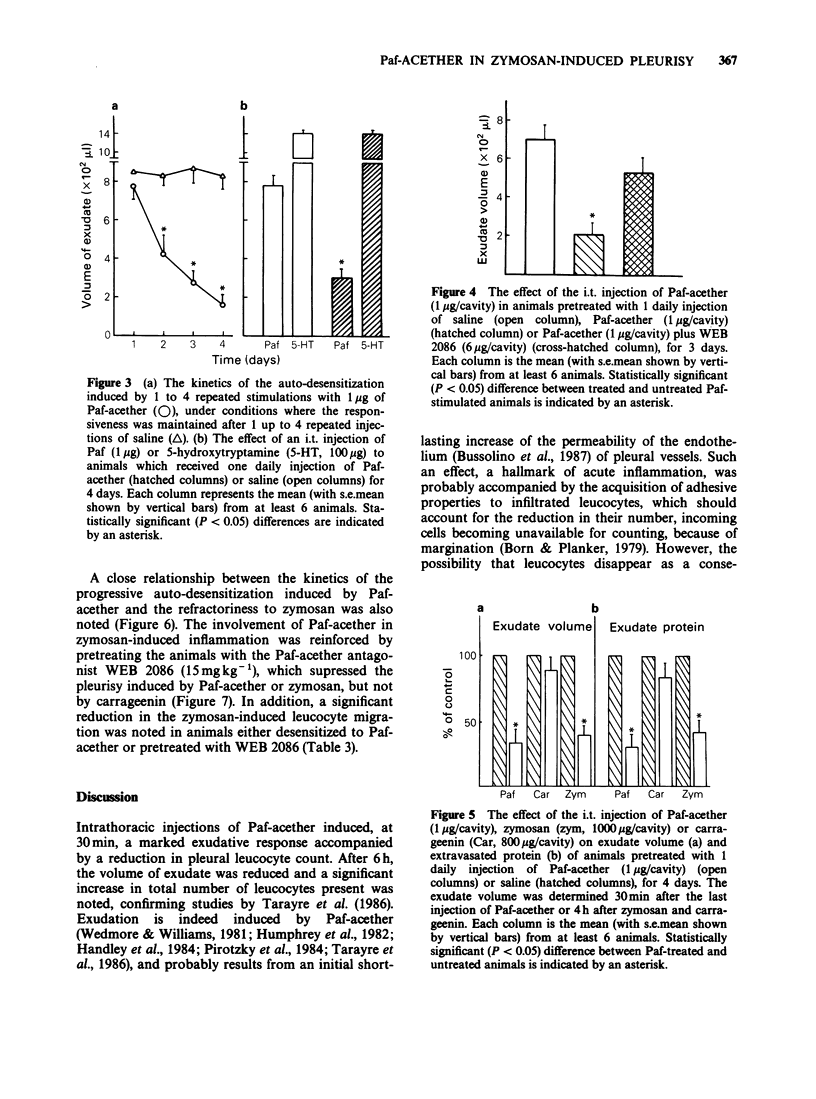
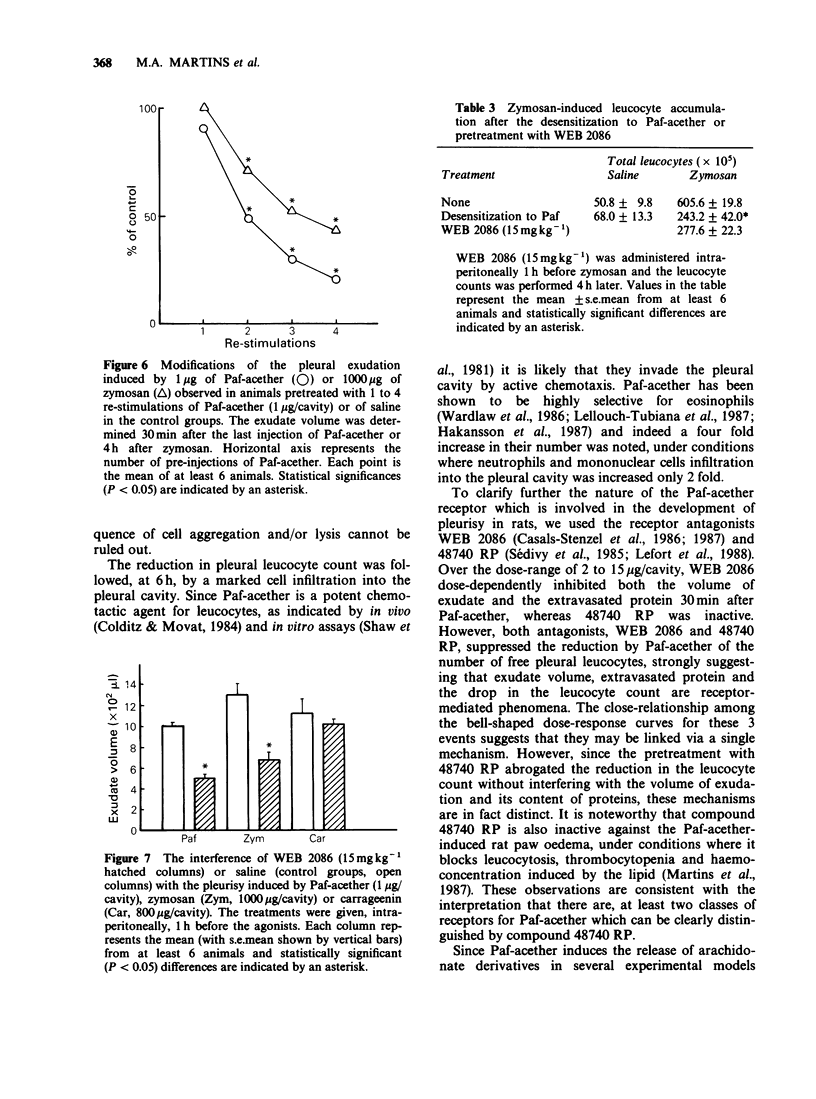
1. The intrapleural injection of Paf-acether into rats caused, at 30 min, a marked exudation accompanied by a reduction in the pleural leucocyte count. At 6 h, the exudate volume had decreased and a significant increase in the total leucocyte count, particularly eosinophils was noted. 2. Two Paf-acether antagonists, WEB 2086 and 48740 RP abrogated the pleural leucopenia observed 30 min after Paf-acether administration, whereas the exudation was inhibited only by the former. Pleurisy was also reduced by about 60% with dexamethasone, by about 45% with BW 755C or LY 171883, a mixed cyclo-oxygenase/lipoxygenase inhibitor and a peptido-leukotriene antagonist respectively, and by about 30% with indomethacin, flurbiprofen or piroxicam. 3. Repeated daily intrapleural injections of Paf-acether led to a state of progressive desensitization to Paf-acether itself, whereas responsiveness to 5-hydroxytryptamine was maintained. In addition, the Paf-induced auto-desensitization was largely inhibited by WEB 2086. 4. Pleurisy induced by zymosan, but not by carrageenin, was significantly reduced in Paf-acether-desensitized animals. These results were consistent with those obtained with WEB 2086 which suppressed zymosan-induced but not carrageenin-induced pleurisy. 5. This study suggests that Paf-acether-induced pleurisy in the rat may be mediated by lipoxygenase arachidonic acid metabolites and that pleurisy induced by zymosan, but not by carrageenin, is largely dependent upon Paf-acether.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk J., Smedegård G. Acute microvascular effects of PAF-acether, as studied by intravital microscopy. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M., Joseph D., Vargaftig B. B. Desensitization and antagonism of rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated with PAF acether. Prostaglandins. 1987 Jan;33(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(87)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Aglietta M., Braquet P., Bosia A., Pescarmona G., Sanavio F., D'Urso N., Marchisio P. C. Human endothelial cells are target for platelet-activating factor. I. Platelet-activating factor induces changes in cytoskeleton structures. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2439–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals-Stenzel J., Muacevic G., Weber K. H. Pharmacological actions of WEB 2086, a new specific antagonist of platelet activating factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz I. G., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of neutrophil accumulation in acute inflammatory lesions induced by chemotaxins and chemotaxinigens. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2169–2173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro R. S., Martins M. A., Silva P. M., Faria Neto H. C., Castanheira J. R., Vargaftig B. B. Desensitization to PAF-induced rat paw oedema by repeated intraplantar injections. Life Sci. 1986 Nov 17;39(20):1871–1878. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detsouli A., Lefort J., Vargaftig B. B. Histamine and leukotriene-independent guinea-pig anaphylactic shock unaccounted for by Paf-acether. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):801–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay S. