Abstract
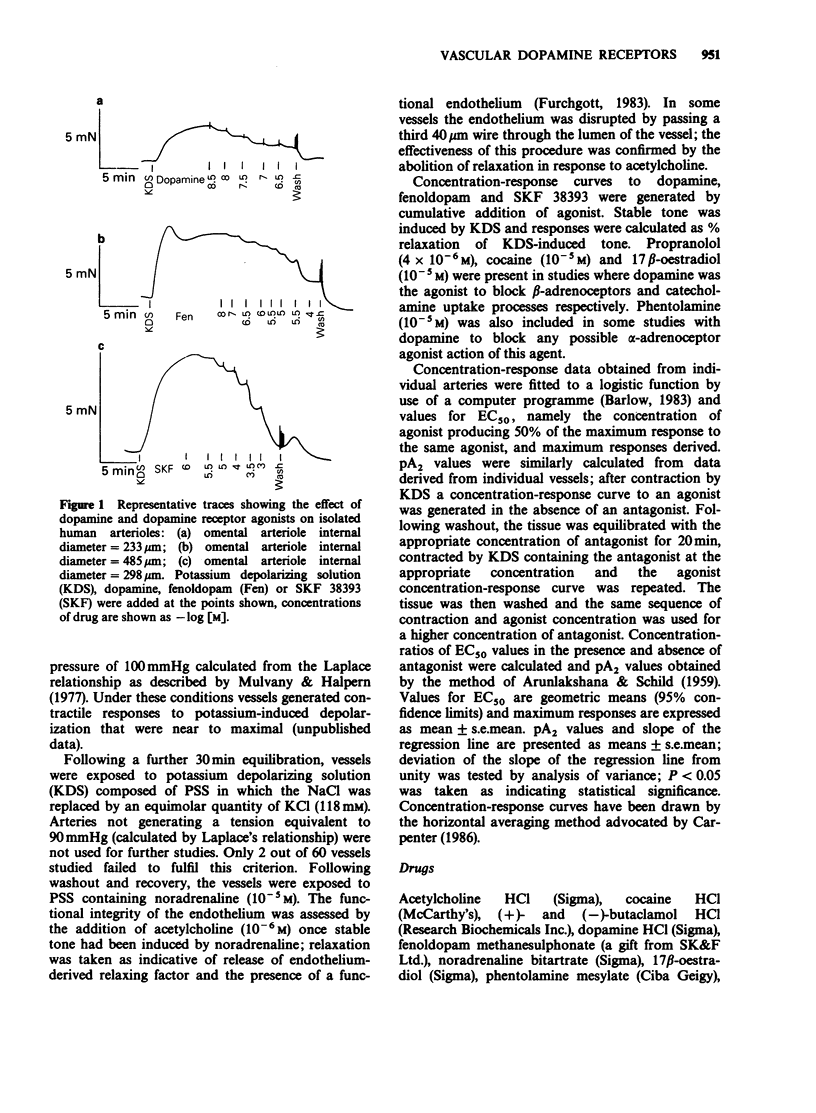
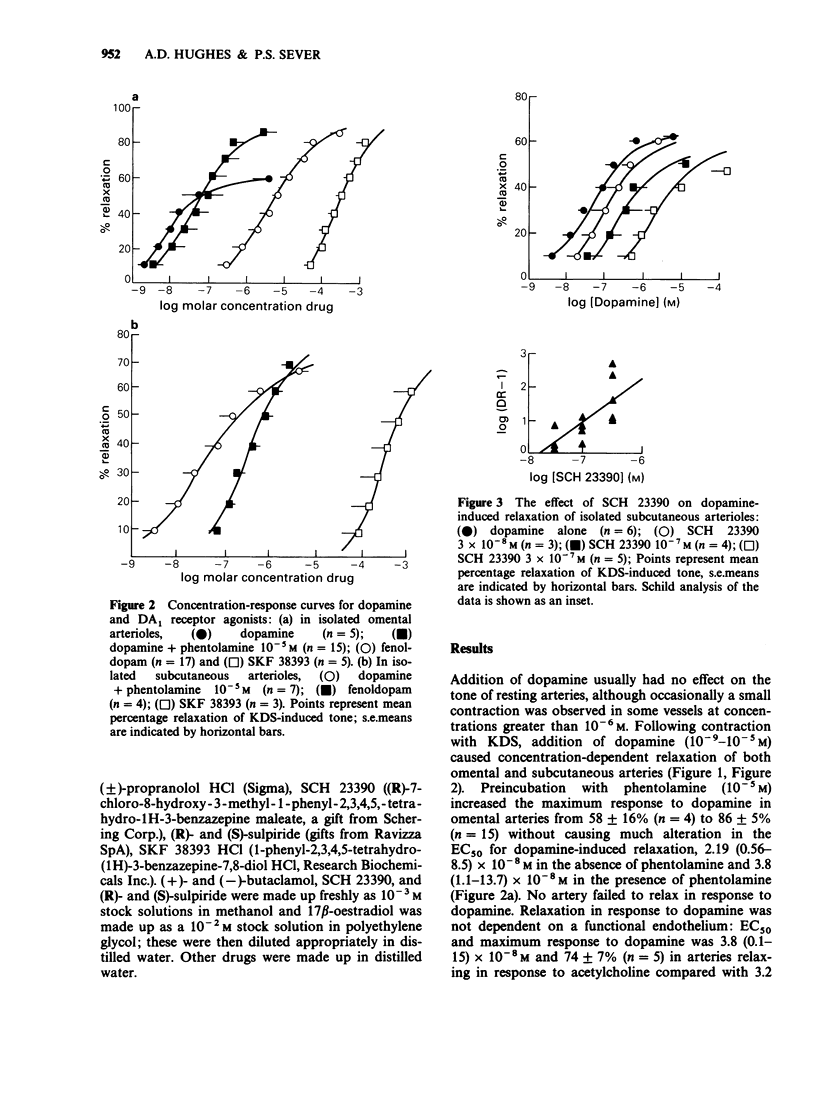
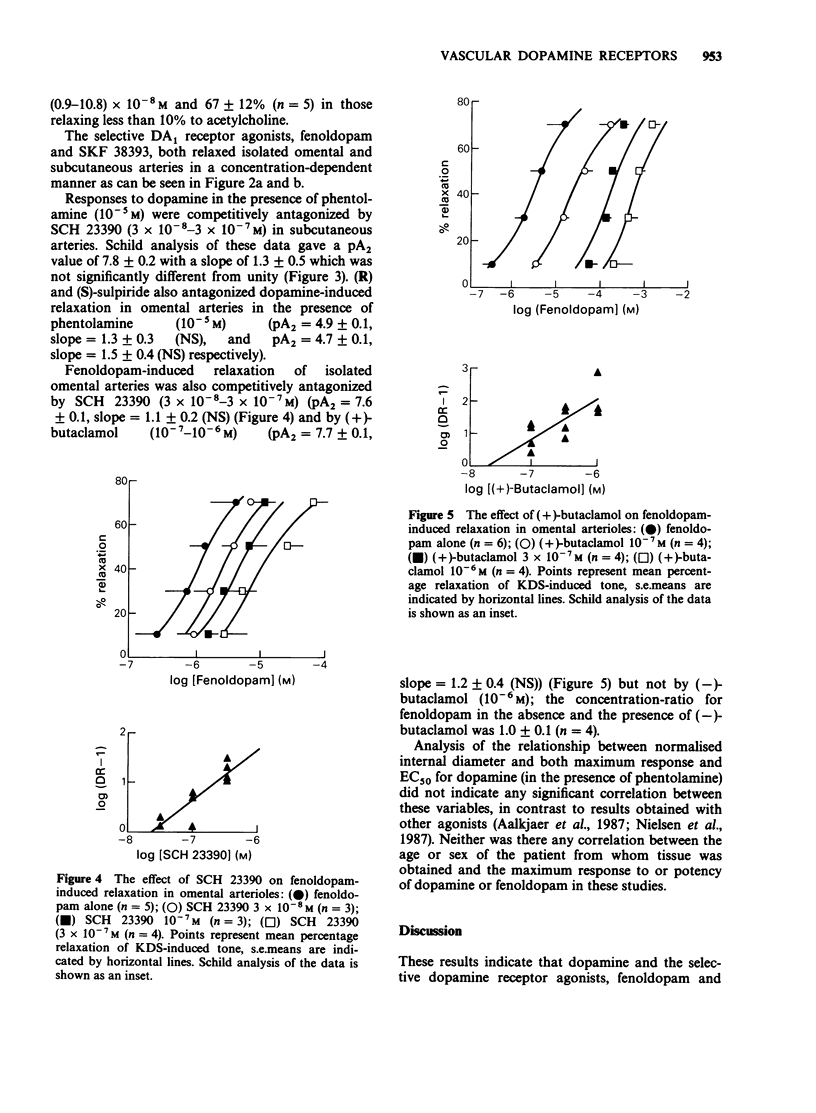
1. Human small arteries were obtained from surgical specimens and studied in vitro by use of a myograph technique. Following induction of tone with a potassium depolarizing solution, dopamine in the presence of beta-adrenoceptor and catecholamine uptake blockade relaxed isolated omental and subcutaneous arteries. Preincubation of tissues with phentolamine increased the maximum relaxation in response to dopamine. 2. The selective vascular dopamine receptor agonists, fenoldopam and SKF 38393 also relaxed isolated subcutaneous and omental arteries in a concentration-dependent manner. The order of potency for agonists was dopamine greater than fenoldopam greater than SKF 38393. 3. Dopamine-induced relaxation was competitively antagonized by SCH 23390, (R)- and (S)-sulpiride, and fenoldopam induced relaxation by SCH 23390 and (+)- but not (-)-butaclamol. 4. These results indicate the presence of vascular dopamine receptors (DA1 subtype) on human isolated resistance arteries from omental and subcutaneous sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P. H., Braestrup C. Evidence for different states of the dopamine D1 receptor: clozapine and fluperlapine may preferentially label an adenylate cyclase-coupled state of the D1 receptor. J Neurochem. 1986 Dec;47(6):1822–1831. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmforth A. J., Lyall F., Morton J. I., Ball S. G. Cultured mesenteric vascular smooth muscle cells express dopamine DA1-receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 18;155(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90519-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Lang W. J. Evidence for dopaminergic vasodilator innervation of the canine paw pad. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Lang W. J., Laska F. Dopamine-containing vasomotor nerves in the dog kidney. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Ohlstein E. H. Cardiovascular dopamine receptors: recent advances in agonists and antagonists of the DA1-receptor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 4):S559–S563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlen H. G. Determinants of resting and passive intestinal vascular pressures in rat and rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):G587–G595. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.5.G587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E. Vascular dopamine receptors: Demonstration and characterization by in vitro studies. Life Sci. 1982 Jul 26;31(4):289–306. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzowej N. H., Niznik H. B., Seeman P. Dopamine D1 receptors with enhanced agonist affinity and reduced antagonist affinity revealed by chemical modification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):933–939. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. R. A method for presenting and comparing dose-response curves. J Pharmacol Methods. 1986 Jul;15(4):283–303. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., McCulloch J., Sharkey J. Vasomotor responses of cerebral arterioles in situ to putative dopamine receptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. M. Comparison of the effects of fenoldopam, SK & F R-87516 and dopamine on renal arterioles in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 15;126(1-2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90756-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. M. Response of isolated renal arterioles to acetylcholine, dopamine, and bradykinin. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F183–F189. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster C., Drew G. M., Hilditch A., Whalley E. T. Dopamine receptors in human basilar arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 18;87(2-3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. I. Cardiovascular and renal actions of dopamine: potential clinical applications. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Mar;24(1):1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. I. Dopamine receptors and hypertension. Physiologic and pharmacologic implications. Am J Med. 1984 Oct 5;77(4A):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(84)80036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. I., Kohli J. D. Peripheral pre- and post-synaptic dopamine receptors: are they different from dopamine receptors in the central nervous system? Commun Psychopharmacol. 1979;3(6):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilditch A., Drew G. M. Characteristics of the dopamine receptors in the rabbit isolate splenic artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilditch A., Drew G. M. Peripheral dopamine receptor blockade by SCH 23390 and domperidone in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 8;116(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilditch A., Drew G. M. Subclassification of peripheral dopamine receptors. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1987;9(5-6):853–872. doi: 10.3109/10641968709161454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. D., Thom S. A., Woodall N. M., Redman D., Sever P. S. Dopamine produces forearm vasodilatation following alpha-adrenoceptor blockade by an action on vascular dopamine (DA1) receptors in man. J Hypertens. 1987 Jun;5(3):337–340. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198706000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Halpern W. Contractile properties of small arterial resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):19–26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J. The fourth Sir George Pickering memorial lecture. The structure of the resistance vasculature in essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1987 Apr;5(2):129–136. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198704000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Zabko-Potapovich B., Berkowitz B. A. Studies on vascular dopamine receptors with the dopamine receptor agonist: SK&F 82526. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 May;229(2):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Imbs J. L., Giesen-Crouse E. M., Schwartz J. Effects of SK&F 82526 and SK&F 83742 on the renal vascular dopamine receptor. J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Mar;16(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Imbs J. L., Giesen E. M., Schwartz J. Blockade of dopamine receptors in the renal vasculature by isomers of flupenthixol and sulpiride. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):86–89. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198301000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Imbs J. L., Giesen E. M., Schwartz J. Vasodilator effects of dopaminomimetics in the perfused rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Imbs J. L. Pharmacological characterization of renal vascular dopamine receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980 Sep-Oct;2(5):595–605. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198009000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Krieger J. P., Giesen-Crouse E. M., Imbs J. L. Vascular effects of selective dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists in the rat kidney. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1987 Apr;286(2):195–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stote R. M., Dubb J. W., Familiar R. G., Erb B. B., Alexander F. A new oral renal vasodilator, fenoldopam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Sep;34(3):309–315. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N. Dopamine vasodilates human cerebral artery. Experientia. 1983 Oct 15;39(10):1131–1132. doi: 10.1007/BF01943144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Yano S., Sakanashi M. In vitro evidence for dopaminergic receptors in human renal artery. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):76–81. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198201000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. G., Liepmann P., Baldessarini R. J. Inhibition of dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity by phenoxybenzamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 15;52(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


