Abstract
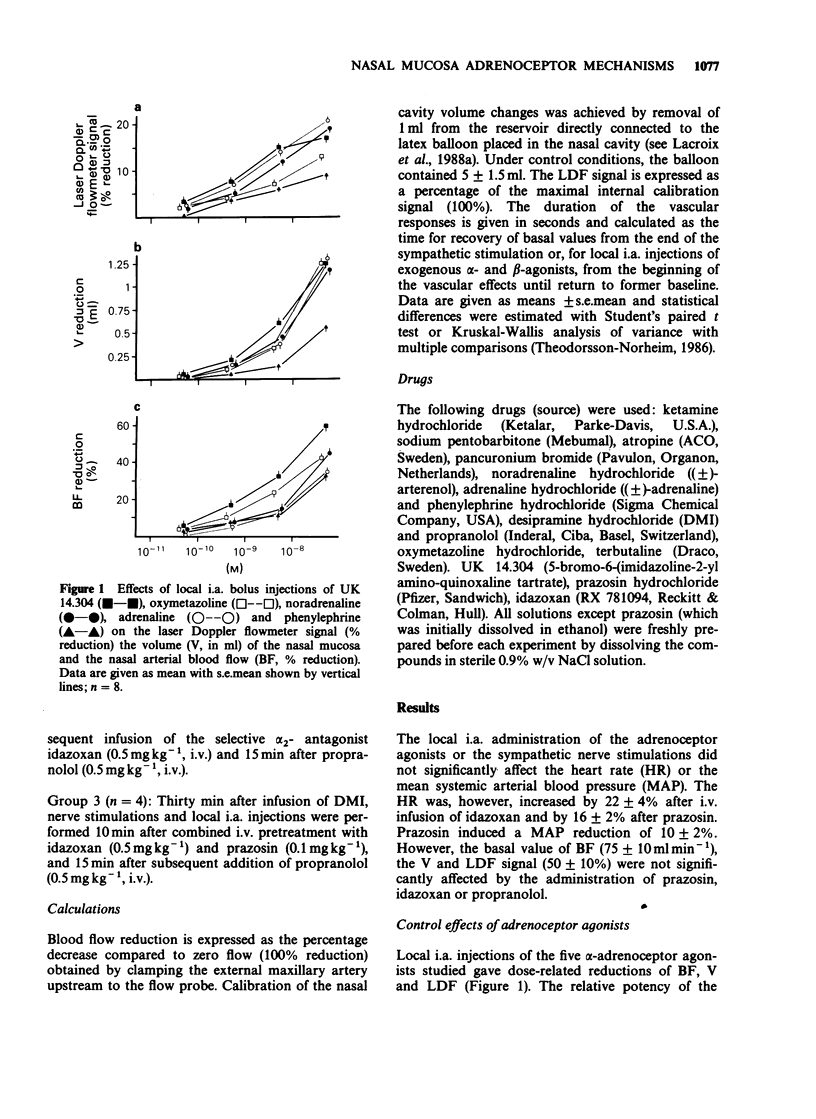
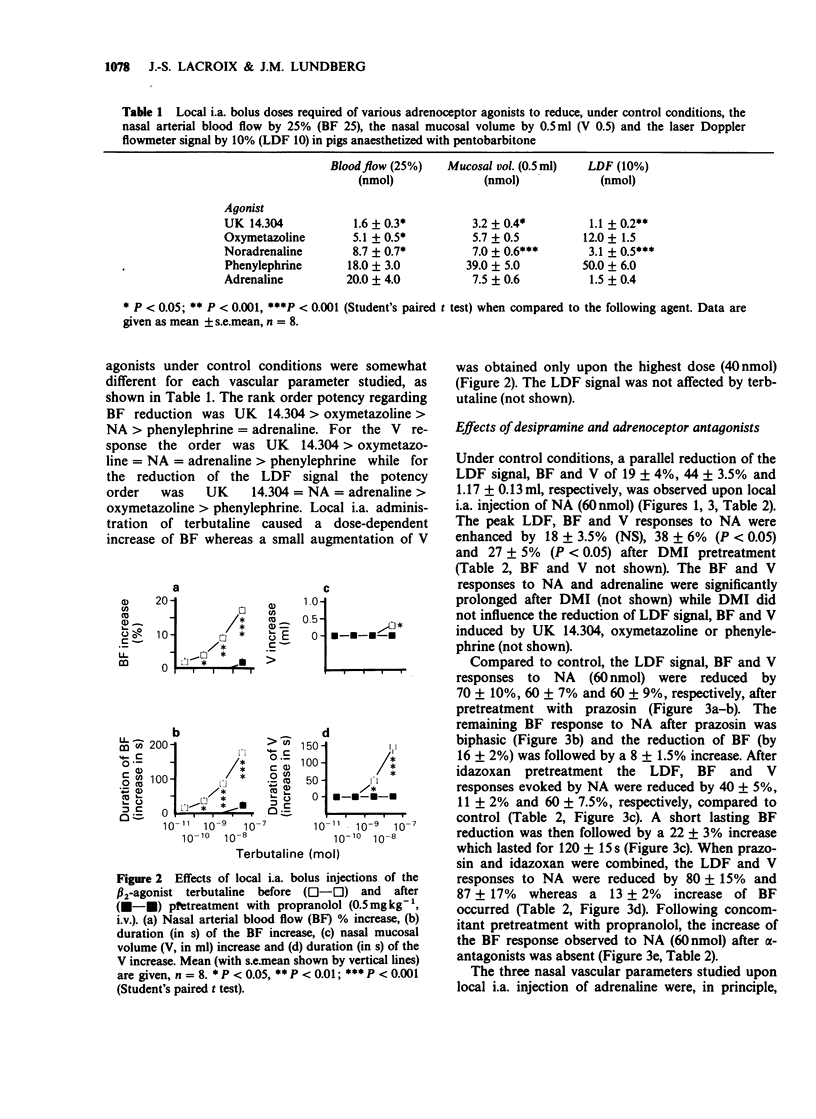
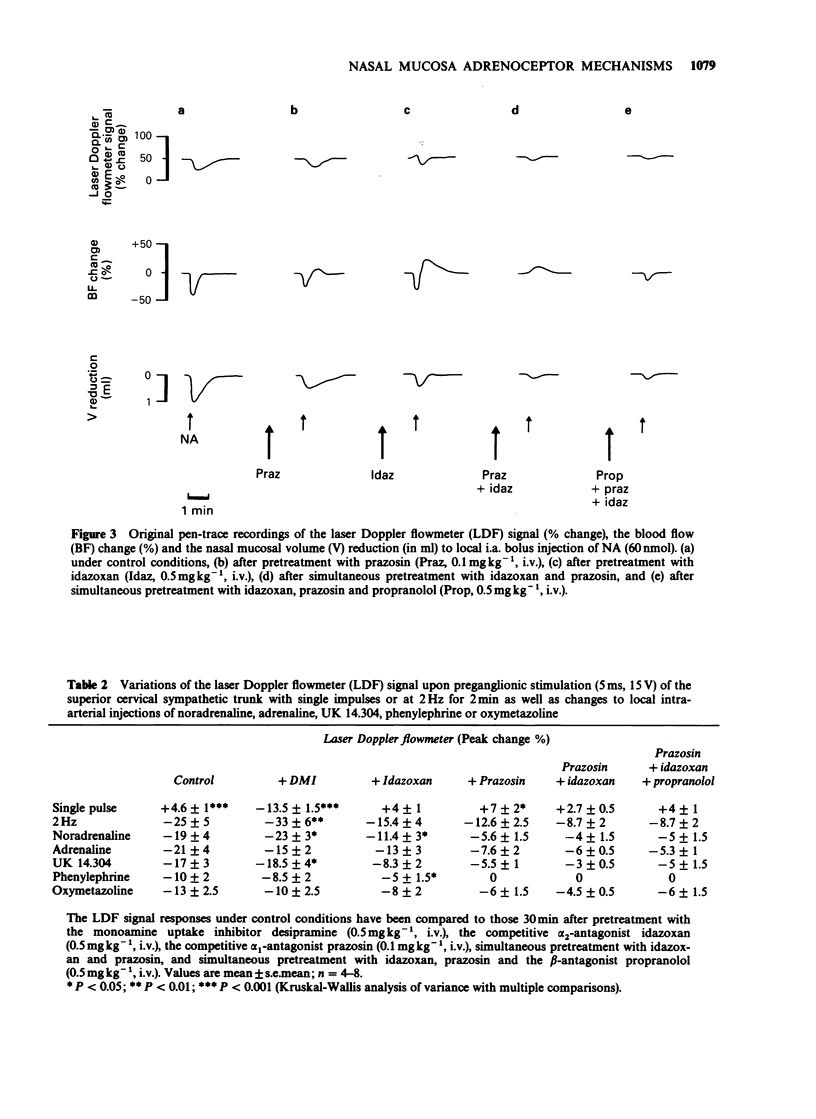
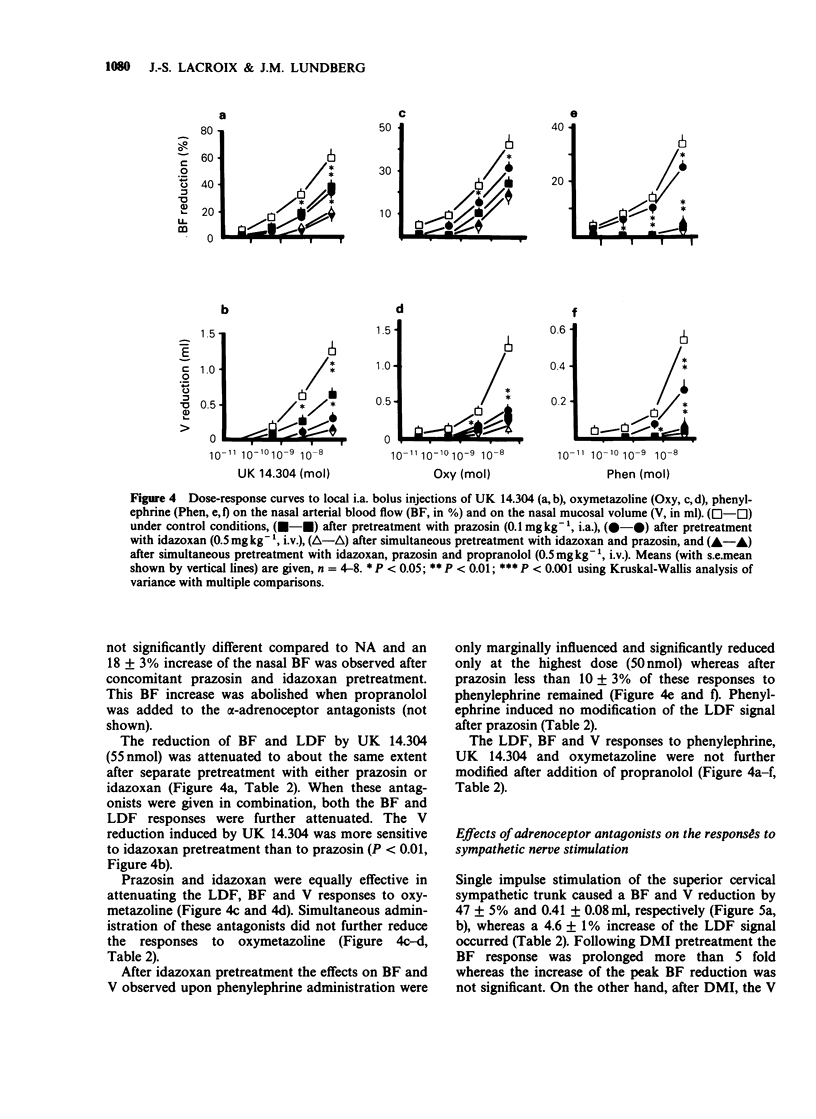
1. The adrenoceptor mechanisms influencing the total blood flow, volume and superficial blood flow in the nasal mucosa of pigs anaesthetized with pentobarbitone have been characterized by use of various agonists and antagonists. 2. Local intra-arterial bolus injection of the selective alpha 1-agonist phenylephrine, the selective alpha 2-agonist UK 14.304, the mixed alpha 1/alpha 2-agonist oxymetazoline and the mixed alpha/beta-agonists noradrenaline (NA) and adrenaline induced dosed-related reduction of nasal arterial blood flow (BF), nasal mucosal volume (V, reflecting capacitance vessel function) and the laser Doppler flowmetry signal (LDF, reflecting superficial movement of blood cells). The rank order of alpha-agonist potency regarding BF reduction was UK 14.304 greater than oxymetazoline greater than phenylephrine = adrenaline. For the volume response the potency order was UK 14.304 greater than oxymetazoline = NA = adrenaline greater than phenylephrine while for the reduction of the LDF signal the potency was UK 14.304 = NA = adrenaline greater than oxymetazoline greater than phenylephrine. The selective beta 2-agonist terbutaline caused dose-dependent increase of BF whereas only a small augmentation of the V was obtained upon the highest dose (40 nmol) while no modification of the LDF signal was observed. 3. After pretreatment with the selective alpha 1-antagonist prazosin, the response to phenylephrine was abolished while the selective alpha 2-antagonist idazoxan attenuated the effect of UK 14.304. After pretreatment with alpha-antagonists, both NA and adrenaline caused biphasic effects with constriction followed by vasodilatation for BF, but not for V or LDF. This vasodilatation was blocked by the beta-antagonist propranolol. 