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Contraction of guinea pig ileal smooth muscle by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):C130–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.3.C130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisch J. H., Rinkema L. E., Haisch K. D., Swanson-Bean D., Goodson T., Ho P. P., Marshall W. S. LY171883, 1-less than 2-hydroxy-3-propyl-4-less than 4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) butoxy greater than phenyl greater than ethanone, an orally active leukotriene D4 antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):148–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Lohman I. C., McManus L. M., Pinckard R. N. Respiratory and circulatory alterations induced by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine, a mediator of IgE anaphylaxis in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Dec;122(6):915–924. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Arbeeny C. M., Lee M. L., Van Valen R. G., Saunders R. N. Effect of platelet activating factor on endothelial permeability to plasma macromolecules. Immunopharmacology. 1984 Dec;8(3-4):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(84)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henocq E., Vargaftig B. B. Accumulation of eosinophils in response to intracutaneous PAF-acether and allergens in man. Lancet. 1986 Jun 14;1(8494):1378–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91683-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) as a mediator of neutrophil-platelet interactions in inflammation. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):545–547. doi: 10.1007/BF01978732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., McManus L. M., Satouchi K., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Vasoactive properties of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine and analogues. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lam M. H., Li C. L., Shen T. Y. Release of platelet activating factor and its involvement in the first phase of carrageenin-induced rat foot edema. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 14;120(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90636-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Li C. L., Lam M. H., Shen T. Y. Characterization of cutaneous vascular permeability induced by platelet-activating factor in guinea pigs and rats and its inhibition by a platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):617–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson L., Westerlund D., Venge P. New method for the measurement of eosinophil migration. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Dec;42(6):689–696. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.6.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancar S., Braquet P., Sirois P. Interactions of arachidonic acid metabolites and platelet activating factor and mechanism of action in hypersensitivity reactions. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1987;20(5):487–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keraly C. L., Benveniste J. Specific desensitization of rabbit platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) and derivatives. Br J Haematol. 1982 Jun;51(2):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort J., Sedivy P., Desquand S., Randon J., Coëffier E., Maridonneau-Parini I., Floch A., Benveniste J., Vargaftig B. B. Pharmacological profile of 48740 R.P., a PAF-acether antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun 10;150(3):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort J., Vargaftig B. B. Role of platelets in aspirin-sensitive bronchoconstriction in the guinea-pig; interactions with salicylic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellouch-Tubiana A., Lefort J., Simon M. T., Pfister A., Vargaftig B. B. Eosinophil recruitment into guinea pig lungs after PAF-acether and allergen administration. Modulation by prostacyclin, platelet depletion, and selective antagonists. