Abstract
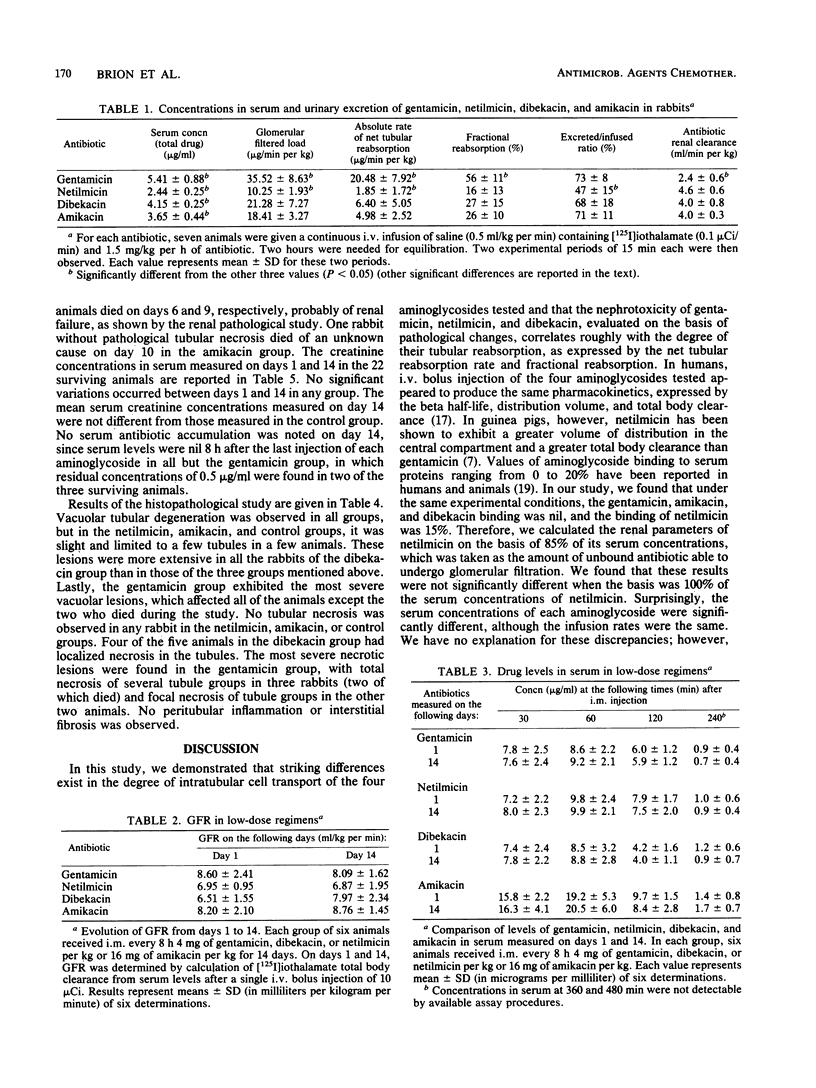
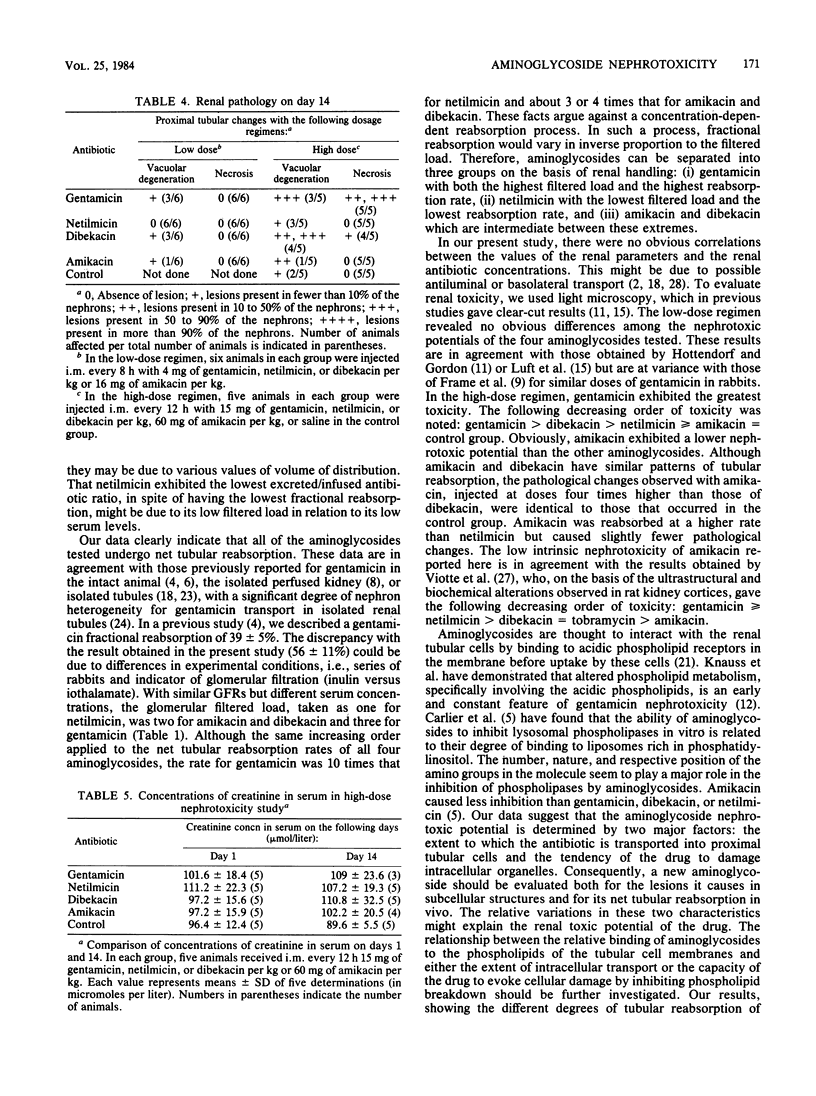
The role of the tubular reabsorption of aminoglycosides in nephrotoxicity was considered. The tubular reabsorption rate, fractional reabsorption, and net balance, expressed as the excreted to infused aminoglycoside ratio, were concomitantly studied in male rabbits by continuous infusion of gentamicin, netilmicin, dibekacin, and amikacin. Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity was evaluated by creatinine levels in serum and pathological renal damage after 14 days of a low- or high-dose regimen, comprising either eight, hourly intramuscular injections of gentamicin, netilmicin, or dibekacin (4 mg/kg) or amikacin (16 mg/kg); twelve, hourly intramuscular injections of gentamicin, netilmicin, or dibekacin (15 mg/kg) or amikacin (60 mg/kg); or injections of saline for the control group. Aminoglycosides exhibited three degrees of tubular reabsorption: gentamicin had the highest, netilmicin had the lowest, and dibekacin and amikacin had intermediate degrees of reabsorption. Nephrotoxicity associated with alteration in renal histology was observed with gentamicin and, to a lesser extent, with dibekacin in the high-dose regiment. No nephrotoxicity was noted with netilmicin or amikacin compared with the control group. Concentrations of the aminoglycosides in renal cortex and serum were not predictive of renal toxicity. Except for amikacin, which appeared to exhibit the lowest intrinsic renal toxicity, nephrotoxicity was correlated with the tubular reabsorption of each aminoglycoside. It was concluded that aminoglycoside renal toxicity can be determined by two major factors: importance of transport into tubular cells and intrinsic intracellular toxicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff G. R., Pottratz S. T., Brier M. E., Walker N. E., Fineberg N. S., Glant M. D., Luft F. C. Aminoglycoside accumulation kinetics in rat renal parenchyma. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Elliott W. C., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. Effect of basis amino acids and aminoglycosides on 3H-gentamicin uptake in cortical slices of rat and human kidney. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Feb;99(2):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon C., Contrepois A., Vigneron A. M., Lamotte-Barrillon S. Effects of furosemide on extravascular diffusion, protein binding and urinary excretion of cephalosporins and aminoglycosides in rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):600–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. B., Laurent G., Claes P. J., Vanderhaeghe H. J., Tulkens P. M. Inhibition of lysosomal phospholipases by aminoglycoside antibiotics: in vitro comparative studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):440–449. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu P. J., Brown A., Miller G., Long J. F. Renal extraction of gentamicin in anesthetized dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):277–282. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung M., Parravicini L., Assael B. M., Cavanna G., Radwanski E., Symchowicz S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of aminoglycoside antibiotics in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1017–1021. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier V. U., Lietman P. S., Mitch W. E. Evidence for luminal uptake of gentamicin in the perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Aug;210(2):247–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame P. T., Phair J. P., Watanakunakorn C., Bannister T. W. Pharmacologic factors associated with gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):952–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Plamp C., Starr P., Bennet W. M., Houghton D. C., Porter G. Comparative nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):34–40. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottendorf G. H., Gordon L. L. Comparative low-dose nephrotoxicities of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Alterations in renal cortical phospholipid content induced by gentamicin: time course, specificity, and subcellular localization. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):F535–F546. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.5.F535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky J. J., Cheng L., Sacktor B., Lietman P. S. Gentamicin uptake by renal tubule brush border membrane vesicles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Nov;215(2):390–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Bloch R., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N., Costello R., Maxwell D. R. Comparative nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):541–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Fineberg N. S., Yum M. N., Wong L. Comparative low-dose nephrotoxicities of dibekacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Apr;9(4):297–301. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.4.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin J. P., Viotte G., Vandewalle A., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P., Fillastre J. P. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: a cell biology approach. Kidney Int. 1980 Nov;18(5):583–590. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastoriza-Munoz E., Bowman R. L., Kaloyanides G. J. Renal tubular transport of gentamicin in the rat. Kidney Int. 1979 Oct;16(4):440–450. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastoriza-Munoz E., Timmerman D., Feldman S., Kaloyanides G. J. Ultrafiltration of gentamicin and netilmicin in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):604–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. A., Bennett W. M. Nephrotoxic acute renal failure due to common drugs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F1–F8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastrasinh M., Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Identification of the aminoglycoside binding site in rat renal brush border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Cumbo T. J., Jusko W. J., Plaut M. E. Gentamicin tissue accumulation and nephrotoxic reactions. JAMA. 1978 Nov 3;240(19):2067–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senekjian H. O., Knight T. F., Weinman E. J. Micropuncture study of the handling of gentamicin by the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1981 Mar;19(3):416–423. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth A. U., Senekjian H. O., Babino H., Knight T. F., Weinman E. J. Renal handling of gentamicin by the Munich-Wistar rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):F645–F648. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.6.F645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon L., Bowman R. L., Pastoriza-Munoz E., Kaloyanides G. J. Comparative nephrotoxicities of gentamicin, netilmicin and tobramycin in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Sep;210(3):334–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandewalle A., Farman N., Morin J. P., Fillastre J. P., Hatt P. Y., Bonvalet J. P. Gentamicin incorporation along the nephron: autoradiographic study on isolated tubules. Kidney Int. 1981 Apr;19(4):529–539. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viotte G., Olier B., Morin J. P., Godin M. Modifications fonctionnelles, histologiques, biochimiques rénales. Etude comparative entre dibékacine, gentamicine, tobramycine, nétilmicine et amikacine. Nouv Presse Med. 1982 Nov 18;11(46):3419–3425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton A., Solez K. Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity--a tale of two transports. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Feb;99(2):148–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


