Abstract
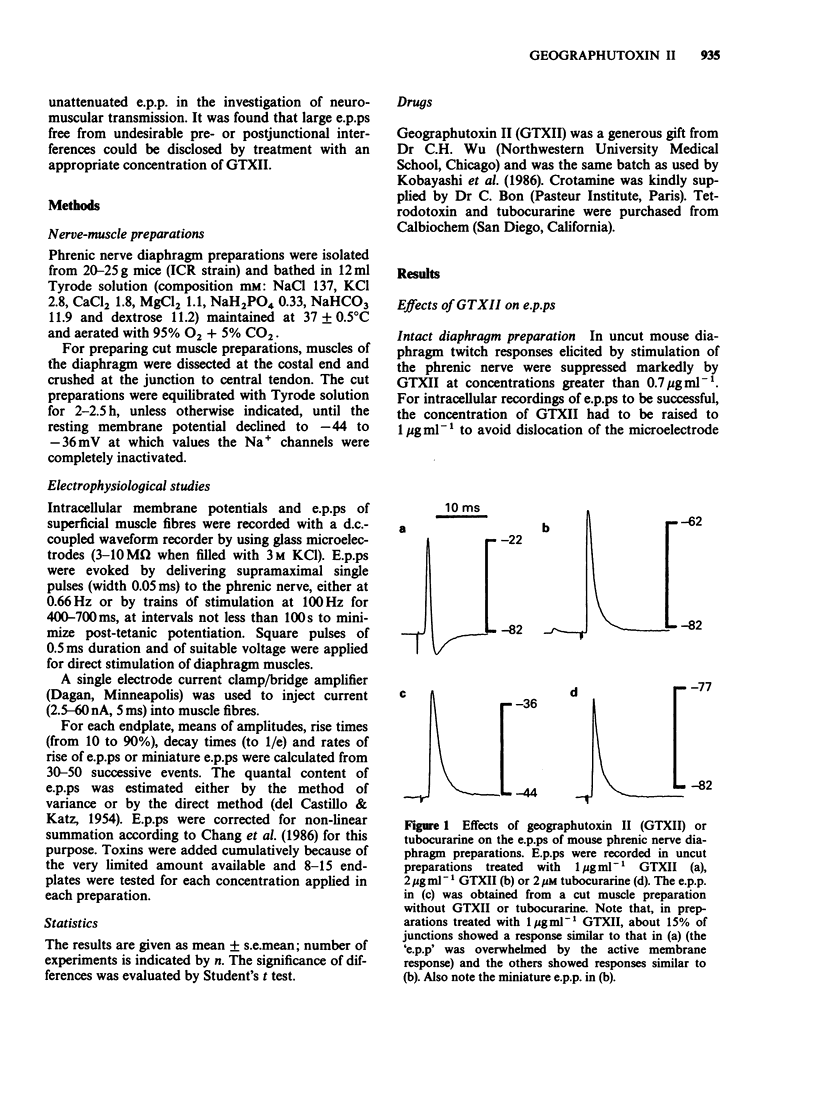
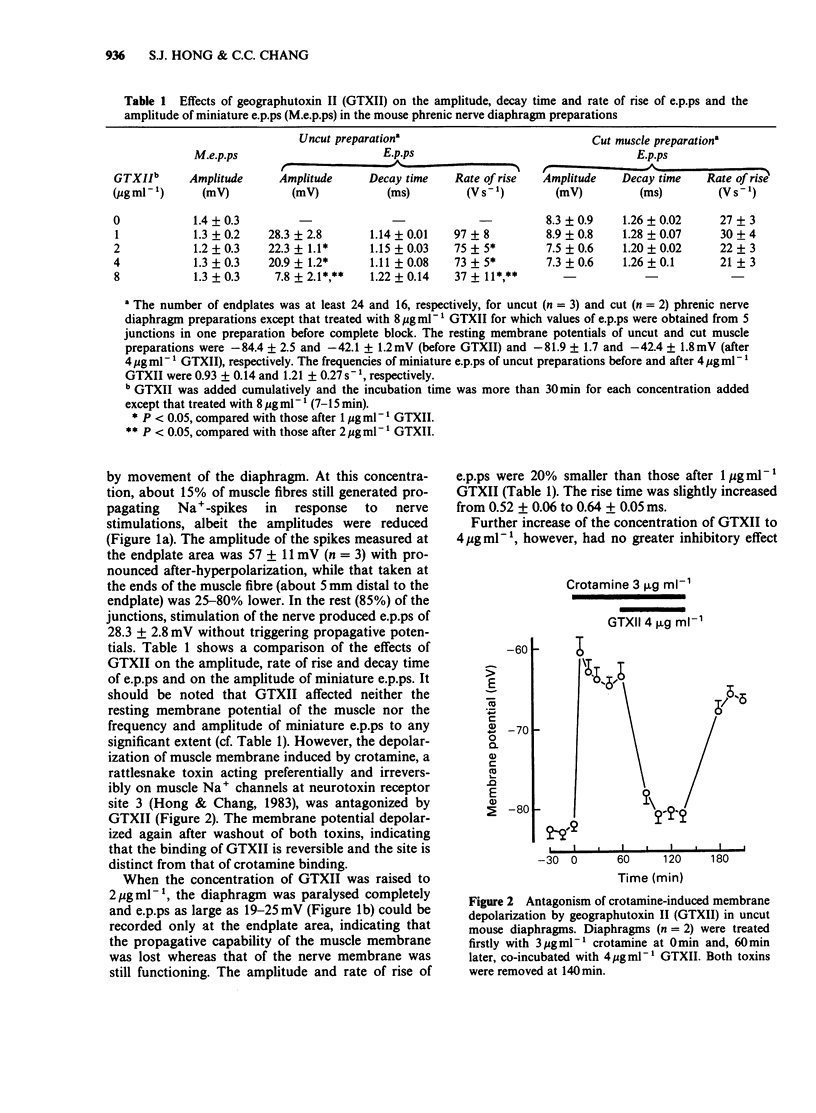
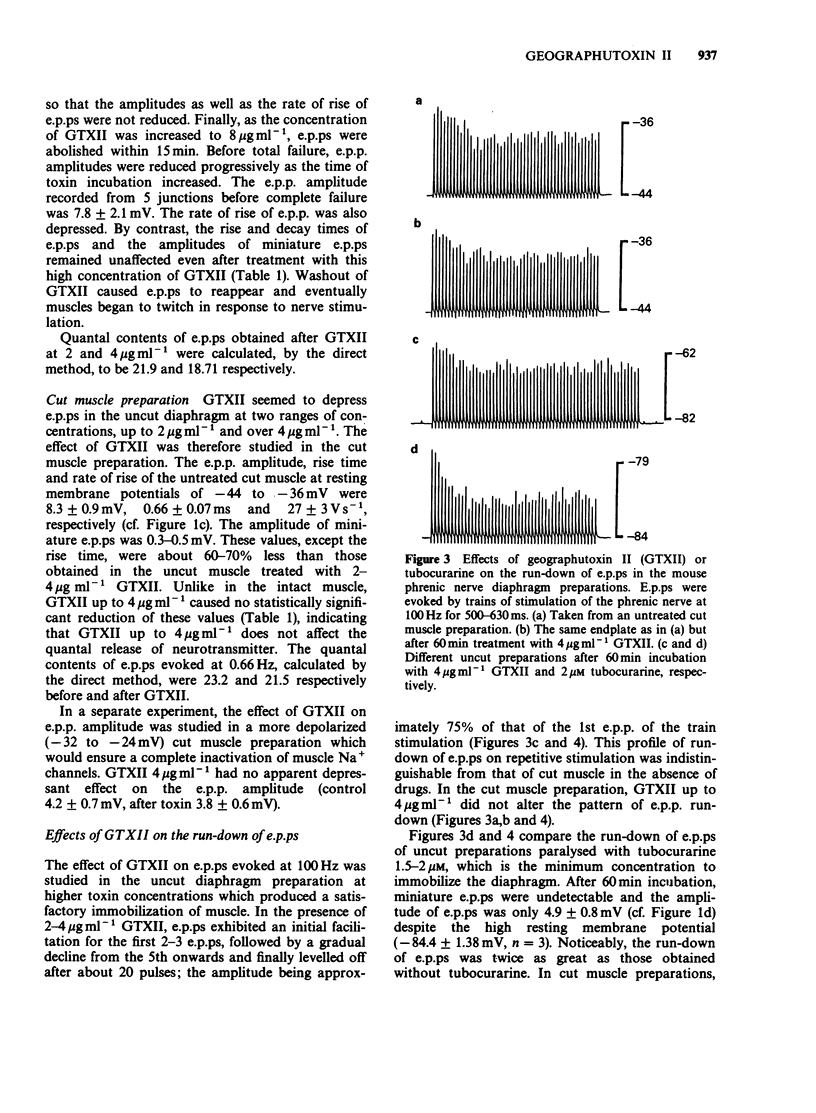
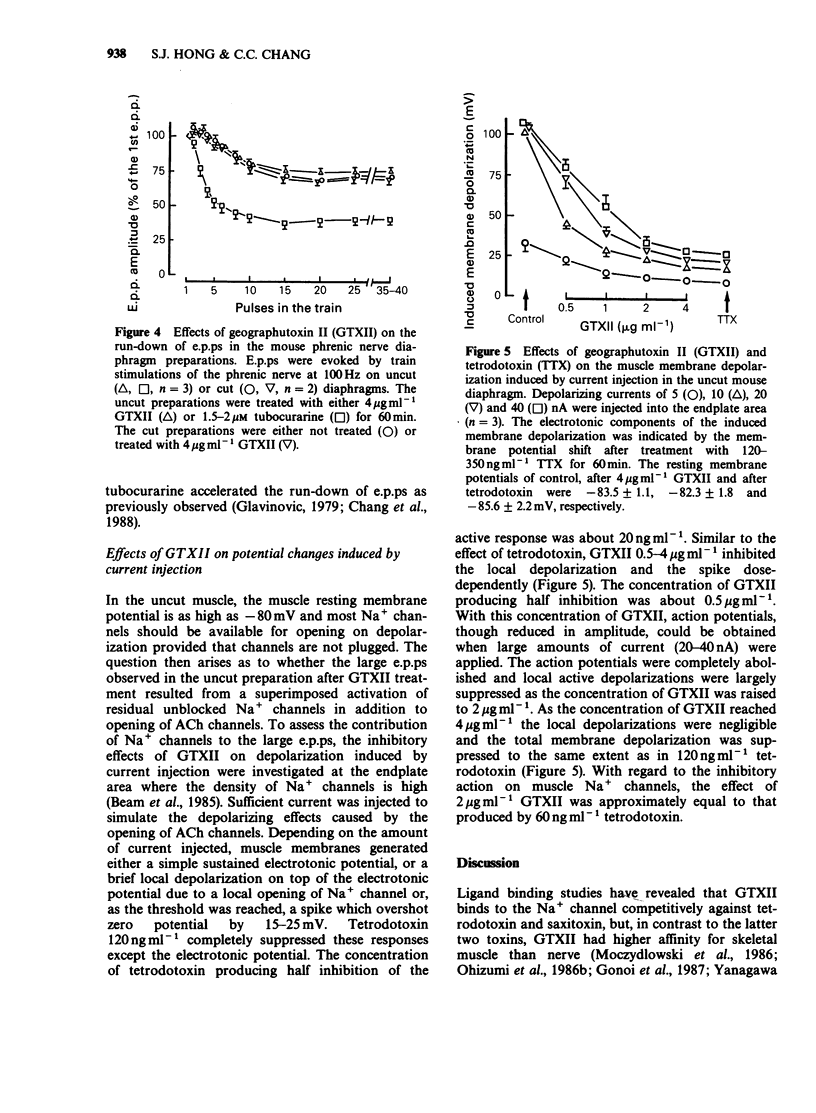
1. Endplate potentials (e.p.ps) were investigated in the presence of geographutoxin II (GTXII) in the mouse phrenic nerve diaphragm preparation. This toxin preferentially blocks muscle Na+ channels which allows the study of e.p.ps in the absence of nicotinic receptor antagonists or substances to depress acetylcholine release. 2. GTXII abolished muscle action potentials and antagonized the depolarization of the muscle membrane produced by the crotamine-induced opening of Na+ channels. 3. E.p.ps as large as 19-25 mV were observed after 2-4 micrograms ml-1 GTXII. These concentrations of GTXII did not cause discernible changes of resting membrane potential and frequency and amplitude of miniature e.p.ps. 4. Lower concentrations (1-2 micrograms ml-1) of GTXII caused incomplete blockade of the muscle Na+ channel resulting in exaggerated 'e.p.ps', while higher concentrations of GTXII (8 micrograms ml-1) abolished e.p.ps by a prejunctional effect. 5. Trains of e.p.ps on repetitive stimulation after GTXII neither ran down, as in tubocurarine-treated preparations, nor facilitated, as in low Ca2+ and/or high Mg2+-treated preparations, and were indistinguishable from those of untreated cut muscle preparation. 