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):948–954. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maridonneau-Parini I., Lagente V., Lefort J., Randon J., Russo-Marie F., Vargaftig B. B. Desensitization to PAF-induced bronchoconstriction and to activation of alveolar macrophages by repeated inhalations of PAF in the guinea pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91767-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins M. A., Silva P. M., Castro H. C., Neto F., Lima M. C., Cordeiro R. S., Vargaftig B. B. Interactions between local inflammatory and systemic haematological effects of PAF-acether in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencia-Huerta J. M., Benveniste J. Platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) and macrophages. II. Phagocytosis-associated release of PAF-acether from rat peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 15;57(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotzky E., Page C. P., Roubin R., Pfister A., Paul W., Bonnet J., Benveniste J. PAF-acether-induced plasma exudation in rat skin is independent of platelets and neutrophils. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics. 1984 Feb;1(1):107–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotzky E., Pfister A., Benveniste J. A role for Paf-acether (platelet-activating factor) in acute skin inflammation? Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jul;113 (Suppl 28):91–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb15632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Pinckard R. N., Ferrigni K. S., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J. Activation of human neutrophils with 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine (platelet activating factor). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1250–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. M., Cordeiro R. S., Martins M. A., Henriques M. G., Vargaftig B. B. Platelet involvement in rat paw edema induced by 2-methoxy-PAF. Inflammation. 1986 Dec;10(4):393–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00915823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Bowman B. J., Iden S. S. Stimulation of the human neutrophil superoxide anion-generating system with 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3- phosphorylcholine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 1;33(7):973–978. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarayre J. P., Delhon A., Bruniquel F., Puech L., Tisne-Versailles J., Couzinier J. P. Exudative, cellular and humoral reactions to platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) in the pleural cavity of rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 27;124(3):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Harada K., Fukuzawa K., Tsukatani H. Biphasic action of platelet-activating factor on isolated guinea-pig ileum. Lipids. 1983 Nov;18(11):848–850. doi: 10.1007/BF02534647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Ferreira S. H. Blockade of the inflammatory effects of platelet-activating factor by cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1981 Jul;14(2-3):187–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel N. F., Worthen S., Reeves J. T., Henson P. M., Murphy R. C. Nonimmunological production of leukotrienes induced by platelet-activating factor. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.7123233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Moqbel R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Platelet-activating factor. A potent chemotactic and chemokinetic factor for human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI112765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


