Abstract
1. Changes in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]1) were measured simultaneously with force by a microfluorometric method using a calcium indicator, fura-2, in canine coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. 2. Depolarization by high (30-90 mM) KCl-physiological salt solution (PSS) produced concentration-dependent increases in force and [Ca2+]i. 3. The KCl-induced increase in [Ca2+]i abolished by Ca2+-free conditions and almost abolished by verapamil 10-5 M, suggesting that it was entirely due to the increased Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. 4. The [Ca2+]i force relationship in the presence of verapamil was not distinguishable from that of control. 5. Nitroglycerin produced a concentration-dependent, reversible contraction of the coronary artery that had been contracted by high KCl-PSS, without reduction of the increased [Ca2+]i. 6. The KCl-induced increase in [Ca2+]i was not affected by nitroglycerin and in a presence of nitroglycerin it was abolished by 10-5 M verapamil suggesting that it was caused by the influx of extracellular Ca2+. 7. The [Ca2+]-force curve was shifted to the right by nitroglycerin. 8. It is likely that nitroglycerin relaxes the coronary arterial smooth muscle b reducing the amount of myosin light chain phosphorylation even in the presence of raised [Ca2+]i produced by increased Ca2+ influx following depolarization.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
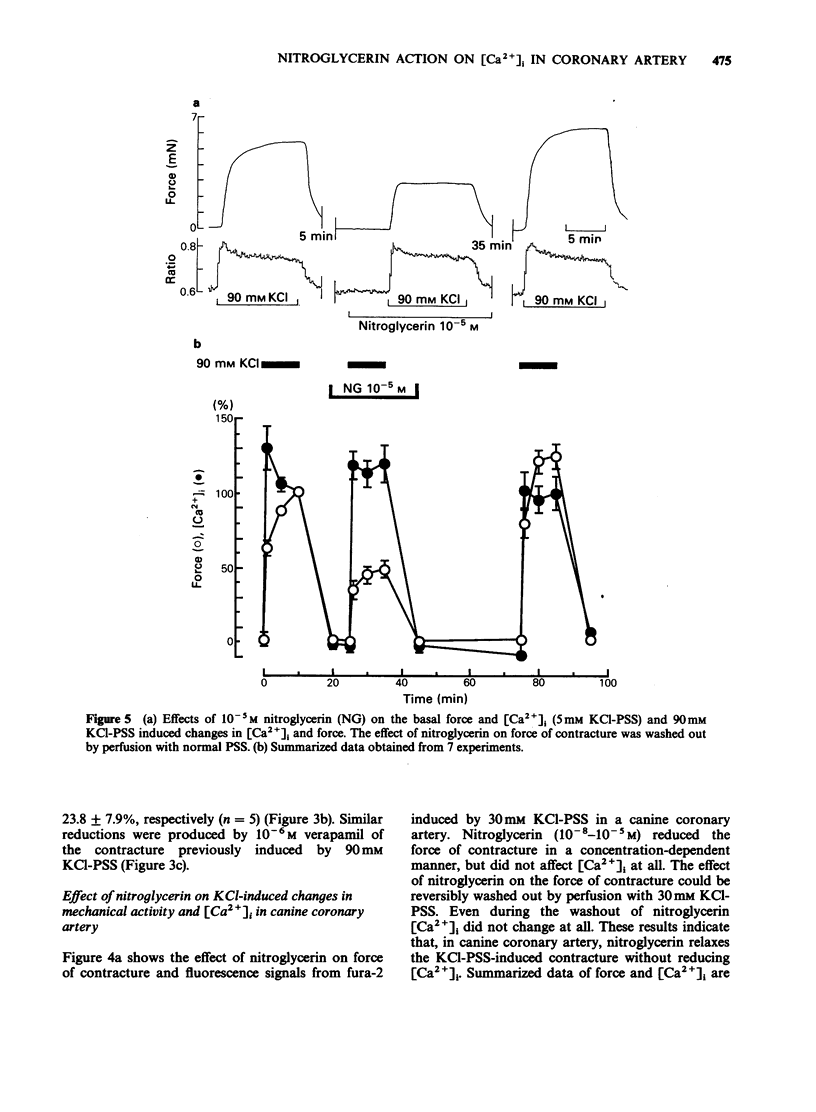
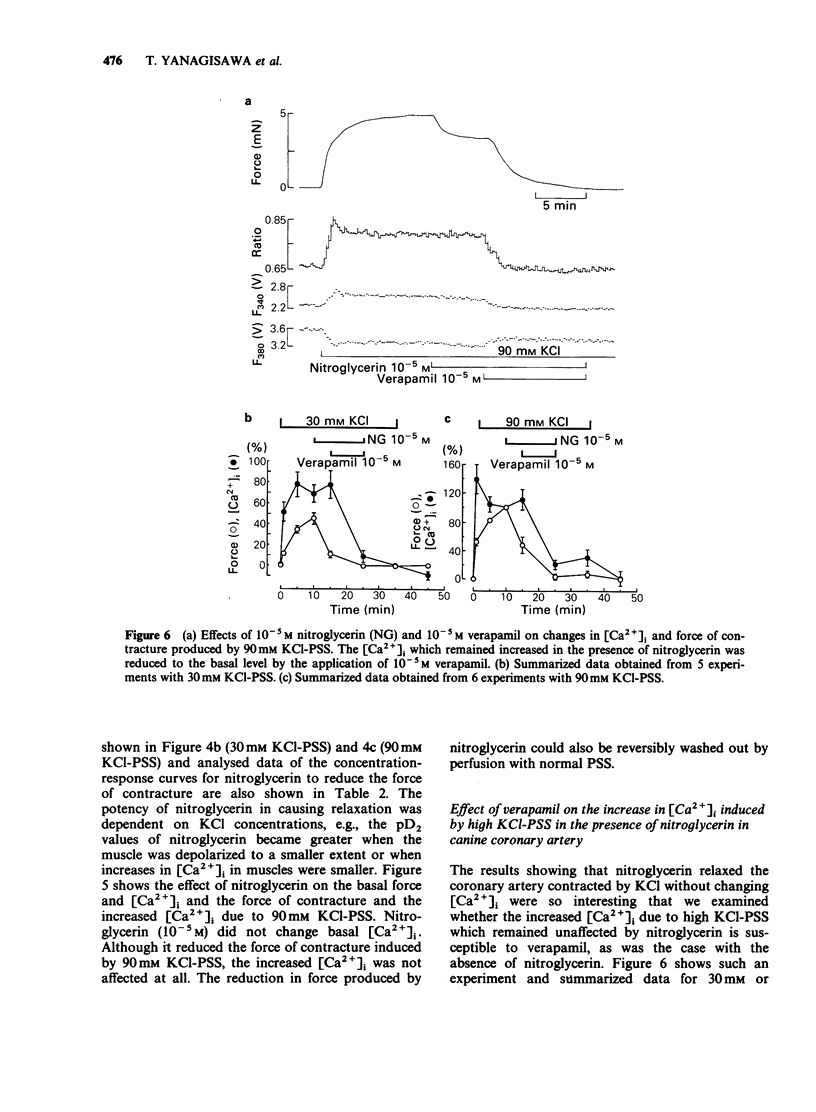
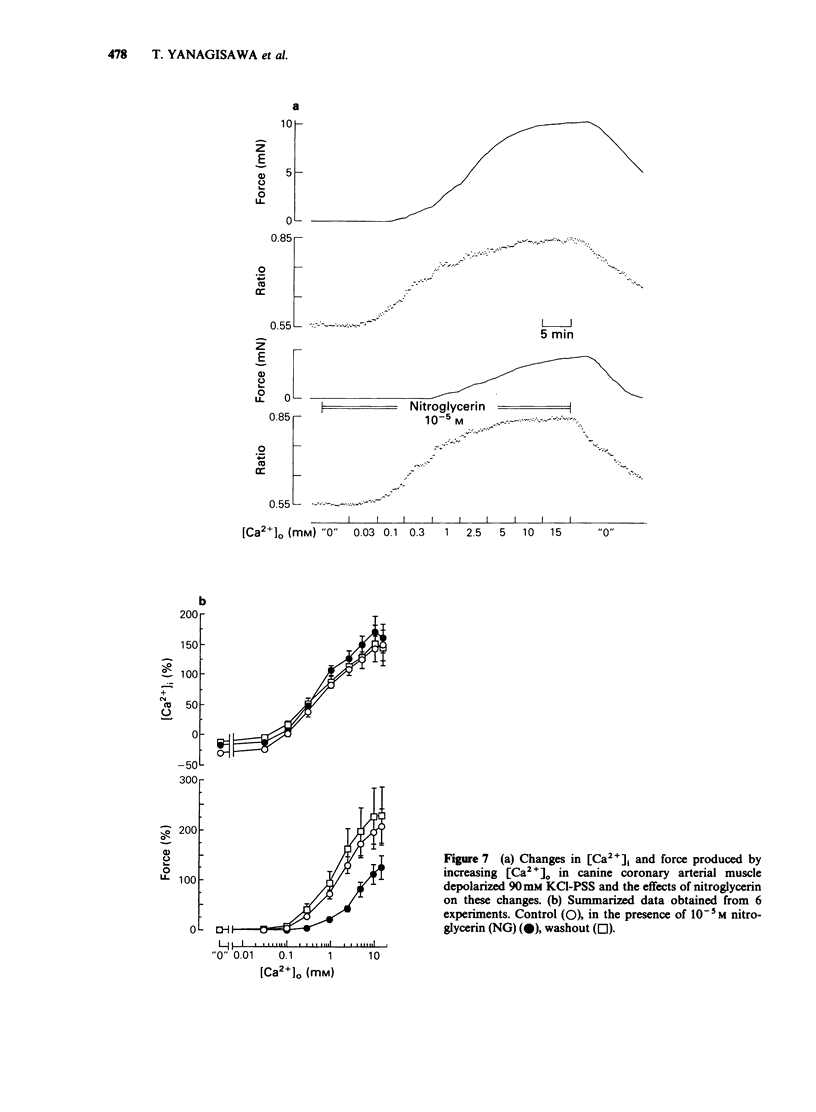
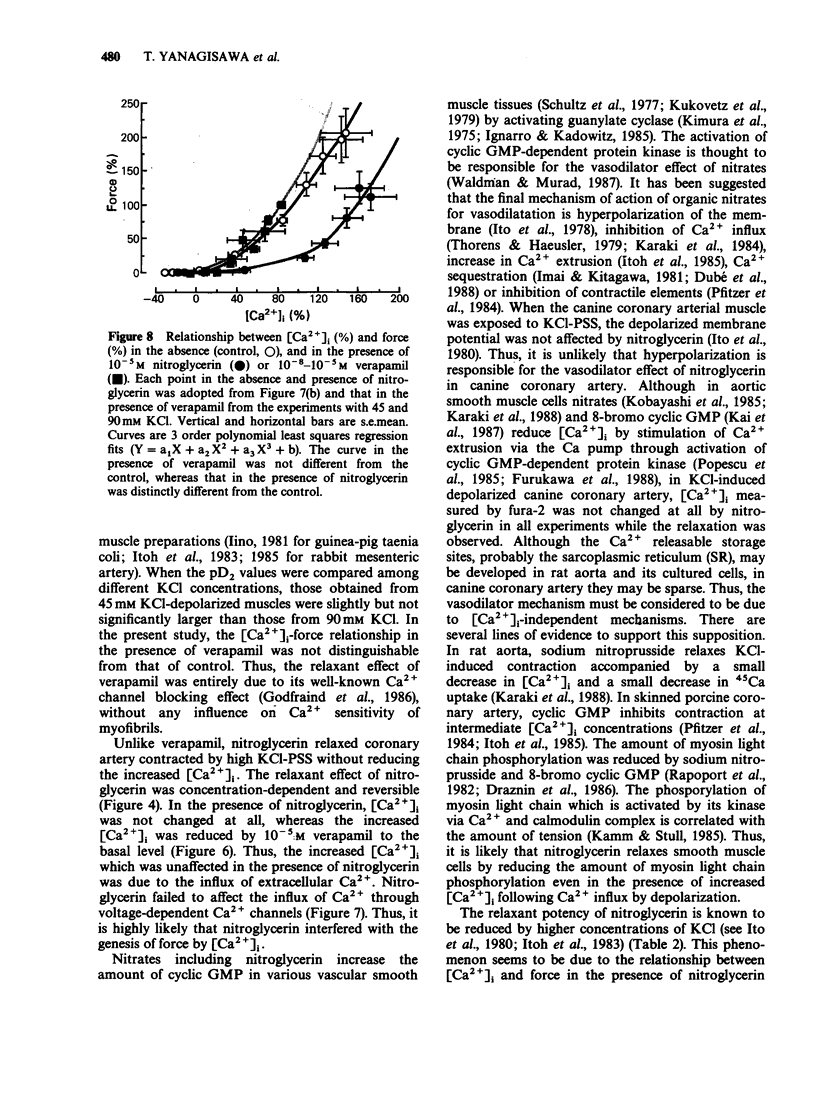
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Photobleaching of fura-2 and its effect on determination of calcium concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C613–C618. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi G., Bruschi M. E., Regolisti G., Borghetti A. Myoplasmic Ca2+-force relationship studied with fura-2 during stimulation of rat aortic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):H840–H854. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.5.H840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin M. B., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Myosin light chain phosphorylation in contraction and relaxation of intact rat thoracic aorta. Int J Biochem. 