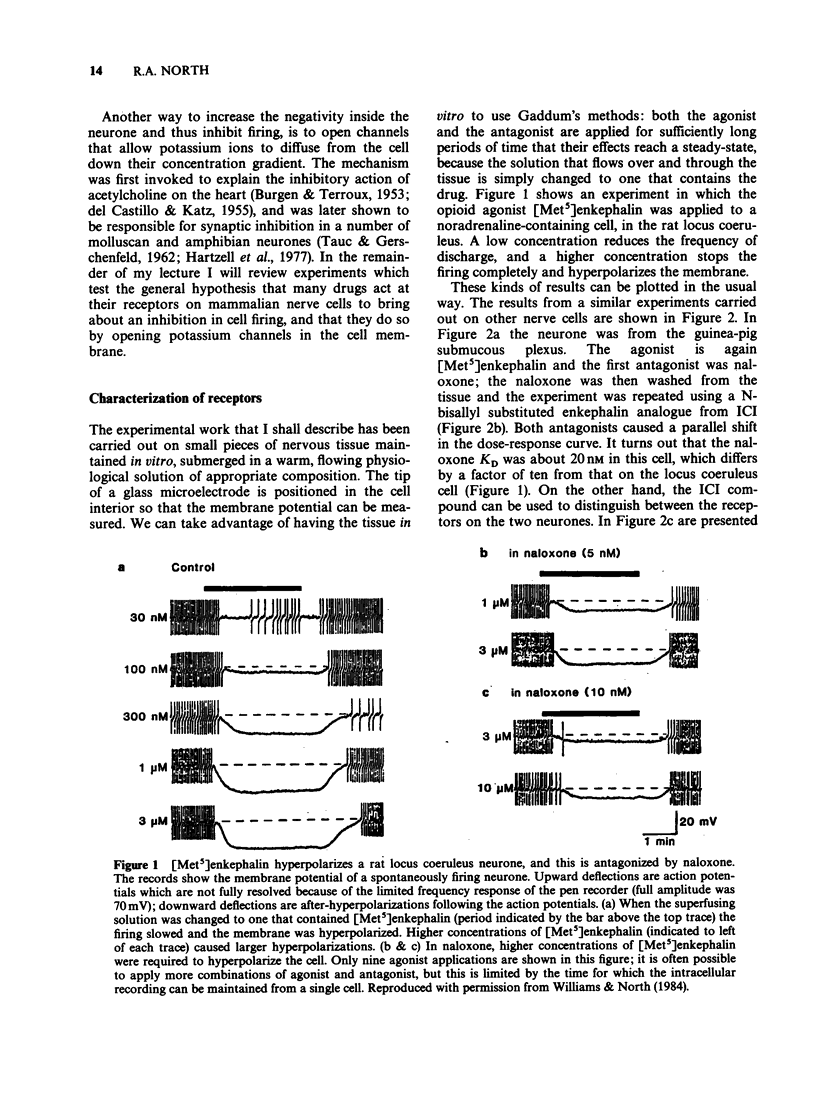
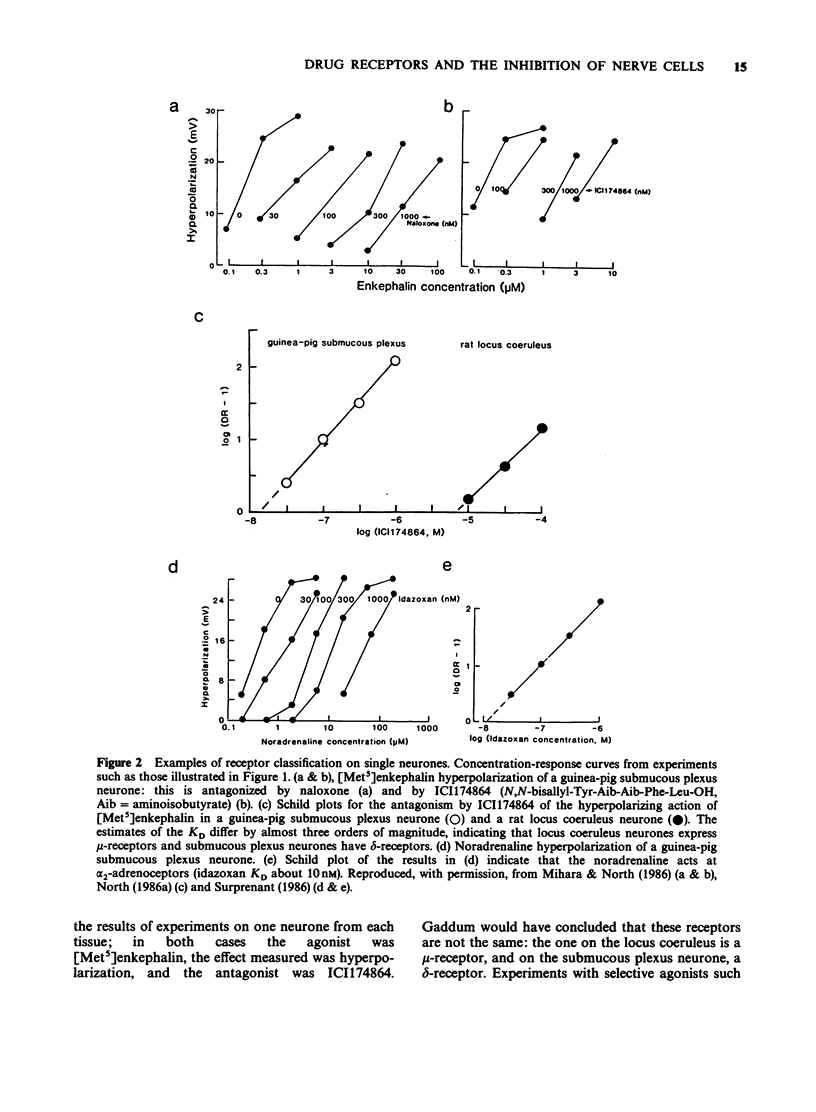
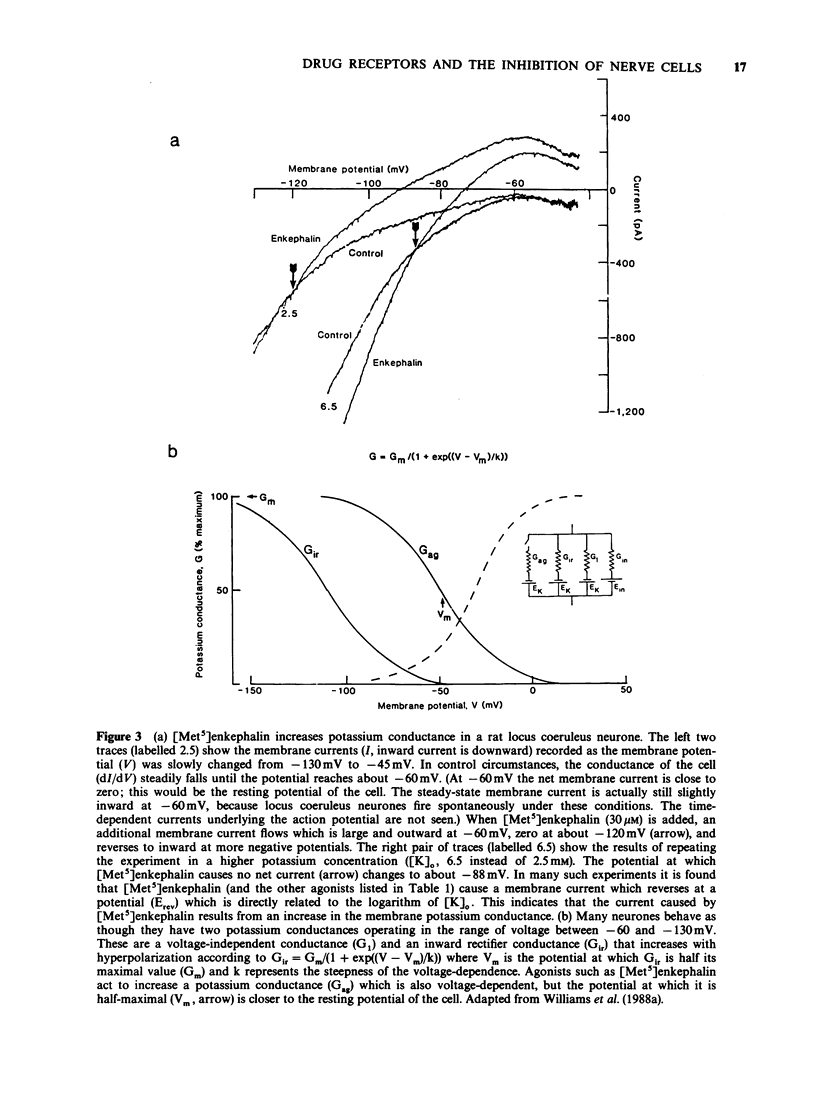
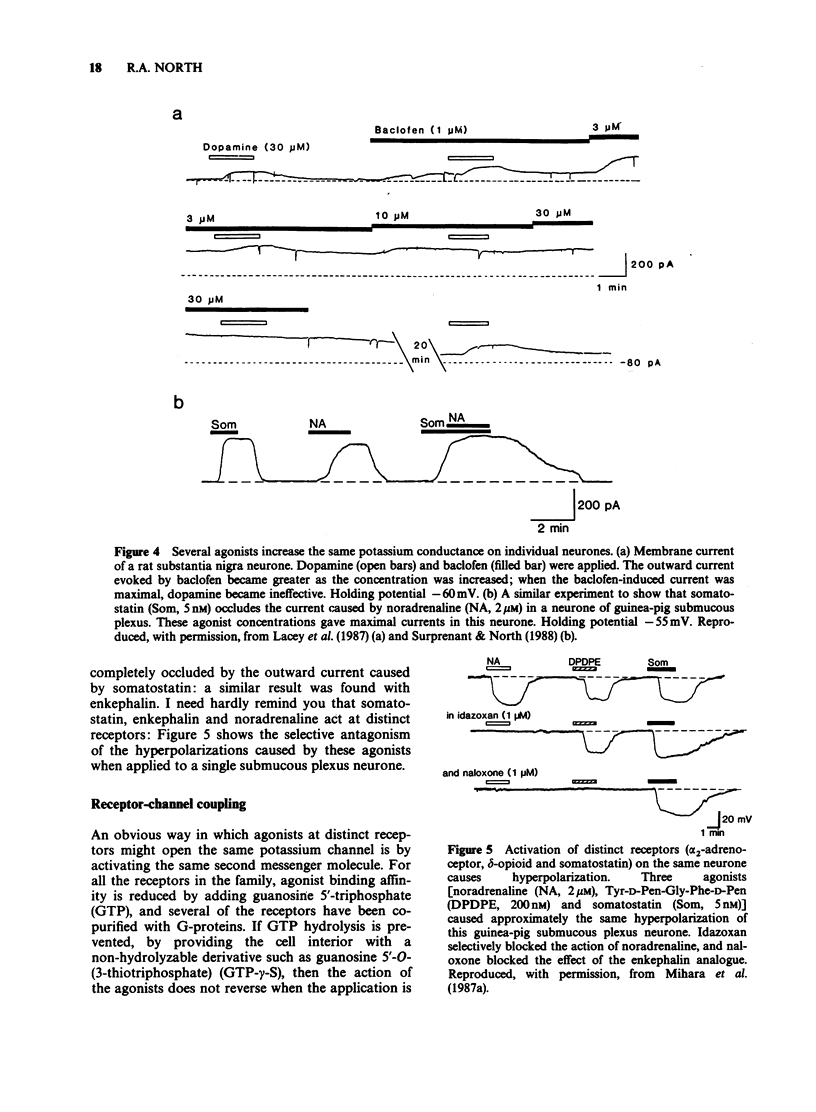
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K., Wang Y. Y. Pertussis toxin blocks the outward currents evoked by opiate and alpha 2-agonists in locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 23;371(2):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:99–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P. Inhibitory and excitatory effects of dopamine on Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):173–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S., TERROUX K. G. On the negative inotropic effect in the cat's auricle. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):449–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. A., Levitan I. B. Serotonin increases an anomalously rectifying K+ current in the Aplysia neuron R15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3522–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Dubois-Dauphin M., Raggenbass M., Dreifuss J. J. Direct inhibition by opioid peptides of neurones located in the ventromedial nucleus of the guinea pig hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1988 May 31;450(1-2):124–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91551-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Israel J. M., Vincent J. D. Electrophysiological responses to somatostatin of rat hypophysial cells in somatotroph-enriched primary cultures. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:493–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., North R. A. Agonists at mu-opioid, M2-muscarinic and GABAB-receptors increase the same potassium conductance in rat lateral parabrachial neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):896–902. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippocampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):73–77. doi: 10.1038/328073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmers W. F., Williams J. T. Pertussis toxin pretreatment discriminates between pre- and postsynaptic actions of baclofen in rat dorsal raphe nucleus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):300–306. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Production of membrane potential changes in the frog's heart by inhibitory nerve impulses. Nature. 1955 Jun 11;175(4467):1035–1035. doi: 10.1038/1751035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., Henderson G., North R. A., Williams J. T. Noradrenaline-mediated synaptic inhibition in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:477–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., North R. A. Acetylcholine acts on m2-muscarinic receptors to excite rat locus coeruleus neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;85(4):733–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11070.