Abstract
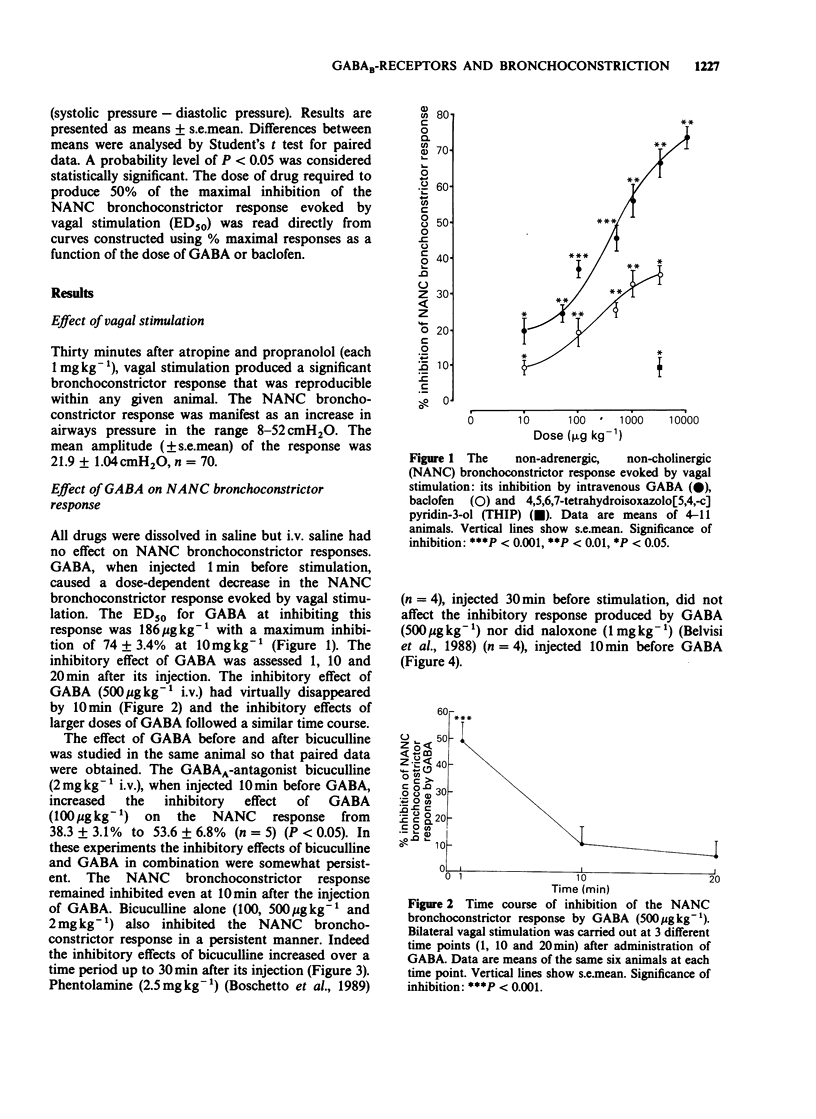
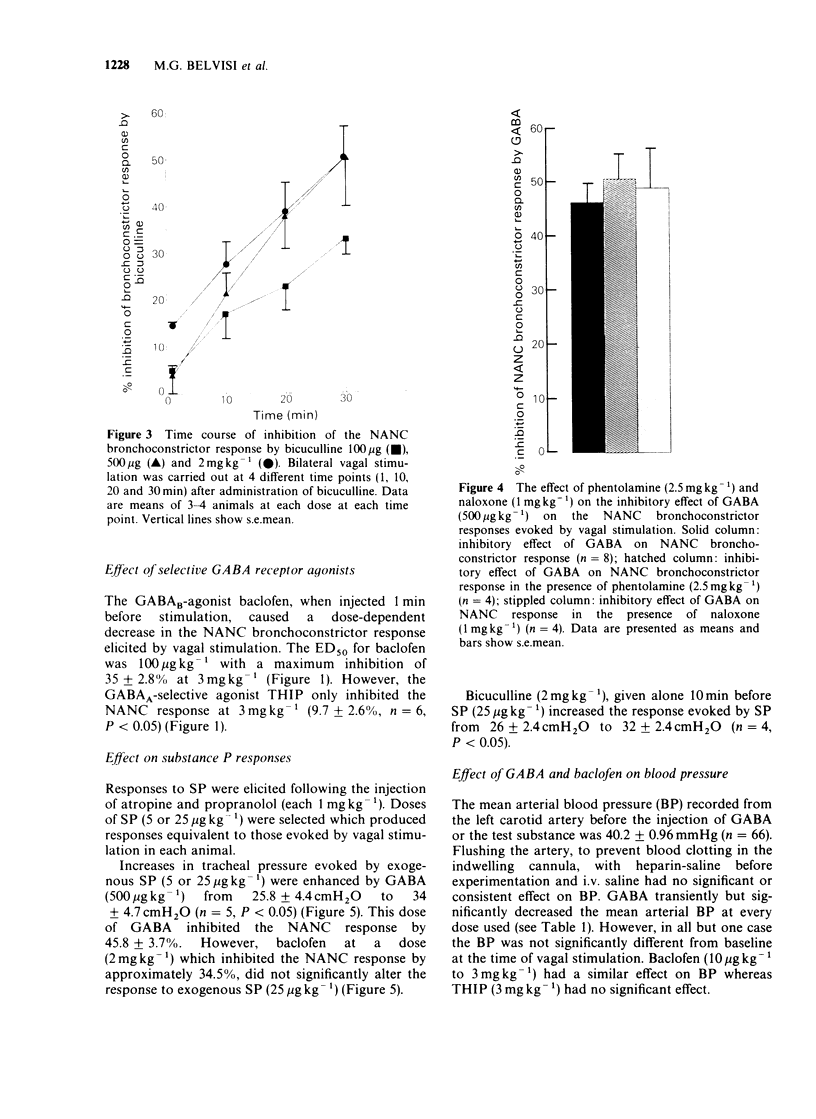
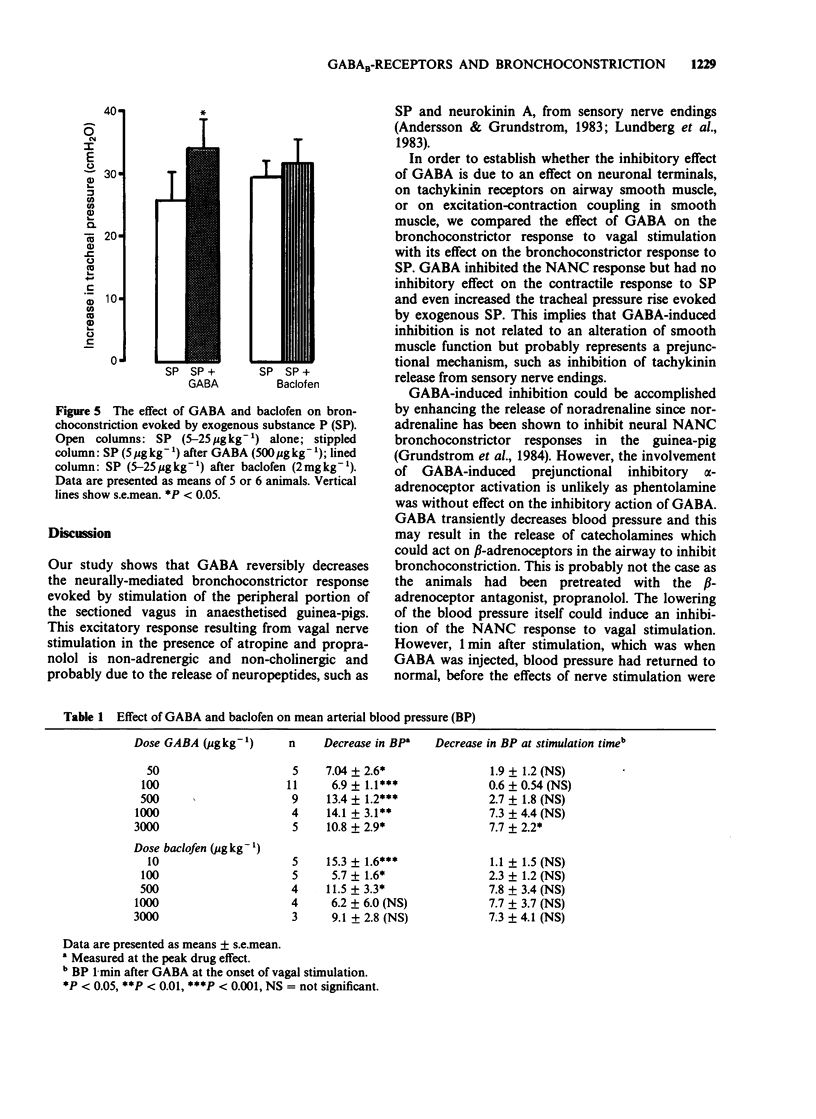
1. Evidence suggests that gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and its receptors are present in the peripheral nervous system. We have now investigated the effect of GABA and related substances on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) neurally-evoked bronchoconstriction in the anaesthetised guinea-pig. 2. Bilateral vagal stimulation (5 V, 5 ms, 3 or 5 Hz) for 30 s, after propranolol (1 mg kg-1 i.v.) and atropine (1 mg kg-1 i.v.) evoked a NANC bronchoconstrictor response manifest as a mean tracheal pressure rise of 21.9 +/- 1.04 cmH2O (n = 70). The bronchoconstrictor response was reproducible for any given animal. 3. GABA (10 micrograms-10 mg kg-1 i.v.) did not alter basal tracheal pressure but reduced the NANC bronchoconstrictor response to vagal stimulation in a dose-dependent manner (ED50 = 186 micrograms kg-1 with a maximal inhibition of 74 +/- 3.4% at 10 mg kg-1). Neither the opioid antagonist naloxone (1 mg kg-1 i.v.) nor the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist phentolamine (2.5 mg kg-1 i.v.) had any significant effect on the inhibitory response produced by GABA (500 micrograms kg-1). 4. GABA-induced inhibition was not antagonised by the GABAA-antagonist bicuculline (2 mg kg-1 i.v.). 5. The GABAB-agonist baclofen (10 micrograms-3 mg kg-1 i.v.) caused a dose-dependent inhibition of the NANC response (ED50 = 100 micrograms kg-1 with a maximal inhibition of 35.5 +/- 2.8% at 3 mg kg-1). The GABAA-agonist, 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-C] pyridin-3-ol (THIP), also inhibited the NANC bronchoconstrictor response.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson R. G., Grundström N. The excitatory non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nervous system of the guinea-pig airways. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;131:141–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Asthma as an axon reflex. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Chung K. F., Jackson D. M., Barnes P. J. Opioid modulation of non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschetto P., Roberts N. M., Rogers D. F., Barnes P. J. Effect of antiasthma drugs on microvascular leakage in guinea pig airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):416–421. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Artaud F., Cesselin F., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Local and remote effects of intra-caudate administration of GABA-related drugs on Met-enkephalin release in the basal ganglia. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Doble A., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Shaw J. S., Turnbull M. J., Warrington R. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard N., Barnes P. J. Mu-opioid receptors modulate non-cholinergic constrictor nerves in guinea-pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90578-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giotti A., Luzzi S., Spagnesi S., Zilletti L. GABAA and GABAB receptor-mediated effects in guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):469–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Inhibition of the excitatory non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurotransmission in the guinea pig tracheo-bronchial tree mediated by alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1984 Jan;54(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Hills J. M., Saffrey M. J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of GABAergic neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1628–1634. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01628.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Mirsky R., Dennison M. E., Burnstock G. GABA may be a neurotransmitter in the vertebrate peripheral nervous system. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):71–74. doi: 10.1038/281071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Hailstone M. H., Freeman C. G. Baclofen: stereoselective inhibition of excitant amino acid release. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;32(3):230–231. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplita P. V., Waters D. H., Triggle D. J. gamma-Aminobutyric acid action in guinea-pig ileal myenteric plexus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 8;79(1-2):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Prager R. H., Gynther B. D., Curtis D. R. Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Brodin E., Rosell S., Folkers K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Meli A. The postganglionic excitatory innervation of the mouse urinary bladder and its modulation by prejunctional GABAB receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1986.tb00631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Labella F. S. GABA and baclofen potentiate the K+-evoked release of methionine-enkephalin from rat striatal slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 12;70(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki J., Graf P. D., Nadel J. A. Effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid on neurally mediated contraction of guinea pig trachealis smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka C. gamma-Aminobutyric acid in peripheral tissues. Life Sci. 1985 Dec 16;37(24):2221–2235. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