4. The reduction in nasal BF and V upon sympathetic nerve stimulation was attenuated both by prazosin and idazoxan. Propranolol enhanced the remaining reduction of BF but not of V in the presence of alpha-antagonists. 5. It is concluded that alpha 2-adrenoceptor mechanisms in the pig nasal mucosa are dominating for the BF, V and LDF responses to exogenous agonists. alpha 1-Adrenoceptors also seem to be involved in the sympathetic control of BF, V and LDF. Activation of beta 2-receptors increases mainly BF and does not influence the LDF signal.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn H., Lindhagen J., Nilsson G. E., Salerud E. G., Jodal M., Lundgren O. Evaluation of laser Doppler flowmetry in the assessment of intestinal blood flow in cat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):951–957. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson K. E., Bende M. Adrenoceptors in the control of human nasal mucosal blood flow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984 Mar-Apr;93(2 Pt 1):179–182. doi: 10.1177/000348948409300216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård A., Edwall L. The effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation on the tracer disappearance rate and local blood content in the nasal mucosa of the cat. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Jan-Feb;77(1):131–139. doi: 10.3109/00016487409124608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge T. L., Roach A. G. Characterization of alpha-adrenoceptors in the vasculature of the canine nasal mucosa. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10210.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLSTROEM A., FUXE K. THE ADRENERGIC INNERVATION OF THE NASAL MUCOSA OF CERTAIN MAMMALS. Acta Otolaryngol. 