Abstract
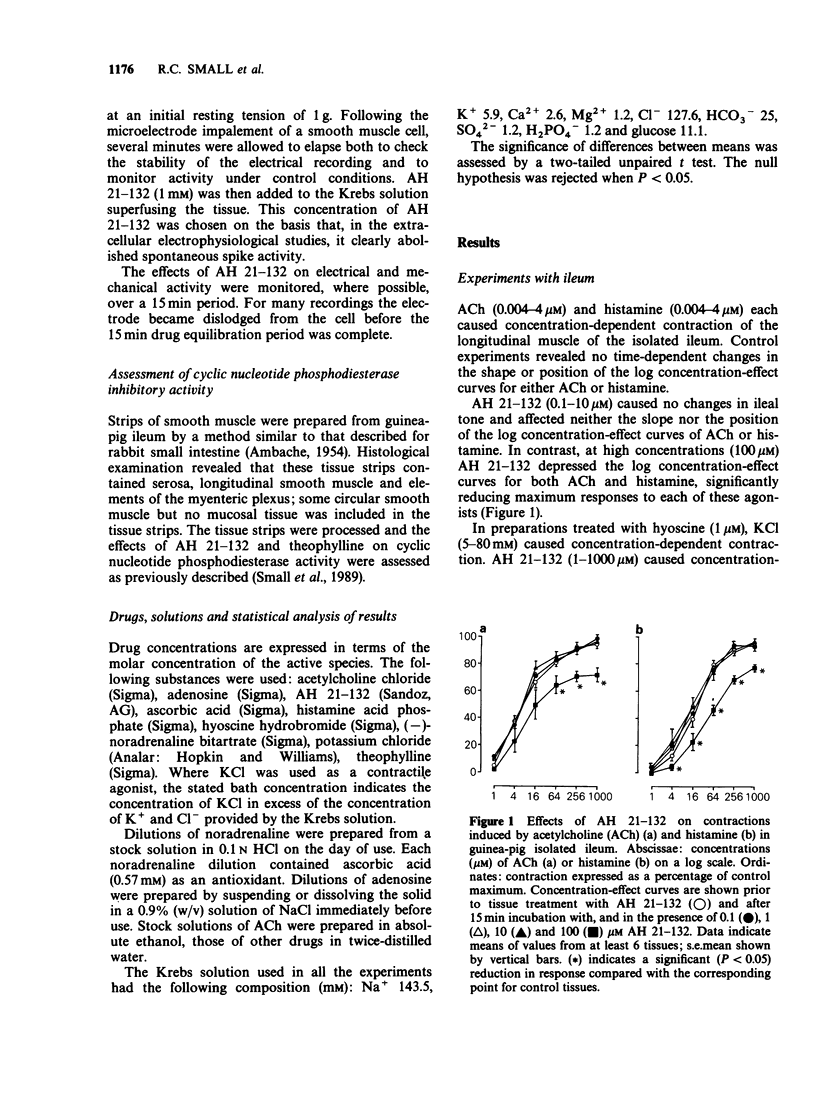
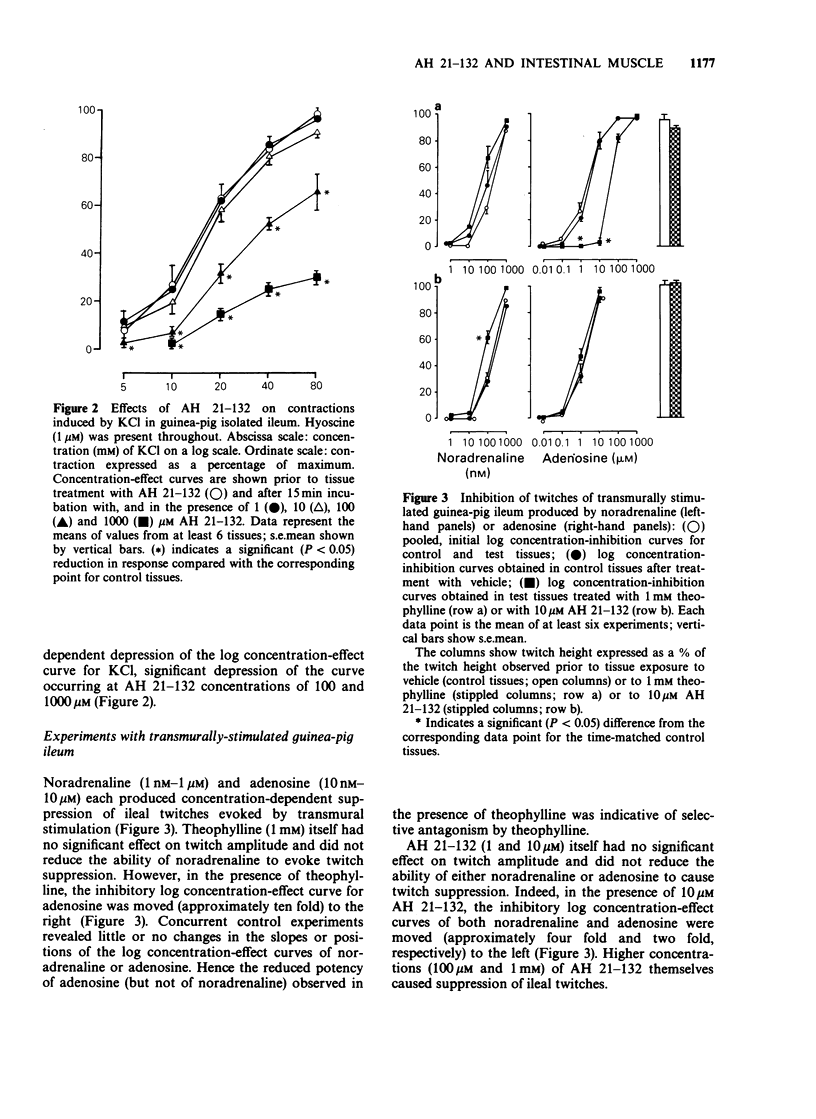
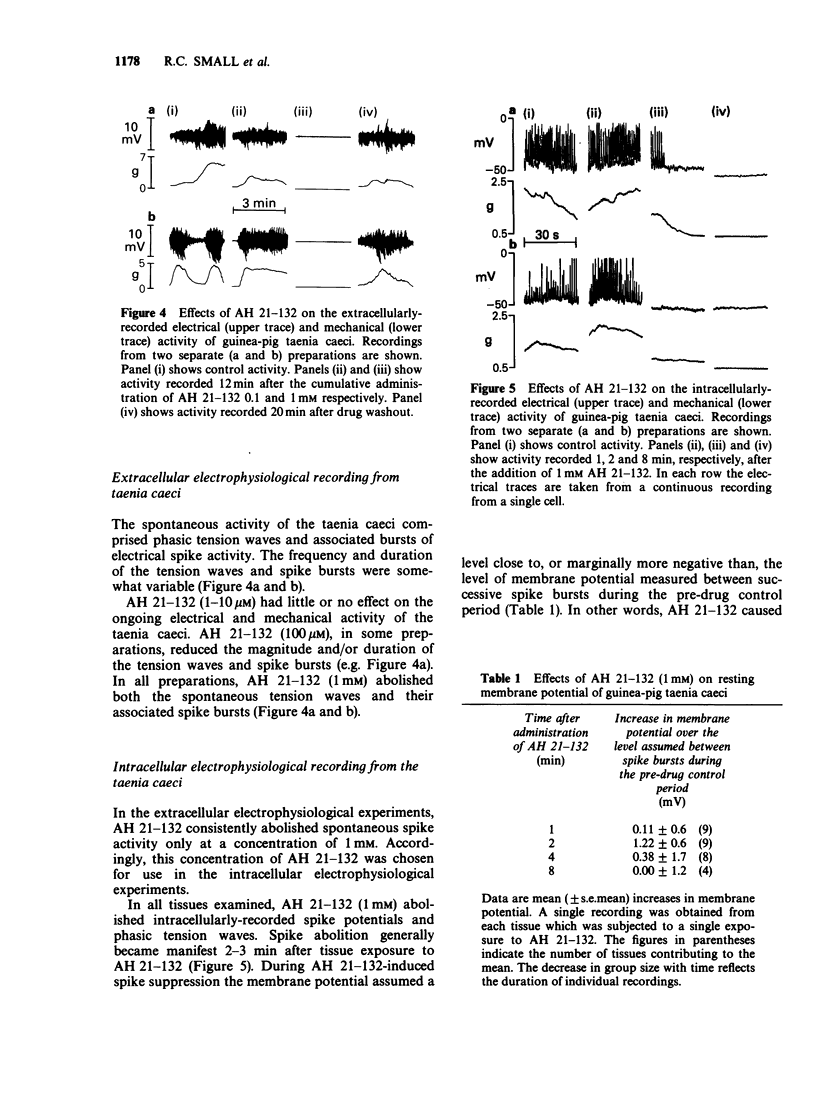
1. AH 21-132 is being investigated as a potential chemotherapeutic agent for bronchial asthma. The present experiments were designed to determine whether AH 21-132 shares the activity of theophylline as an antagonist at adenosine A1 receptors and to assess its potency as a relaxant in intestinal smooth muscle. 2. In the transmurally-stimulated guinea-pig ileum, theophylline (1 mM), but not AH 21-132 (1 and 10 microM), antagonized twitch depression induced by adenosine. Higher concentrations (100 microM and 1 mM) of AH 21-132 themselves had a depressant effect. Neither theophylline (1 mM) nor AH 21-132 (1 and 10 microM) antagonized twitch depression induced by noradrenaline. 3. AH 21-132 (100 microM and 1 mM) depressed maximum contractions of ileum induced by both acetylcholine (ACh) and histamine. 4. In ileum treated with hyoscine (1 microM), AH 21-132 (greater than 10 microM) caused a concentration-dependent depression of the log concentration-effect curve for potassium chloride. 5. Simultaneous extracellular electrophysiological and mechanical recording from taenia caeci showed that AH 21-132 (100 microM-1 mM) inhibited spontaneous tension waves and their associated bursts of electrical spike activity. 