6. In cut muscle preparations, GTXII did not affect the rise and decay times, amplitude or rundown of e.p.ps. 7. It is concluded that GTXII is a useful agent for studying neuromuscular transmission. This method provides e.p.ps which are neither attenuated nor modified because manipulations that alter transmitter release and postjunctional receptor responses are avoided.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barstad J. A., Lilleheil G. Transversaly cut diaphragm preparation from rat. An adjuvant tool in the study of the physiology and pbarmacology of the myoneural junction. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1968 Oct;175(2):373–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Caldwell J. H., Campbell D. T. Na channels in skeletal muscle concentrated near the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):588–590. doi: 10.1038/313588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. The effects of prolonged repetitive stimulation in hemicholinium on the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):163–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chen S. M., Hong S. J. Reversals of the neostigmine-induced tetanic fade and endplate potential run-down with respect to the autoregulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1255–1261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Hong S. J., Ko J. L. Mechanisms of the inhibition by neostigmine of tetanic contraction in the mouse diaphragm. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):757–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Hong S. J., Su M. J. A study on the membrane depolarization of skeletal muscles caused by a scorpion toxin, sea anemone toxin II and crotamine and the interaction between toxins. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;79(3):673–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L. J., Gray W. R., Olivera B. M., Zeikus R. D., Kerr L., Yoshikami D., Moczydlowski E. Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9280–9288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavinović M. I. Presynaptic action of curare. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):499–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Ohizumi Y., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Catterall W. A. The Conus toxin geographutoxin IL distinguishes two functional sodium channel subtypes in rat muscle cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1728–1731. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01728.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. J., Chang C. C. Potentiation by crotamine of the depolarizing effects of batrachotoxin, protoveratrine A and grayanotoxin I on the rat diaphragm. Toxicon. 1983;21(4):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Wu C. H., Yoshii M., Narahashi T., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Ohizumi Y. Preferential block of skeletal muscle sodium channels by geographutoxin II, a new peptide toxin from Conus geographus. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):241–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00580684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Olivera B. M., Gray W. R., Strichartz G. R. Discrimination of muscle and neuronal Na-channel subtypes by binding competition between [3H]saxitoxin and mu-conotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5321–5325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Ohizumi Y., Hirata Y. Isolation and amino acid compositions of geographutoxin I and II from the marine snail Conus geographus. Experientia. 1983 Jun 15;39(6):590–591. doi: 10.1007/BF01971110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Minoshima S., Takahashi M., Kajiwara A., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J. Geographutoxin II, a novel peptide inhibitor of Na channels of skeletal muscles and autonomic nerves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Oct;239(1):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Catterall W. A. Specific inhibition of [3H] saxitoxin binding to skeletal muscle sodium channels by geographutoxin II, a polypeptide channel blocker. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6149–6152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y., Kobayashi J., Hirata Y. The amino acid sequences of homologous hydroxyproline-containing myotoxins from the marine snail Conus geographus venom. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80620-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa Y., Abe T., Satake M. Mu-conotoxins share a common binding site with tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin on eel electroplax Na channels. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1498–1502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01498.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


