Abstract
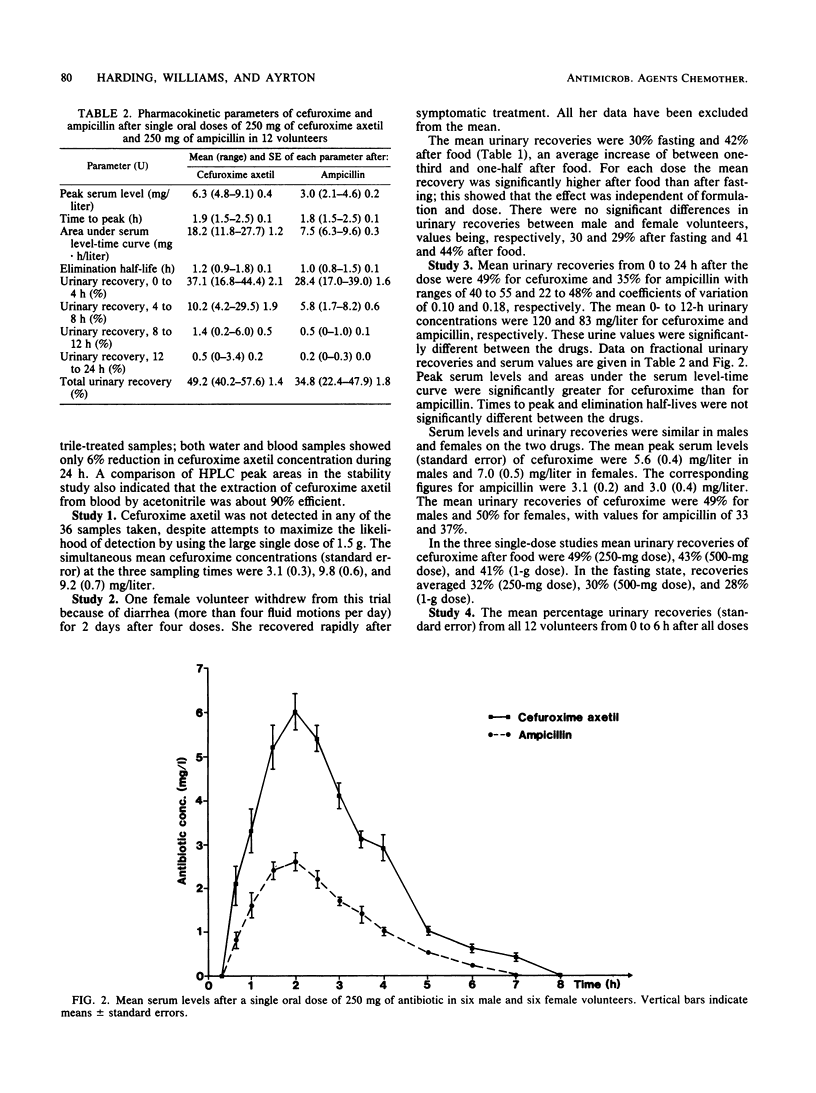
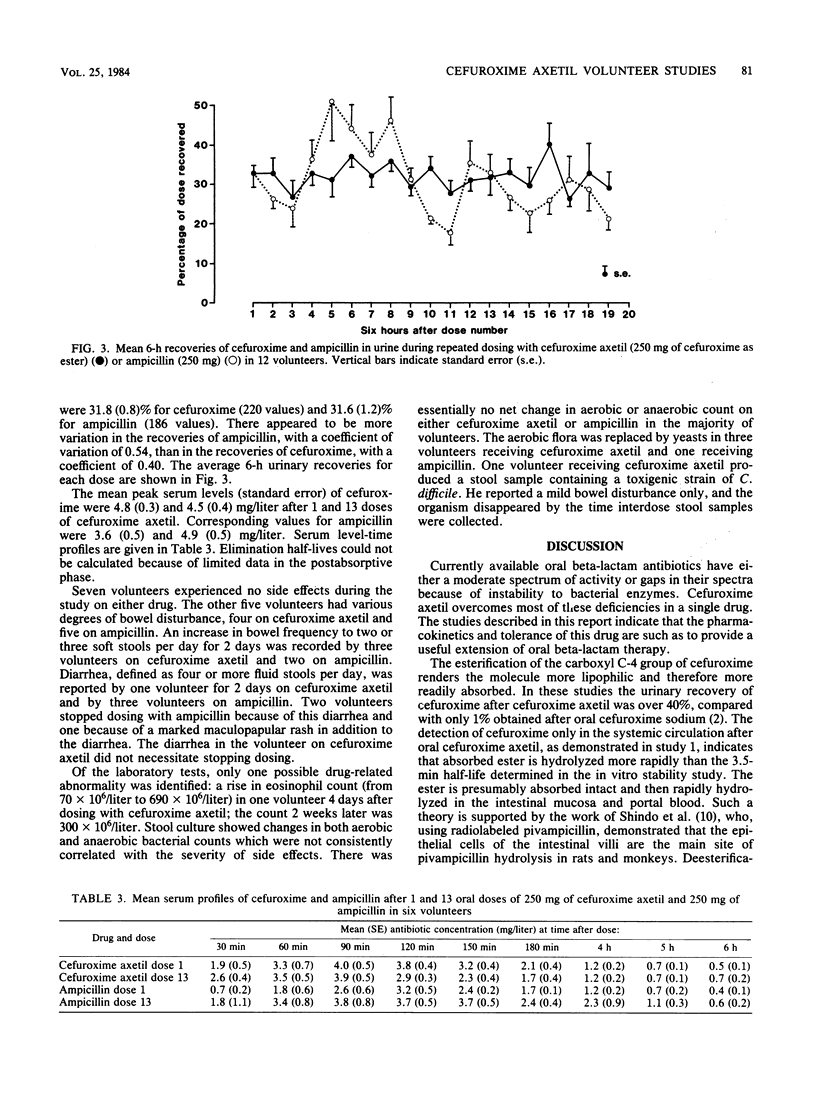
Cefuroxime axetil is a new orally absorbed prodrug of the antibiotic cefuroxime. The results of pharmacological studies in 52 healthy volunteers are presented. Intact cefuroxime axetil was not detected in the systemic circulation, indicating that deesterification to yield cefuroxime occurs rapidly after absorption. The bioavailability as measured by urinary recovery of cefuroxime was 40 to 50% if the drug was taken after food and 30% if the drug was taken after overnight fasting. Absorption was similar for three different formulations at 500 mg and independent of dose over the range of 250 mg to 1 g. When the drug was taken after food, serum levels and urinary recoveries were significantly greater for cefuroxime than for ampicillin, but when the drug was taken after fasting the values were similar for the two drugs. The kinetic behavior of cefuroxime axetil and ampicillin was not influenced by repeated dosing at 250 mg. Cefuroxime axetil was well tolerated. Although changes in bowel flora and habit were noted during repeated dosing, these changes were no greater than with ampicillin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Foord R. D. Cefuroxime: human pharmacokinetics.. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):741–747. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godtfredsen W. O. An introduction to mecillinam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3 (Suppl B):1–4. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. H., Langley P. F., Lees L. J. Bioavailability and metabolism of talampicillin. Chemotherapy. 1978;24(4):217–226. doi: 10.1159/000237784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Parry J. V., Price A. B., Davies D. R., Dolby J., Tyrrell D. A. Undescribed toxin in pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1977 May 14;1(6071):1246–1248. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6071.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh D. A. Antimicrobial usage in forty-three hospitals in England. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jan;9(1):75–84. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F. Gastrointestinal absorption of drugs. Med Clin North Am. 1974 Sep;58(5):907–916. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Huang H., Koch P. A., Craig W. A., Madsen P. O. Bioavailability of ampicillin and amoxicillin in fasted and nonfasted subjects. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Apr;66(4):549–552. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