6. Intracellular electrophysiological recording from taenia caeci showed that the mechano-inhibitory effect of 1 mM AH 21-132 was accompanied by abolition of spontaneous spike activity. Following spike abolition, the membrane potential assumed a value very close to that observed during periods of electrical quiescence prior to drug exposure. 7. AH 21-132 inhibited the activity of cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic GMP-dependent phosphodiesterases derived from homogenates of ileal smooth muscle.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBACHE N. Separation of the longitudinal muscle of the rabbit's ileum as a broad sheet. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):53–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenhoffen K., von Loh D. Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen zur normalen Spontanaktivität der isolierten Taenia coli des Meerschweinchens. Pflugers Arch. 1970;314(4):312–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00592289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Digges K., Marshall N. R., Starke K. Forskolin and the release of noradrenaline in cerebrocortical slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;325(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00507049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The response of the guineapig ileum to electrical stimulation by coaxial electrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Feb 28;127(2):40–1P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton D. M. Structure-activity relations for presynaptic inhibition of noradrenergic and cholinergic transmission by adenosine: evidence for action on A1 receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;1(4):287–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: antagonism by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C., Boyle J. P., Cortijo J., Curtis-Prior P. B., Davies J. M., Foster R. W., Hofer P. The relaxant and spasmogenic effects of some xanthine derivatives acting on guinea-pig isolated trachealis muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C., Boyle J. P., Duty S., Elliott K. R., Foster R. W., Watt A. J. Analysis of the relaxant effects of AH 21-132 in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1165–1173. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C., Weston A. H. Simultaneous long-term recording of the mechanical and intracellular electrical activity of smooth muscles. J Pharmacol Methods. 1980 Jan;3(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(80)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C., Weston A. H. Simultaneous recording of electrical and mechanical activity from intestinal and vascular smooth muscle [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;61(3):491P–492P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J. Action of mediators on airway smooth muscle: functional antagonism as a mechanism for bronchodilator drugs. Agents Actions Suppl. 1988;23:37–53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9156-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


