Abstract
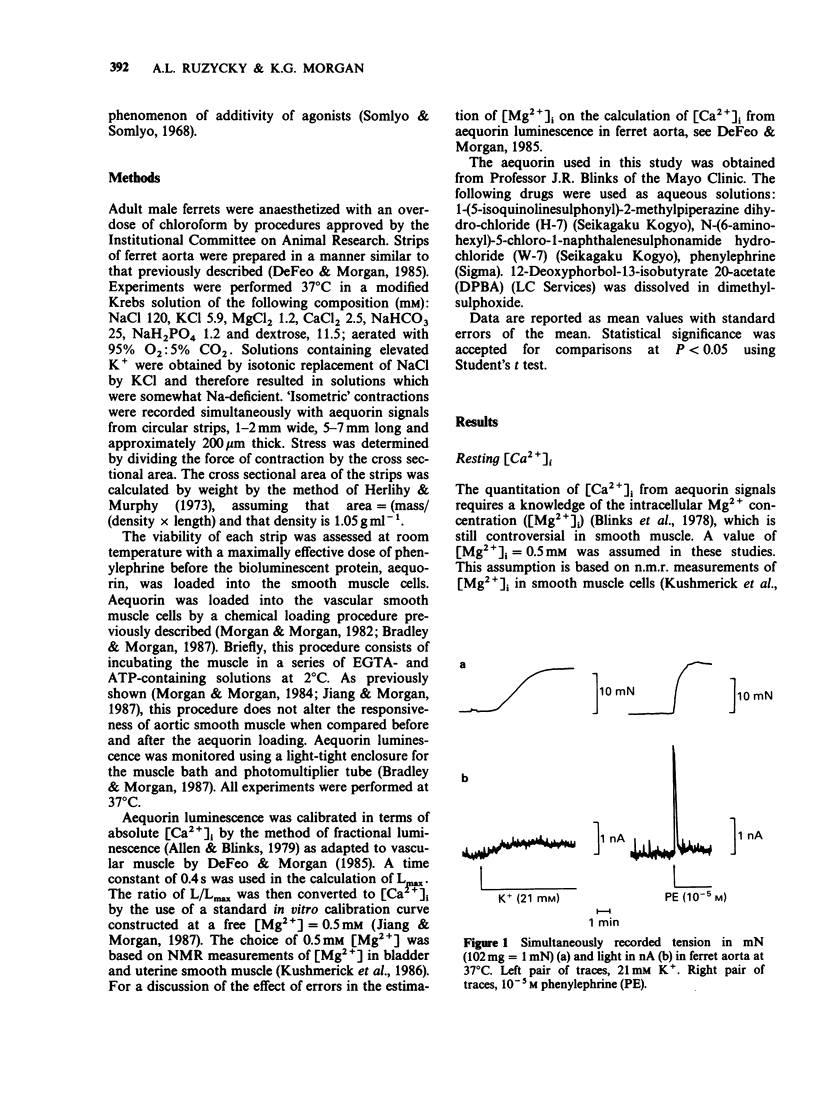
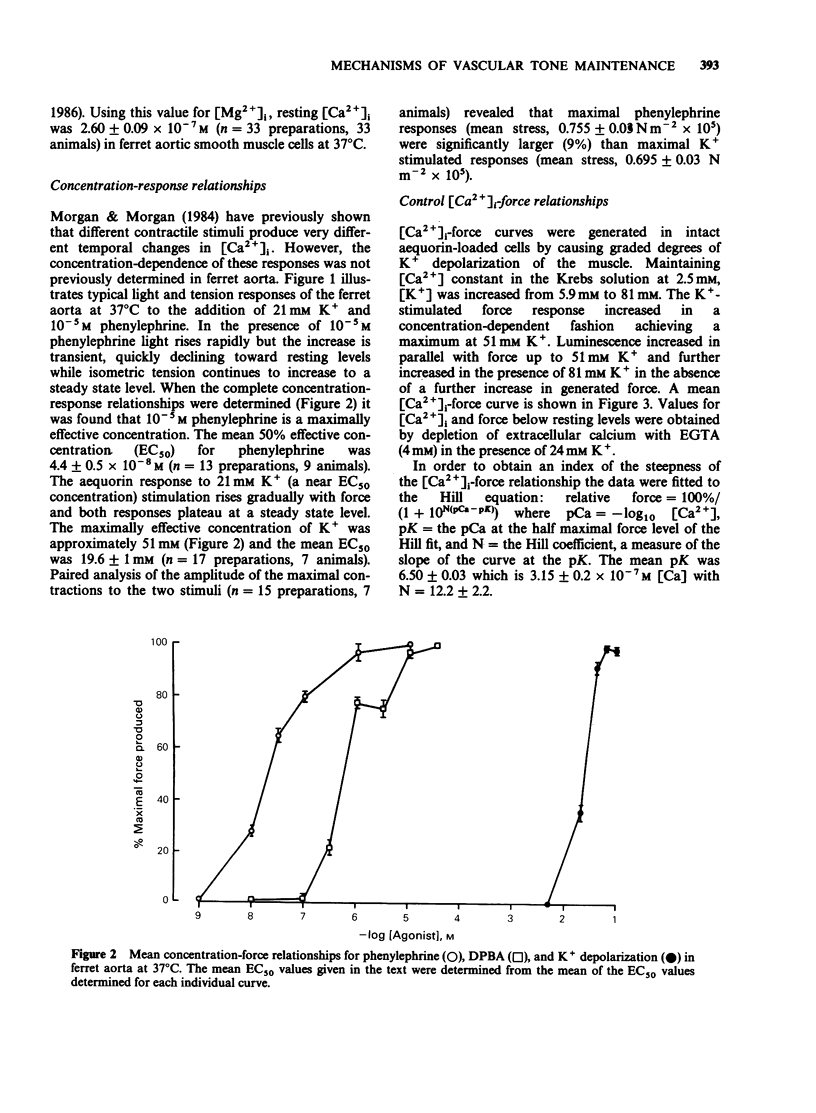
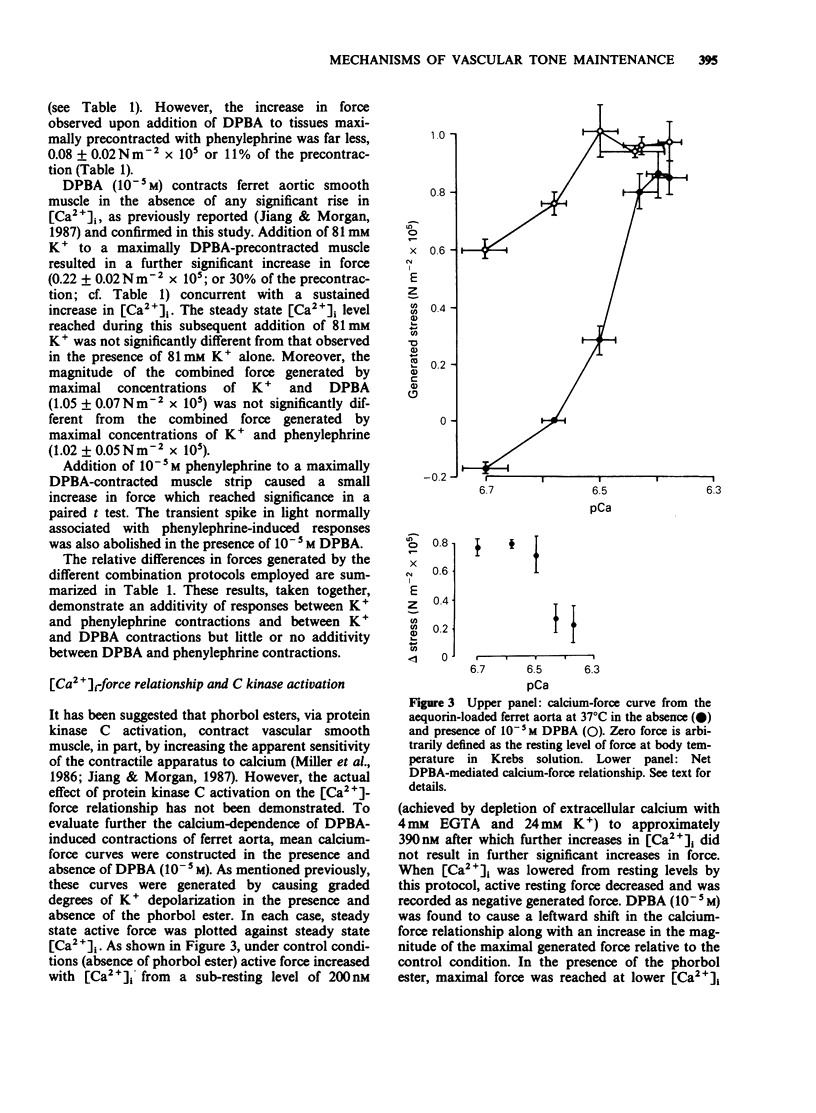
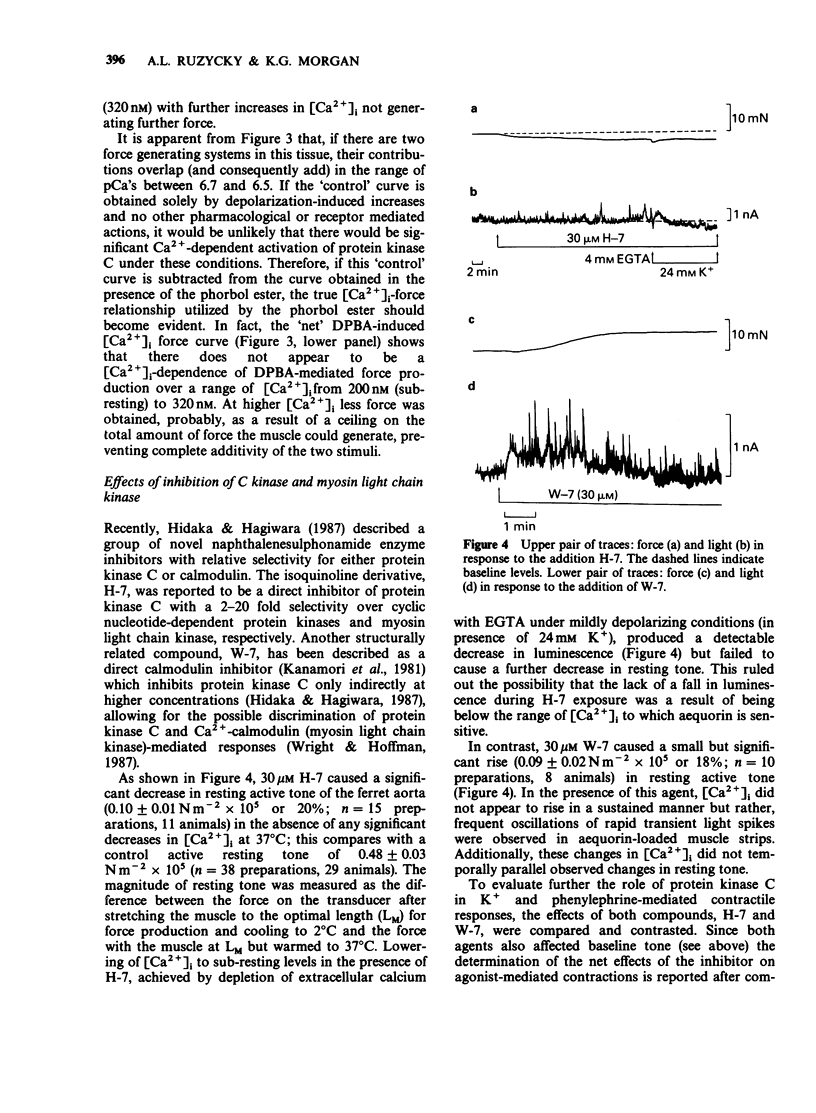
1. Intracellular Ca2+-force relationships were investigated in ferret aortic smooth muscle by the simultaneous measurement of aequorin luminescence and isometric force. Complete calcium-force curves were constructed by plotting calibrated aequorin luminescence versus force, while intracellular [Ca2+] was made to change by increasing degrees of K+ depolarization or decreasing extracellular [Ca2+]. 2. The steady state calcium-force curve in response to K+ depolarization exhibited maximal force generation at an intracellular [Ca2+] of approximately 4 x 10(-7) M. Further increases in intracellular [Ca2+] did not yield additional increments in force. 3. Protein kinase C activation with the phorbol ester, 12-deoxyphorbol-13-isobutyrate 20 acetate (DPBA) produced contractions accompanied by no detectable increases in aequorin luminescence. DPBA significantly shifted the control [Ca2+]-force relationship leftward to lower intracellular [Ca2+] with an increase in the magnitude of maximal generated force. 4. In aorta maximally precontracted by K+ depolarization, the addition of DPBA resulted in a significant increase in force in the absence of further increases in intracellular [Ca2+]. Conversely, in muscles maximally precontracted with DPBA, responses to K+ depolarization resulted in subsequent increases in force in the presence of simultaneous sustained increases in intracellular [Ca2+]. 