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., North R. A. Acetylcholine hyperpolarizes central neurones by acting on an M2 muscarinic receptor. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):405–407. doi: 10.1038/319405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H. Theories of drug antagonism. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaddum J. H. The action of adrenalin and ergotamine on the uterus of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1926 Mar 18;61(1):141–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1926.sp002280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., Surprenant A., Tonini M., North R. A. Differential localization of 5-HT1 receptors on myenteric and submucosal neurons. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):G603–G611. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.5.G603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M., Paupardin-Tritsch D. Ionic mechanisms and receptor properties underlying the responses of molluscan neurones to 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(2):427–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Mechanisms of slow postsynaptic potentials. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):539–544. doi: 10.1038/291539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Sutor B., Zieglgänsberger W. Baclofen reduces post-synaptic potentials of rat cortical neurones by an action other than its hyperpolarizing action. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:539–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Aghajanian G. K. Pertussis toxin blocks autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of dopaminergic neurons in rat substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1987 May 12;411(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90690-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Somatostatin induces an inward rectification in rat locus coeruleus neurones through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:177–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel J. M., Jaquet P., Vincent J. D. The electrical properties of isolated human prolactin-secreting adenoma cells and their modification by dopamine. Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1448–1455. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Multiple actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:459–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A. The action of somatostatin on neurones of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:315–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. Ionic mechanisms of a two-component cholinergic inhibition in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):85–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Frielle