Abstract
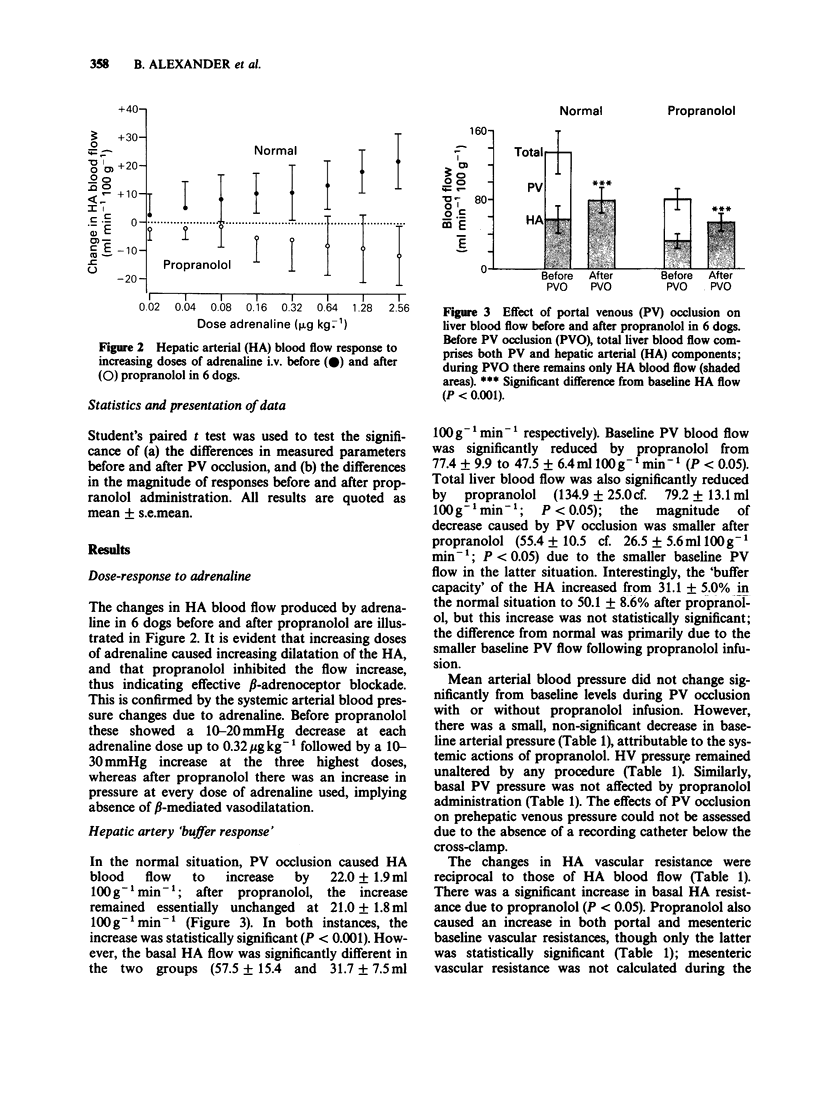
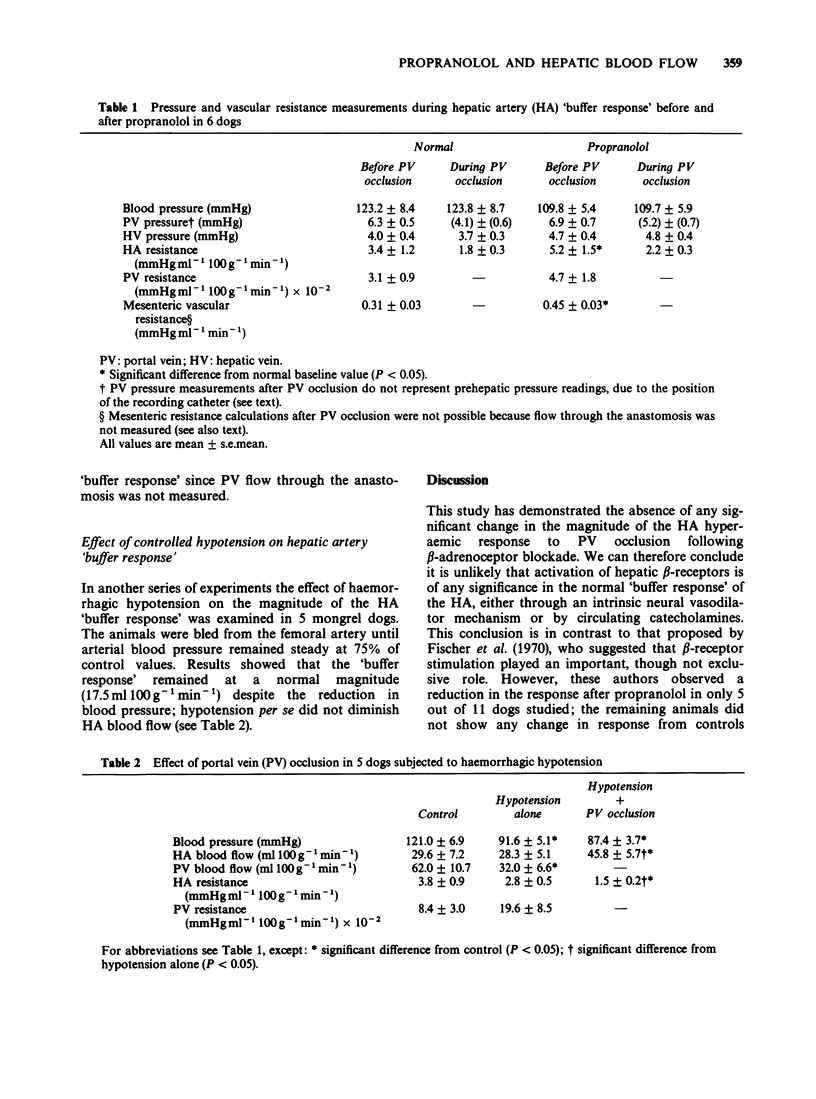
1. It has been reported that activation of beta-adrenoceptors may be responsible for the hyperaemic response of the hepatic artery to portal venous blood flow reduction. 2. The effect of beta-adrenoceptor blockade on the hepatic arterial response to portal vein occlusion was investigated in 6 anaesthetized dogs. A side-to-side portacaval shunt was established to prevent loss of venous return and arterial blood pressure during periods of portal occlusion. Measurements of hepatic arterial and portal venous blood flows were made by use of electromagnetic flow probes. 3. Intravenous propranolol injection, at a dose sufficient to block the vasodilator effect of low doses of exogenous adrenaline, did not alter the magnitude of the hyperaemic response of the hepatic artery. Propranolol also produced no change in baseline portal venous pressure. 4. It is concluded that hepatic beta-adrenoceptors are unlikely to be involved in the arterial response to portal occlusion. The absence of any reduction in basal portal venous pressure by propranolol is of interest in view of the current application of the drug in the treatment of patients with portal hypertension.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderberg B., Andersson P. A., Heuman R., Jansson L., Jorfeldt L., Rutberg H., Sjödahl R. Effect of propranolol and sclerotherapy in bleeding esophageal varices. A case report. Acta Chir Scand. 1984;150(1):109–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercoff E., Bataille C., Pariente A. E., Valla D., Delhotal B., Lebrec D. Assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):451–453. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs A. K., Jenkins W. J., Sherlock S., Dunk A., Walt R. P., Osuafor T. O., Mackie S., Dick R. Controlled trial of propranolol for the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 22;309(25):1539–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312223092502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Propranolol in portal hypertension: problems in paradise? Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):560–564. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Takács L., Bencsáth P., Vaslaki L. The rôle of beta-receptors in the regulation of the arterial circulation of the liver. Acta Hepatosplenol. 1970 Nov-Dec;17(6):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Stark R. D. Hepatic vascular bed. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):23–65. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillon P., Lebrec D., Muńoz C., Jungers M., Goldfarb G., Benhamou J. P. Comparison of the effects of a cardioselective and a nonselective beta-blocker on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):528–531. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. L., Mathie R. T., Fitch W., Campbell D. Liver blood flow and oxygen consumption during hypocapnia and IPPV in the greyhound. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Aug;47(2):290–295. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins S. A., Baxter J. N., Johnson J. N., Devitt P., Shields R. Effects of propranolol on hepatic haemodynamics in the cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic rat. Br J Surg. 1985 May;72(5):354–358. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kock N. G., Hahnloser P., Roding B., Schenk W. G., Jr Interaction between portal venous and hepatic arterial blood flow: an experimental study in the dog. Surgery. 1972 Sep;72(3):414–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger R. J., Groszmann R. J. Effect of selective blockade of beta 2-adrenergic receptors on portal and systemic hemodynamics in a portal hypertensive rat model. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):896–900. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W. Relationship between hepatic blood flow and overall metabolism: the hepatic arterial buffer response. Fed Proc. 1983 Apr;42(6):1662–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Hillon P., Muńoz C., Goldfarb G., Nouel O., Benhamou J. P. The effect of propranolol on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: a hemodynamic study. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Nouel O., Corbic M., Benhamou J. P. Propranolol--a medical treatment for portal hypertension? Lancet. 1980 Jul 26;2(8187):180–182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T., Blumgart L. H. Haemodynamic and metabolic consequences of reversed portal venous blood flow after side-to-side portacaval shunt in the dog. Acta Chir Scand. 1987 Nov-Dec;153(11-12):653–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T., Blumgart L. H. The hepatic haemodynamic response to acute portal venous blood flow reductions in the dog. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Nov;399(3):223–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00656719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T., Lam P. H., Harper A. M., Blumgart L. H. The hepatic arterial blood flow response to portal vein occlusion in the dog: the effect of hepatic denervation. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(1):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00584191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Nakayama T., Saito M., Hatano H., Tsukamoto T., Terabayashi H., Sugita S., Wada K., Nomura F., Koen H. Effects of propranolol on portal hemodynamics in patients with chronic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1985 Feb;80(2):132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. D., Withrington P. G. Liver blood flow. II. Effects of drugs and hormones on liver blood flow. Gastroenterology. 1981 Aug;81(2):356–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. D., Withrington P. G. The role of beta-adrenoceptors in the responses of the hepatic arterial vascular bed of the dog to phenylephrine, isoprenaline, noradrenaline and adrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;60(2):239–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems B., Villeneuve J. P., Huet P. M. Effect of propranolol on hepatic and systemic hemodynamics in dogs with chronic bile duct ligation. Hepatology. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