1986;18(10):917–928. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(86)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubé G. P., Baik Y. H., Van Breemen C., Schwartz A. Effects of isosorbide dinitrate and diltiazem on Ca2+ flux and contraction in artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 5;145(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tawada Y., Shigekawa M. Regulation of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by cyclic nucleotides in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8058–8065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Miller R., Wibo M. Calcium antagonism and calcium entry blockade. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Dec;38(4):321–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Somlyo A. P. Free-calcium and force transients during depolarization and pharmacomechanical coupling in guinea-pig smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Kadowitz P. J. The pharmacological and physiological role of cyclic GMP in vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:171–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Tension responses of chemically skinned fibre bundles of the guinea-pig taenia caeci under varied ionic environments. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:449–467. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai S., Kitagawa T. A comparison of the differential effects of nitroglycerin, nifedipine and papaverine on contractures induced in vascular and intestinal smooth muscle by potassium and lanthanum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;31(2):193–199. doi: 10.1254/jjp.31.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Takakura S., Sato K., Sutko J. L. Ryanodine inhibits the release of calcium from intracellular stores in guinea pig aortic smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1986 May;58(5):730–734. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.5.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Nitroglycerine and catecholamine actions on smooth muscle cells of the canine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:171–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kuriyama H. Effects of sodium nitroprusside on smooth muscle cells of rabbit pulmonary artery and portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Dec;207(3):1022–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kanmura Y., Kuriyama H., Sasaguri T. Nitroglycerine- and isoprenaline-induced vasodilatation: assessment from the actions of cyclic nucleotides. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):393–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Ueno H. Mechanisms of the nitroglycerine-induced vasodilation in vascular smooth muscles of the rabbit and pig. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:233–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Kanaide H., Matsumoto T., Nakamura M. 8-Bromoguanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate decreases intracellular free calcium concentrations in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Nakagawa H., Urakawa N. Comparative effects of verapamil and sodium nitroprusside on contraction and 45Ca uptake in the smooth muscle of rabbit aorta, rat aorta and guinea-pig taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;81(2):393–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Sato K., Ozaki H., Murakami K. Effects of sodium nitroprusside on cytosolic calcium level in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 1;156(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Mittal C. K., Murad F. Increases in cyclic GMP levels in brain and liver with sodium azide an activator of guanylate cyclase. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):700–702. doi: 10.1038/257700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kanaide H., Nakamura M. Cytosolic-free calcium transients in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: microfluorometric measurements. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.3927484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukovetz W. R., Holzmann S., Wurm A., Pöch G. Evidence for cyclic GMP-mediated relaxant effects of nitro-compounds in coronary smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00500277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kitamura K., Itoh T. Factors modifying contraction-relaxation cycle in vascular smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):H641–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.5.H641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki H., Sato K., Satoh T., Karaki H. Simultaneous recordings of calcium signals and mechanical activity using fluorescent dye fura 2 in isolated strips of vascular smooth muscle. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;45(3):429–433. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzer G., Hofmann F., DiSalvo J., Rüegg J. C. cGMP and cAMP inhibit tension development in skinned coronary arteries. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jul;401(3):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00582596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu L. M., Panoiu C., Hinescu M., Nutu O. The mechanism of cGMP-induced relaxation in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 8;107(3):393–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Sodium nitroprusside-induced protein phosphorylation in intact rat aorta is mimicked by 8-bromo cyclic GMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ozaki H., Karaki H. Changes in cytosolic calcium level in vascular smooth muscle strip measured simultaneously with contraction using fluorescent calcium indicator fura 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jul;246(1):294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz K., Schultz K., Schultz G. Sodium nitroprusside and other smooth muscle-relaxants increase cyclic GMP levels in rat ductus deferens. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):750–751. doi: 10.1038/265750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens S., Haeusler G. Effects of some vasodilators on calcium translocation in intact and fractionated vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fay F. S. Calcium transients and resting levels in isolated smooth muscle cells as monitored with quin 2. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C779–C791. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi S., Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Relationship between force and Ca2+ concentration in smooth muscle as revealed by measurements on single cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4109–4113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


