Abstract
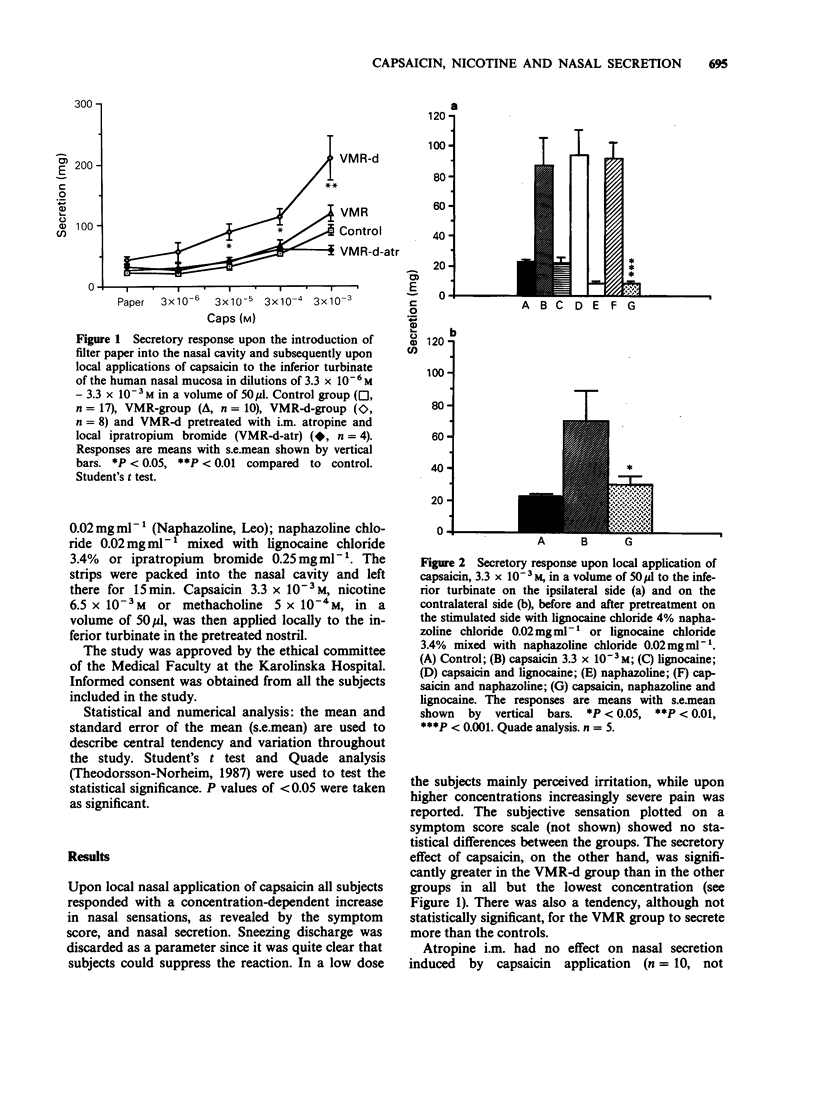
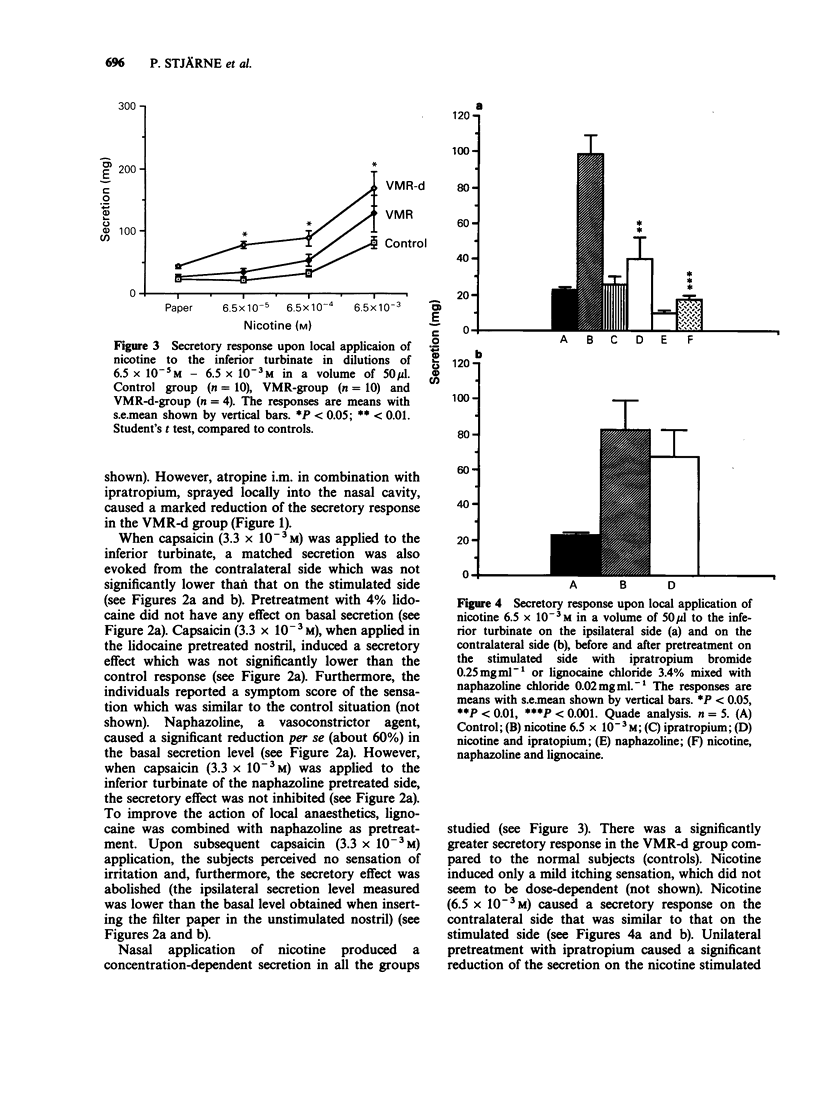
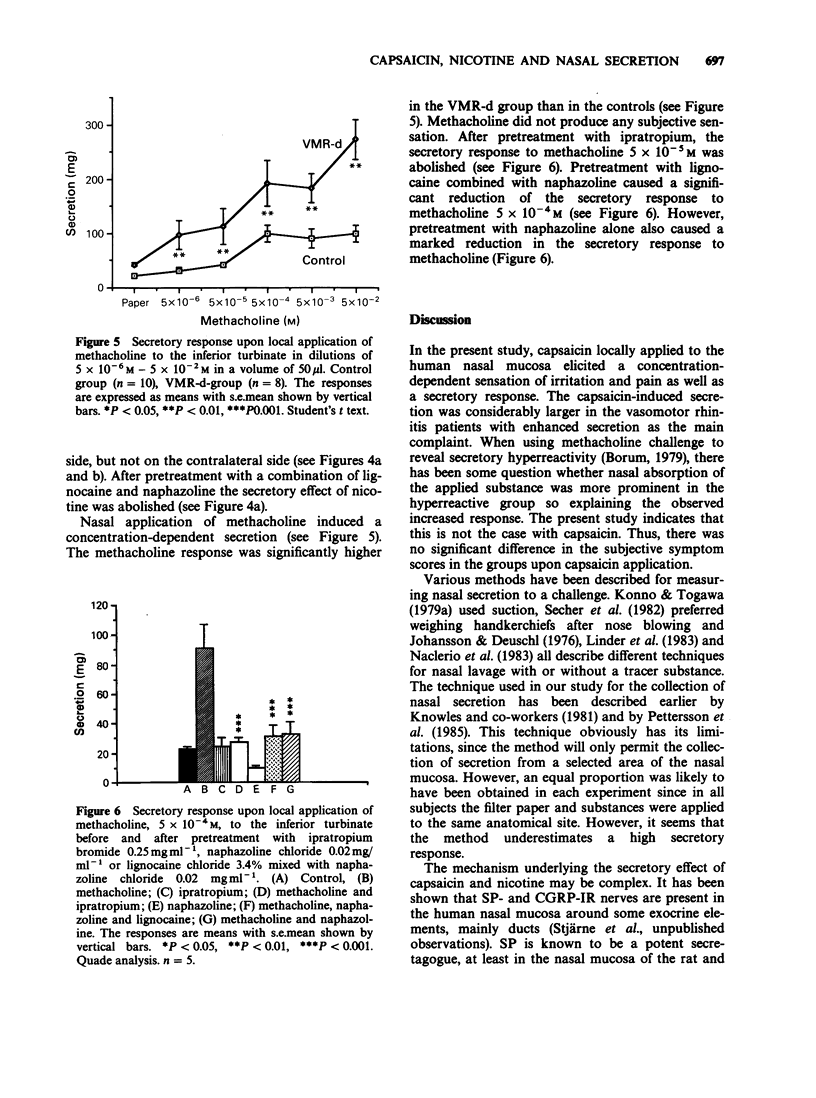
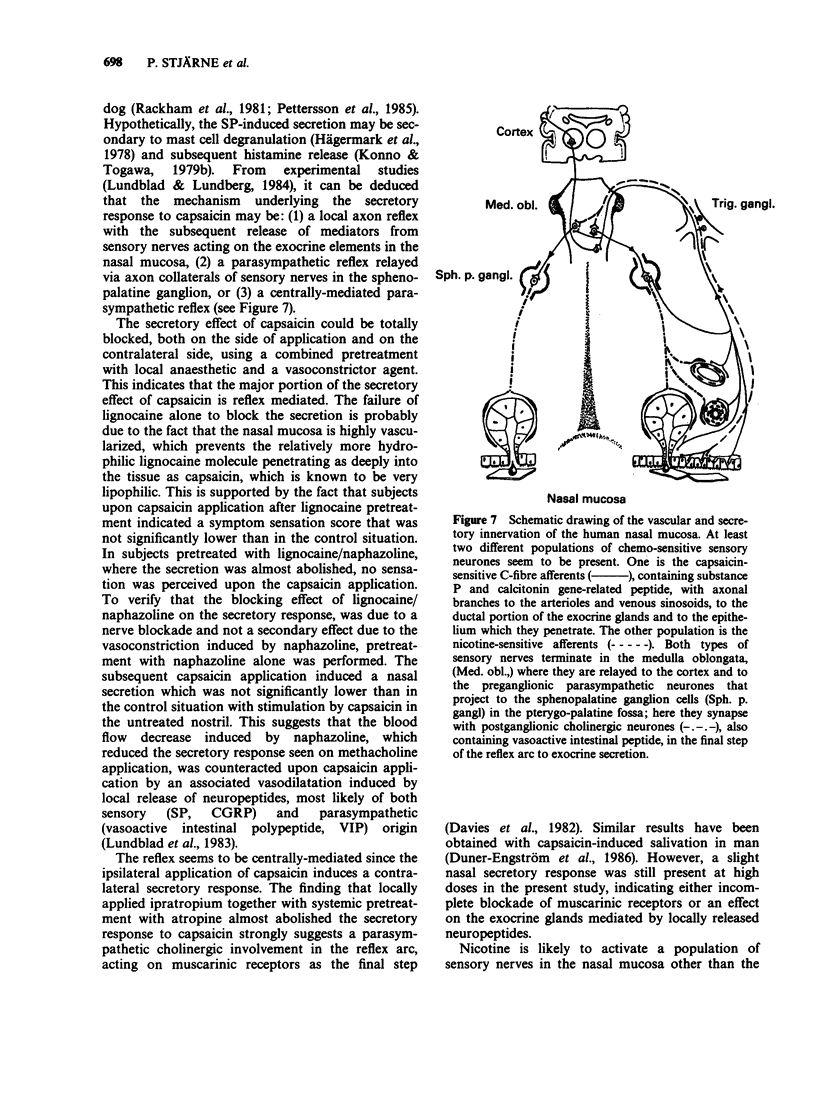
1. Applications of capsaicin, nicotine and methacholine were made locally onto the nasal mucosa in human controls and patients suffering from hyperreactive nasal disorders. Perception of sensation was registered as a sympton score and secretion quantified. The sensory reaction (irritation - pain) to capsaicin was similar in the three groups studied, i.e. controls, a group of patients with the diagnosis of vasomotor rhinitis and a group of patients with increased nasal secretion as the main symptom of the hyperreactive disorder. Nicotine induced only a mild itching sensation in the three groups. However, capsaicin and nicotine challenge caused a significantly larger secretory response in the last group than in the unselected vasomotor rhinitis group and in the control group. 2. Pretreatment with muscarinic receptor antagonists almost completely abolished the secretory response to both capsaicin and nicotine, and blocked methacholine-induced secretion. Furthermore, pretreatment with a combination of local anaesthetic and vasoconstrictor agent abolished the capsaicin-induced irritation, as well as the capsaicin- and nicotine-induced secretion on both the ipsilateral and the contralateral side. Therefore, no clearcut contribution seems to be exerted by locally released peptides from sensory neurones as direct trigger substances for the secretory response to capsaicin. 3. In conclusion, the nasal secretory response, in man, to both capsaicin and nicotine, seems to be mediated via cholinergic parasympathetic reflexes. In patients with hyperreactive non-allergic disorders of the nasal mucosa with rhinorrhea as the main complaint, the enhanced secretion may be due to a hyperreactive efferent cholinergic mechanism rather than hypersensitive irritant receptors on capsaicin- and nicotine-sensitive sensory neurones.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borum P., Grønborg H., Brofeldt S., Mygind N. Nasal reactivity in rhinitis. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borum P. Nasal methacholine challenge. A test for the measurement of nasal reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Apr;63(4):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauna N., Cauna D., Hinderer K. H. Innervation of human nasal glands. J Neurocytol. 1972 Jul;1(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01098645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Roberts A. M., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C. Reflex tracheal gland secretion evoked by stimulation of bronchial C-fibers in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Oct;53(4):985–991. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.4.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunér-Engström M., Fredholm B. B., Larsson O., Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Autonomic mechanisms underlying capsaicin induced oral sensations and salivation in man. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:87–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Molnar A., Lembeck F. Substance P release from spinal cord slices by capsaicin. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 13;25(7):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Fusco B. M., Marabini S., Maggi C. A., Fanciullacci M., Sicuteri F. Secretion, pain and sneezing induced by the application of capsaicin to the nasal mucosa in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):509–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X. Y., Saria A., Gamse R., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Lundberg J. M. Capsaicin induced release of multiple tachykinins (substance P, neurokinin A and eledoisin-like material) from guinea-pig spinal cord and ureter. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hägermark O., Hökfelt T., Pernow B. Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Oct;71(4):233–235. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibe T., Yamashita T., Kumazawa T., Tanaka C. Adrenergic and cholinergic receptors in human nasal mucosa in cases of nasal allergy. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1983;238(2):167–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00454309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Deuschl H. Immunoglobulins in nasal secretion with special reference to IgE. I. Methodological studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;52(1-4):364–375. doi: 10.1159/000231703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles G. K., Townsend P., Turner-Warwick M. A standardized filter paper technique for assessing nasal secretory activity. Clin Allergy. 1981 May;11(3):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1981.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno A., Togawa K. Role of the vidian nerve in nasal allergy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1979 Mar-Apr;88(2 Pt 1):258–266. doi: 10.1177/000348947908800219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno A., Togawa K. Vidian neurectomy for allergic rhinitis. Evaluation of long-term results and some problems concerning operative therapy. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1979;225(1):67–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00455877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder A., Ronquist G., Deuschl H. Random distribution of exogenous lithium in nasal secretion and its application in substance determination. Acta Otolaryngol. 1983 Sep-Oct;96(3-4):287–293. doi: 10.3109/00016488309132901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad L., Brodin E., Lundberg J. M., Anggård A. Effects of nasal capsaicin pretreatment and cryosurgery on sneezing reflexes, neurogenic plasma extravasation, sensory and sympathetic neurons. Acta Otolaryngol. 1985 Jul-Aug;100(1-2):117–127. doi: 10.3109/00016488509108596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad L., Lundberg J. M., Brodin E., Anggård A. Origin and distribution of capsaicin-sensitive substance P-immunoreactive nerves in the nasal mucosa. Acta Otolaryngol. 1983 Nov-Dec;96(5-6):485–493. doi: 10.3109/00016488309132735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad L., Lundberg J. M. Capsaicin sensitive sensory neurons mediate the response to nasal irritation induced by the vapour phase of cigarette smoke. Toxicology. 1984 Oct;33(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(84)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio R. M., Meier H. L., Kagey-Sobotka A., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Meyers D. A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Mediator release after nasal airway challenge with allergen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):597–602. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackham A., Therriault M., Wood P. L. Substance P: evidence for spinal mediation of some behavioural effects. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Aug;20(8):753–755. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Gamse R., Petermann J., Fischer J. A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Lundberg J. M. Simultaneous release of several tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide from rat spinal cord slices. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 30;63(3):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher C., Kirkegaard J., Borum P., Maansson A., Osterhammel P., Mygind N. Significance of H1 and H2 receptors in the human nose: rationale for topical use of combined antihistamine preparations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Sep;70(3):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E. Friedman and Quade tests: BASIC computer program to perform nonparametric two-way analysis of variance and multiple comparisons on ranks of several related samples. Comput Biol Med. 1987;17(2):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(87)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Luts A., Sundler F. Occurrence and distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the mammalian respiratory tract and middle ear. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(3):551–555. doi: 10.1007/BF00214575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Malm L., Sundler F. Substance-P-containing nerve fibers in the nasal mucosa. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1983;238(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00453736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


