Abstract
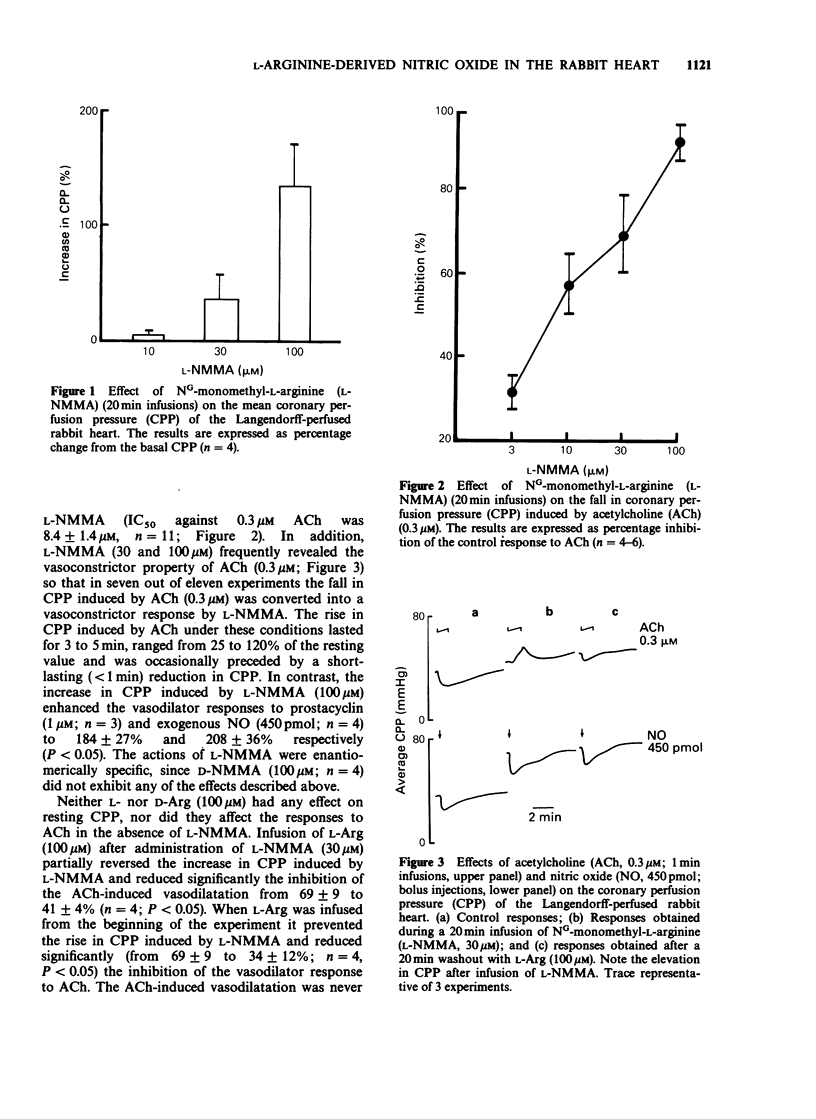
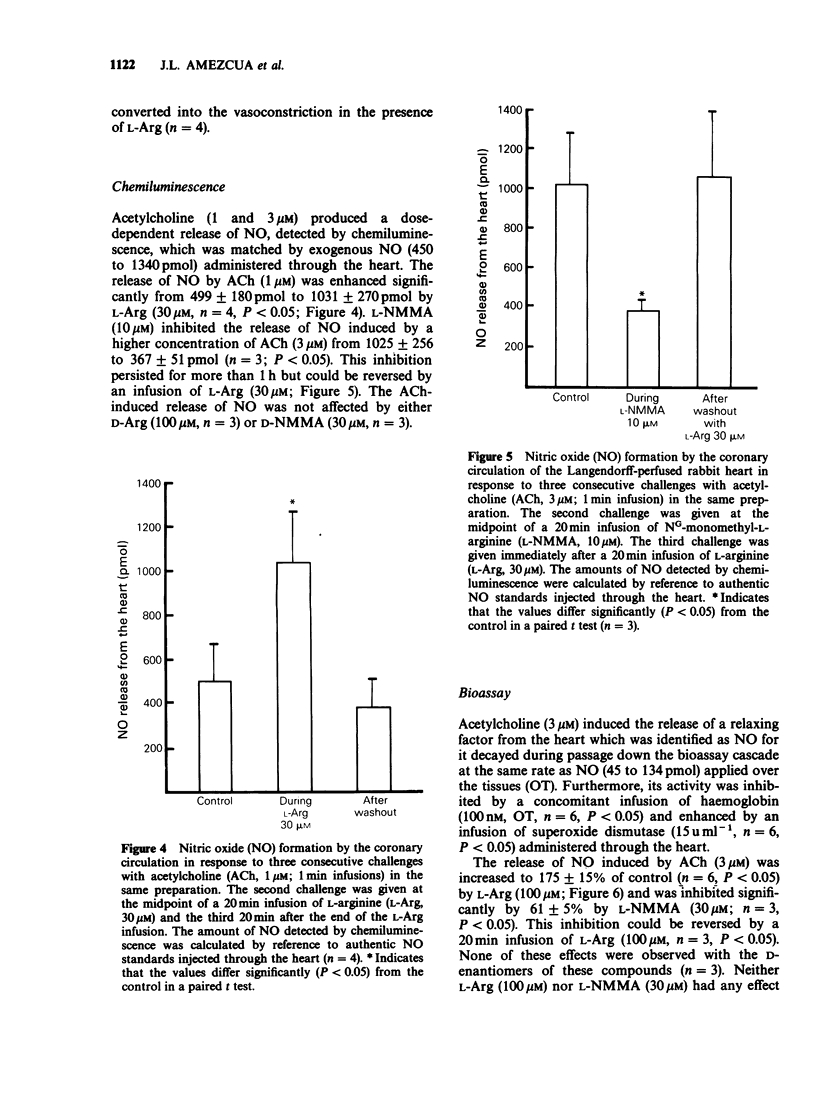
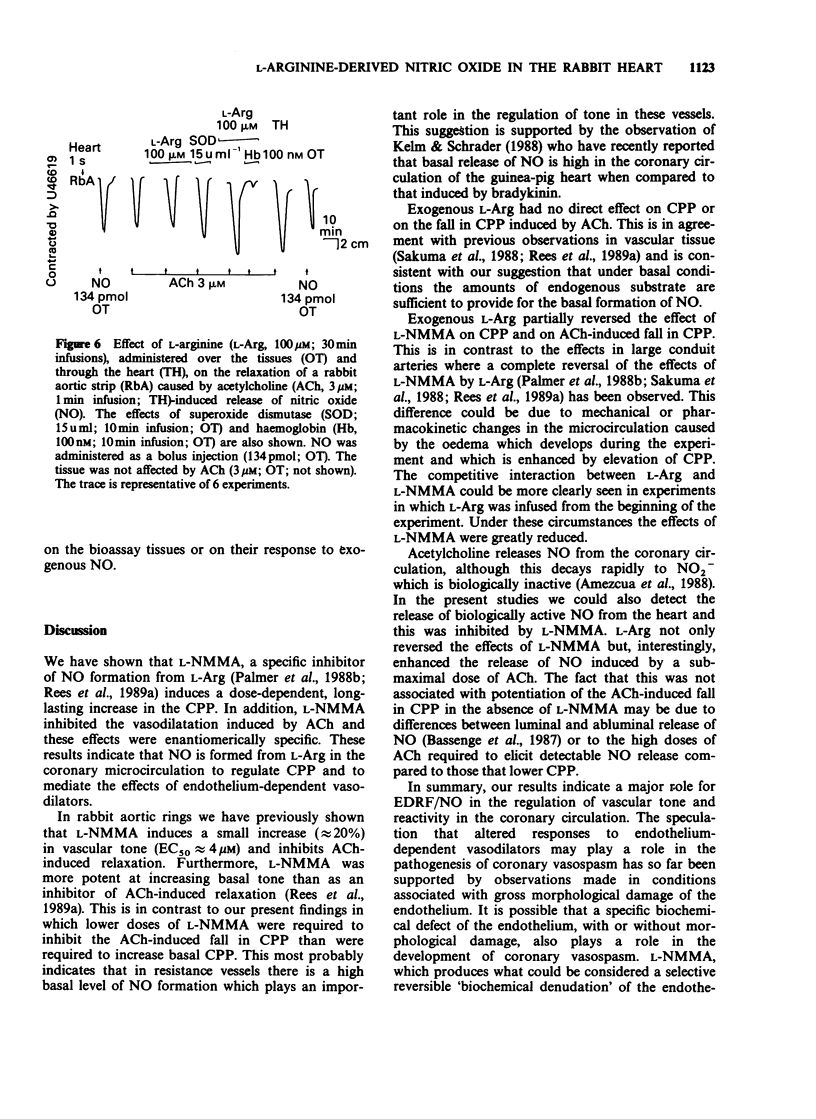
1. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in the regulation of the vascular tone of the coronary circulation of the Langendorff-perfused rabbit heart was investigated. 2. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA; 10-100 microM), a specific inhibitor of NO formation from L-arginine (L-Arg), but not its D-enantiomer (D-NMMA; 100 microM) produced a dose-related, sustained increase in the coronary perfusion pressure (CPP). In addition, L-NMMA inhibited the vasodilator responses of acetylcholine (ACh), unmasking in some instances its direct vasoconstrictor effect. These effects of L-NMMA were attenuated by L-Arg. 3. L-NMMA (10 and 30 microM), but not D-NMMA (30 microM), caused a long-lasting inhibition of NO formation which was reversed by L-Arg (30 and 100 microM), but not by D-Arg (100 microM). 4. This study indicates that the formation of NO from L-Arg in the coronary circulation of the rabbit plays a role both as a regulator of vascular tone and as a mediator of the vasodilatation induced by ACh.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amezcua J. L., Dusting G. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Acetylcholine induces vasodilatation in the rabbit isolated heart through the release of nitric oxide, the endogenous nitrovasodilator. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):830–834. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulu M., Lappalainen J., Pesonen U., Hietala J., Syvälahti E. Chronic treatment with SCH 23390, a selective dopamine D-1 receptor antagonist, decreases dopamine metabolism in rat caudate nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 18;155(3):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy A., Bajusz S., Patthy L. Preparation and characterization of Ng-mono-, di- and trimethylated arginines. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1977;12(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Nau H., Wittfoht W., Gerlach J., Prescher K. E., Klein M. M., Niroomand F., Böhme E. Arginine is a physiological precursor of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