1965 Jan;59:65–72. doi: 10.3109/00016486509128547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles R., MacLean A. G. Relaxation of smooth muscle following contraction elicited by sympathetic nerve stimulation in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):551–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. J., Jackson R. T. Effects of alpha and beta adrenergic agonists on nasal blood flow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1968 Dec;77(6):1120–1130. doi: 10.1177/000348946807700610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. S., Stjärne P., Anggärd A., Lundberg J. M. Sympathetic vascular control of the pig nasal mucosa (III): Co-release of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Jan;135(1):17–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. S., Stjärne P., Anggård A., Lundberg J. M. Sympathetic vascular control of the pig nasal mucosa (2): Reserpine-resistant, non-adrenergic nervous responses in relation to neuropeptide Y and ATP. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jun;133(2):183–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. S., Stjärne P., Anggård A., Lundberg J. M. Sympathetic vascular control of the pig nasal mucosa: (I). Increased resistance and capacitance vessel responses upon stimulation with irregular bursts compared to continuous impulses. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jan;132(1):83–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Massingham R., Shepperson N. B. Presence of postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptors of predominantly extrasynaptic location in the vascular smooth muscle of the dog hind limb. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59 (Suppl 6):225s–228s. doi: 10.1042/cs059225s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Hamberger B. Evidence for co-transmitter role of neuropeptide Y in the pig spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):675–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad L., Anggard A., Saria A., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y and non-adrenergic sympathetic vascular control of the cat nasal mucosa. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Oct;20(3):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm L. Beta-adrenergic receptors in the vessels of the cat nasal mucosa. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Sep-Oct;78(3-4):242–246. doi: 10.3109/00016487409126350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm L. Responses of resistance and capacitance vessels in feline nasal mucosa to vasoactive agents. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Jul-Aug;78(1-2):90–97. doi: 10.3109/00016487409126331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm L. Stimulation of sympathetic nerve fibres to the nose in cats. Acta Otolaryngol. 1973 Jun;75(6):519–526. doi: 10.3109/00016487309139783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H., Clemente E. A new experimental method for evaluating drugs in the nasal cavity. Arch Otolaryngol. 1972 Dec;96(6):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1972.00770090802005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. In vivo evaluation of microcirculation by coherent light scattering. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):56–58. doi: 10.1038/254056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E. Kruskal-Wallis test: BASIC computer program to perform nonparametric one-way analysis of variance and multiple comparisons on ranks of several independent samples. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1986 Aug;23(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi I., Kopin I. J. Differential inhibiton of alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses in pithed rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Aug;214(2):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