5. The relatively specific protein kinase C antagonist H-7 caused a significant decrease in intrinsic myogenic tone in the absence of any statistically significant decrease in intracellular [Ca2+]. 6. These results suggest that protein kinase C may be an important regulator of vascular smooth muscle contractility by: (1) providing a mechanism by which the apparent [Ca2+] sensitivity of the contractile apparatus during agonist-induced contractions is increased, and (2) maintaining intrinsic myogenic tone by a mechanism the [Ca2+] requirement of which is satisfied by the resting [Ca2+]i.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraban J. M., Gould R. J., Peroutka S. J., Snyder S. H. Phorbol ester effects on neurotransmission: interaction with neurotransmitters and calcium in smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):604–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley A. B., Morgan K. G. Alterations in cytoplasmic calcium sensitivity during porcine coronary artery contractions as detected by aequorin. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:437–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Cox R. N., Kawai M., Robinson T. Effect of cross-bridge kinetics on apparent Ca2+ sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):997–1016. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M., Tejada M. Phorbol ester-induced contraction in chemically skinned vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danthuluri N. R., Deth R. C. Phorbol ester-induced contraction of arterial smooth muscle and inhibition of alpha-adrenergic response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Morgan K. G. Calcium-force relationships as detected with aequorin in two different vascular smooth muscles of the ferret. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:269–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlihy J. T., Murphy R. A. Length-tension relationship of smooth muscle of the hog carotid artery. Circ Res. 1973 Sep;33(3):275–283. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang M. J., Morgan K. G. Intracellular calcium levels in phorbol ester-induced contractions of vascular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):H1365–H1371. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.6.H1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori M., Naka M., Asano M., Hidaka H. Effects of N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide and other calmodulin antagonists (calmodulin interacting agents) on calcium-induced contraction of rabbit aortic strips. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):494–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Dillon P. F., Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Krisanda J. M., Sweeney H. L. 31P NMR spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and free Mg2+ of rabbit bladder and uterine smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14420–14429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laher I., Bevan J. A. Protein kinase C activation selectively augments a stretch-induced, calcium-dependent tone in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Aug;242(2):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Hawkins D. J., Wells J. N. Phorbol diesters alter the contractile responses of porcine coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Oct;239(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Stimulus-specific patterns of intracellular calcium levels in smooth muscle of ferret portal vein. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:155–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Sellers J. R., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Protein kinase C modulates in vitro phosphorylation of the smooth muscle heavy meromyosin by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8808–8814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Forder J., Kojima I., Scriabine A. TPA-induced contraction of isolated rabbit vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):776–784. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A. Ca-linked phosphorylation of a light chain of vertebrate smooth-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umekawa H., Hidaka H. Phosphorylation of caldesmon by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):56–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90987-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Hoffman M. D. Comparison of the roles of calmodulin and protein kinase C in activation of the human neutrophil respiratory burst. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. T., Marban E., Wier W. G. Relationship between force and intracellular [Ca2+] in tetanized mammalian heart muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):223–242. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


