Abstract
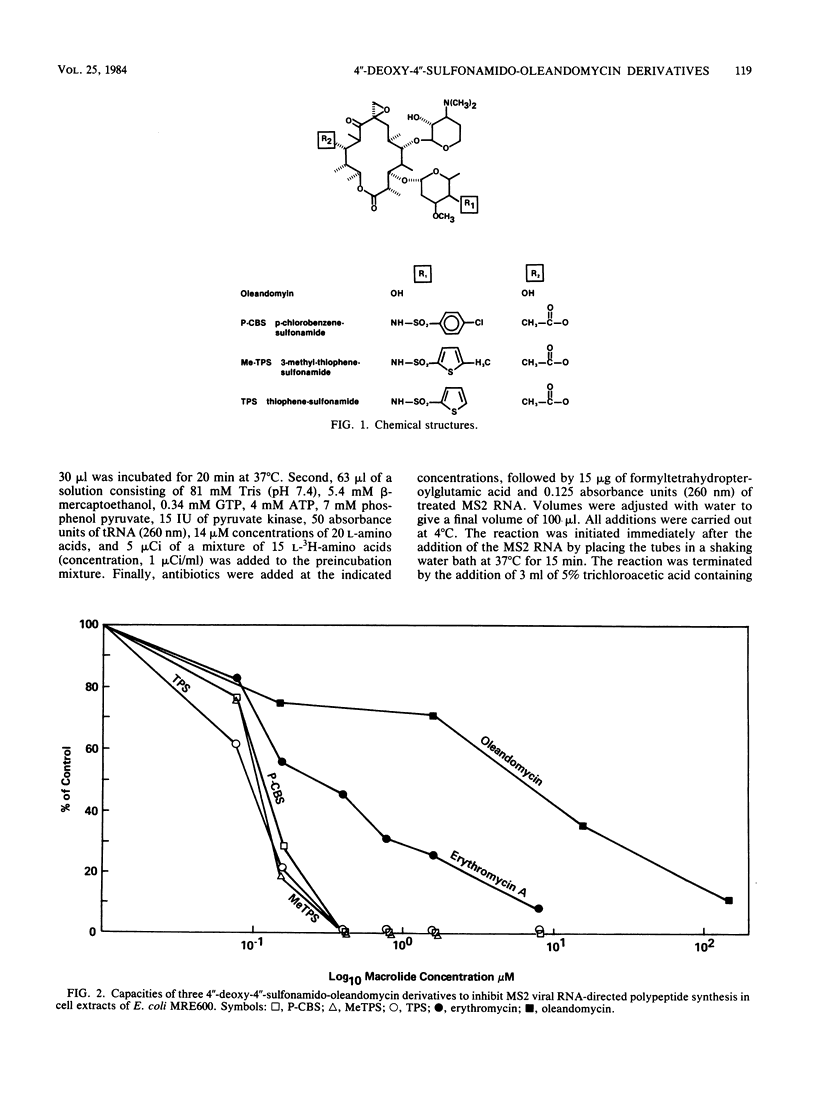
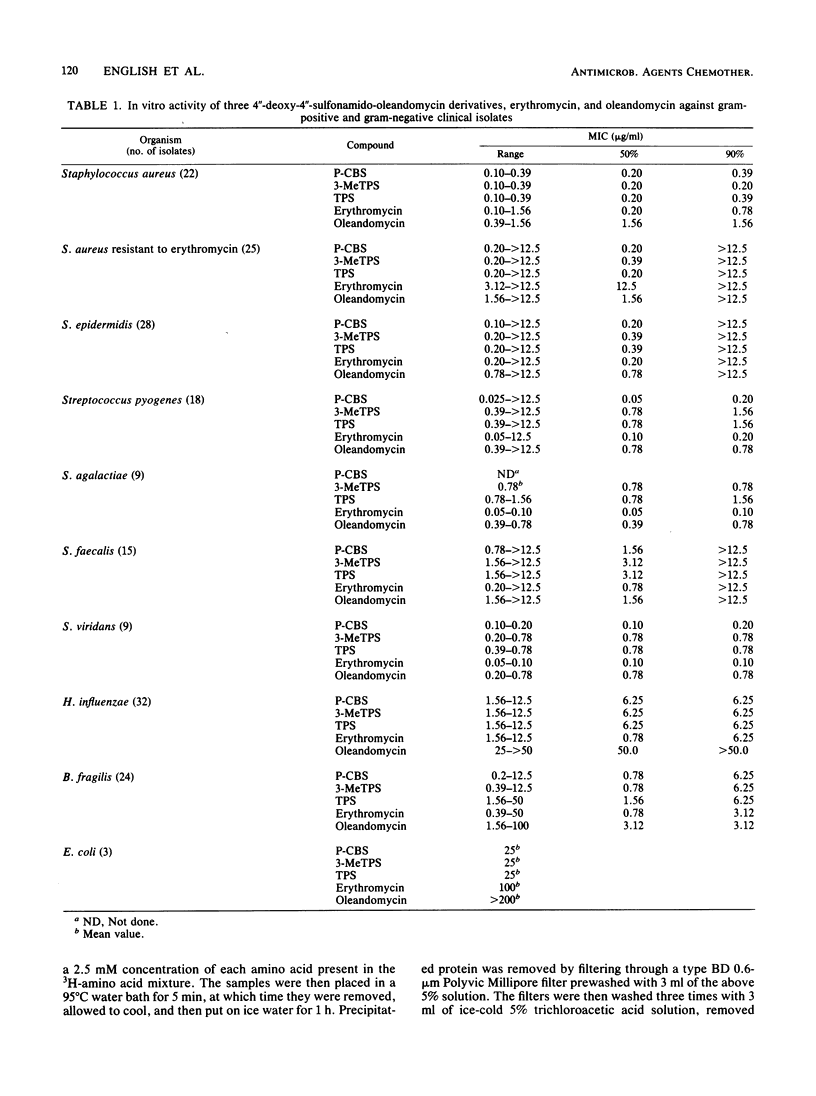
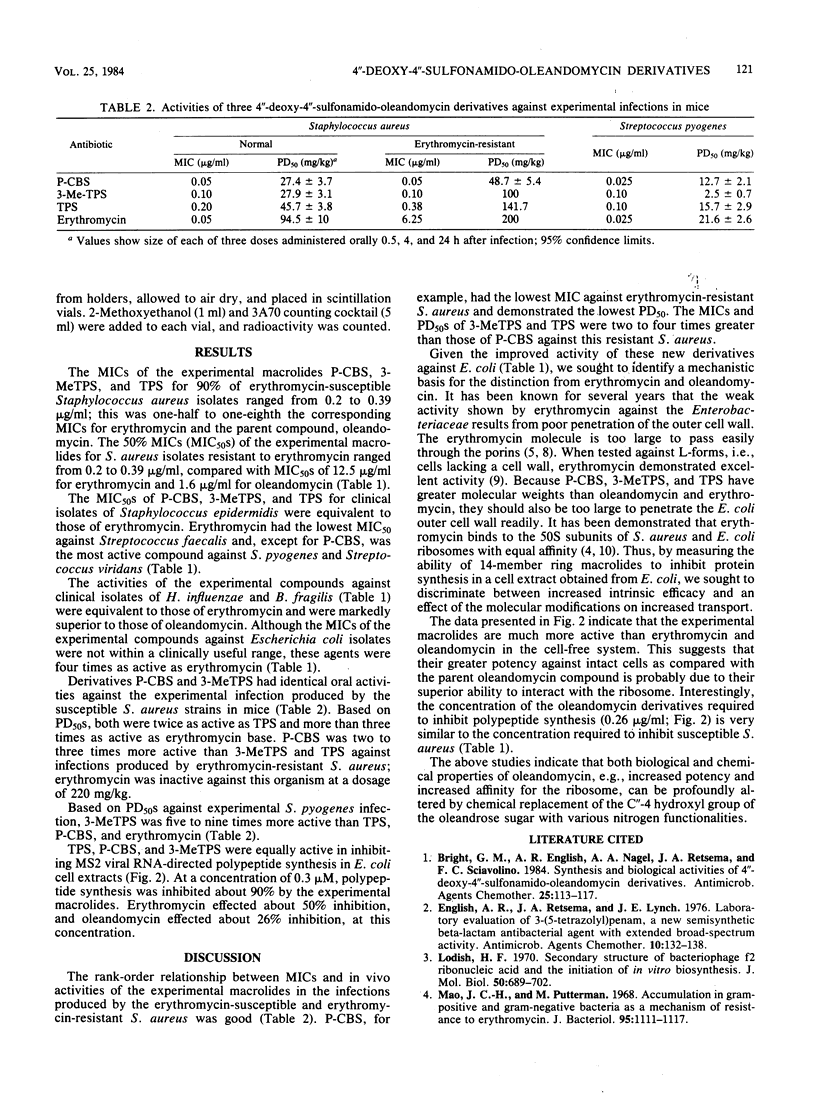
Three derivatives of oleandomycin in which the C"-4 hydroxyl moiety was replaced for the first time with a nitrogen functionality have been compared with erythromycin base and oleandomycin base. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of these derivatives for 90% of a group of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus were one-half to one-fourth those of erythromycin. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of the experimental macrolides for 50% of a group of S. aureus isolates resistant to greater than 12.5 micrograms of erythromycin per ml ranged from 0.2 to 0.39 micrograms/ml. The activities of these experimental compounds were equivalent to the activities of erythromycin against Staphylococcus epidermidis, Bacteroides fragilis, and Haemophilus influenzae isolates. In general, erythromycin was more active against Streptococcus species. Each experimental macrolide was superior to erythromycin in inhibiting RNA-directed, cell-free polypeptide synthesis. The three experimental compounds were markedly more active than erythromycin base after oral administration to mice infected with S. aureus. The 50% protective doses of the experimental compounds ranged from 27.4 to 45.7 mg/kg; that of erythromycin was approximately 100 mg/kg.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bright G. M., English A. R., Nagel A. A., Retsema J. A., Sciavolino F. C. Synthesis and biological activities of 4"-deoxy-4"-sulfonamido-oleandomycin derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Lynch J. E. Laboratory evaluation of 3-(5-tetrazolyl) penam, a new semisynthetic beta-lactam antibacterial agent with extended broad-spectrum activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Putterman M. Accumulation in gram-postive and gram-negative bacteria as a mechanism of resistance to erythromycin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1111–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1111-1117.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Permeability of the outer membrane of bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1979 May;18(5):337–350. doi: 10.1002/anie.197903373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., Conway T. W. Reversible dissociation of Escherichia coli ribosomes by N-ethylmaleimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;179(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., English A. R., Girard A. E. CP-45,899 in combination with penicillin or ampicillin against penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):615–622. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scudamore R. A., Beveridge T. J., Goldner M. Outer-membrane penetration barriers as components of intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam and other antibiotics in Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H. Binding of erythromycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 May;24(5):302–309. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