T., Collins S., Yang-Feng T., Kobilka T. S., Francke U., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. An intronless gene encoding a potential member of the family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):75–79. doi: 10.1038/329075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L. M., McKeon T. W., Parsons R. L. Galanin-induced hyperpolarization and decreased membrane excitability of neurones in mudpuppy cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:107–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. Role of intracellular Mg2+ in the activation of muscarinic K+ channel in cardiac atrial cell membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):572–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00657521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Mercuri N. B., North R. A. Dopamine acts on D2 receptors to increase potassium conductance in neurones of the rat substantia nigra zona compacta. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:397–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Mercuri N. B., North R. A. On the potassium conductance increase activated by GABAB and dopamine D2 receptors in rat substantia nigra neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:437–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Pittman Q. J. Novel synaptic responses mediated by dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in neuroendocrine cells of the intermediate pituitary. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Feb 14;64(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90659-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Enkephalin hyperpolarizes interneurones in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:123–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Prince D. A. Acetylcholine induces burst firing in thalamic reticular neurones by activating a potassium conductance. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):402–405. doi: 10.1038/319402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Nishi S., North R. A., Surprenant A. A non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic slow inhibitory post-synaptic potential in neurones of the guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:357–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A. Opioids increase potassium conductance in submucous neurones of guinea-pig caecum by activating delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M., Christie M. J., North R. A. Single potassium channels opened by opioids in rat locus ceruleus neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3419–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Clonidine activates membrane potassium conductance in myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Opiate activation of potassium conductance in myenteric neurons: inhibition by calcium ion. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 17;242(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90504-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. On the potassium conductance increased by opioids in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Yoshimura M. The actions of noradrenaline on neurones of the rat substantia gelatinosa in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:43–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmanović S. S., Shefner S. A. Baclofen increases the potassium conductance of rat locus coeruleus neurons recorded in brain slices. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):124–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene from Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):749–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2441470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P. S., Heisler S., MacDonald J. F. A potassium conductance contributes to the action of somatostatin-14 to suppress ACTH secretion. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 22;444(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90944-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper C. M., Henderson G. Opiates and opioid peptides hyperpolarize locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):394–395. doi: 10.1126/science.7384811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Peterson G. L., Smith D. H., Ashkenazi A., Ramachandran J., Schimerlik M. I., Capon D. J. Primary structure and biochemical properties of an M2 muscarinic receptor. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):600–605. doi: 10.1126/science.3107123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Sato M. A single GTP-binding protein regulates K+-channels coupled with dopamine, histamine and acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):259–262. doi: 10.1038/325259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1987;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Stocker M., Sakmann B., Seeburg P., Baumann A., Grupe A., Pongs O. Potassium channels expressed from rat brain cDNA have delayed rectifier properties. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Williams J. T. Inhibitory synaptic potentials recorded from mammalian neurones prolonged by blockade of noradrenaline uptake. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:87–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUC L., GERSCHENFELD H. M. A cholinergic mechanism of inhibitory synaptic transmission in a molluscan nervous system. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Mar;25:236–262. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmann R. H. Evidence that guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins control a synaptic response in brain: effect of pertussis toxin and GTP gamma S on the late inhibitory postsynaptic potential of hippocampal CA3 neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4589–4602. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04589.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Adenosine-activated potassium conductance in cultured striatal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4857–4861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., Macdonald R. L. Opioid peptides with differential affinity for mu and delta receptors decrease sensory neuron calcium-dependent action potentials. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):394–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Colmers W. F., Pan Z. Z. Voltage- and ligand-activated inwardly rectifying currents in dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3499–3506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Henderson G., North R. A. Characterization of alpha 2-adrenoceptors which increase potassium conductance in rat locus coeruleus neurones. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A. Opiate-receptor interactions on single locus coeruleus neurones. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):489–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Inward rectification of resting and opiate-activated potassium currents in rat locus coeruleus neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4299–4306. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Shibuya N., Ogata E. Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential caused by somatostatin in dissociated human pituitary adenoma cells that secrete growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6198–6202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Reconstitution of somatostatin and muscarinic receptor mediated stimulation of K+ channels by isolated GK protein in clonal rat anterior pituitary cell membranes. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;1(4):283–289. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-4-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Higashi H. 5-Hydroxytryptamine mediates inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat dorsal raphe neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 7;53(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., North R. A. Substantia gelatinosa neurones hyperpolarized in vitro by enkephalin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):529–530. doi: 10.1038/305529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Polosa C., Nishi S. Slow IPSP and the noradrenaline-induced inhibition of the cat sympathetic preganglionic neuron in vitro. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90613-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


