Abstract
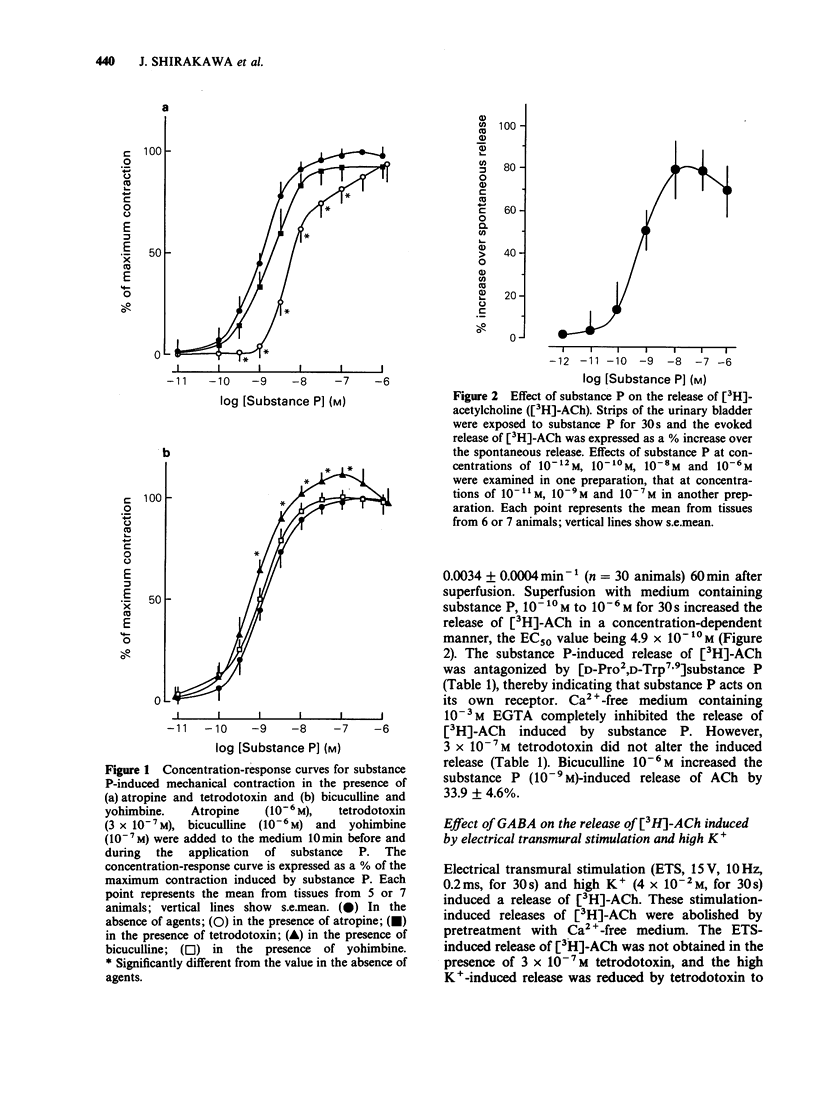
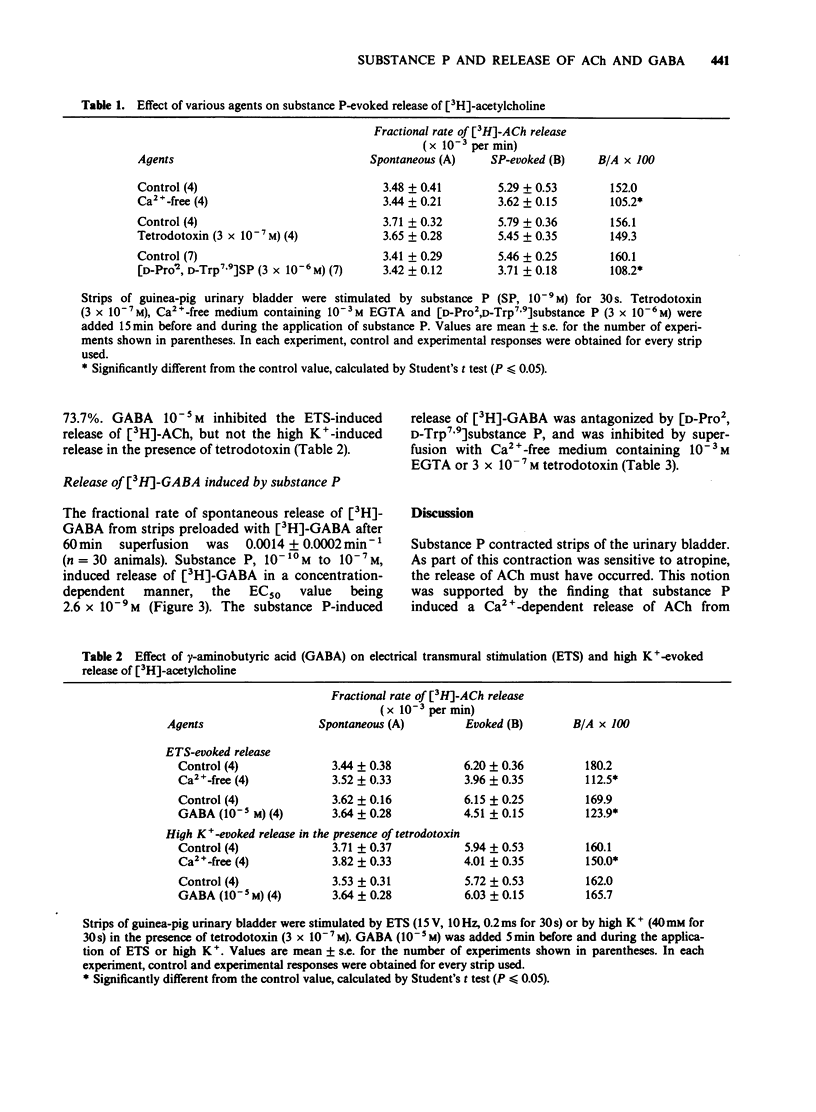
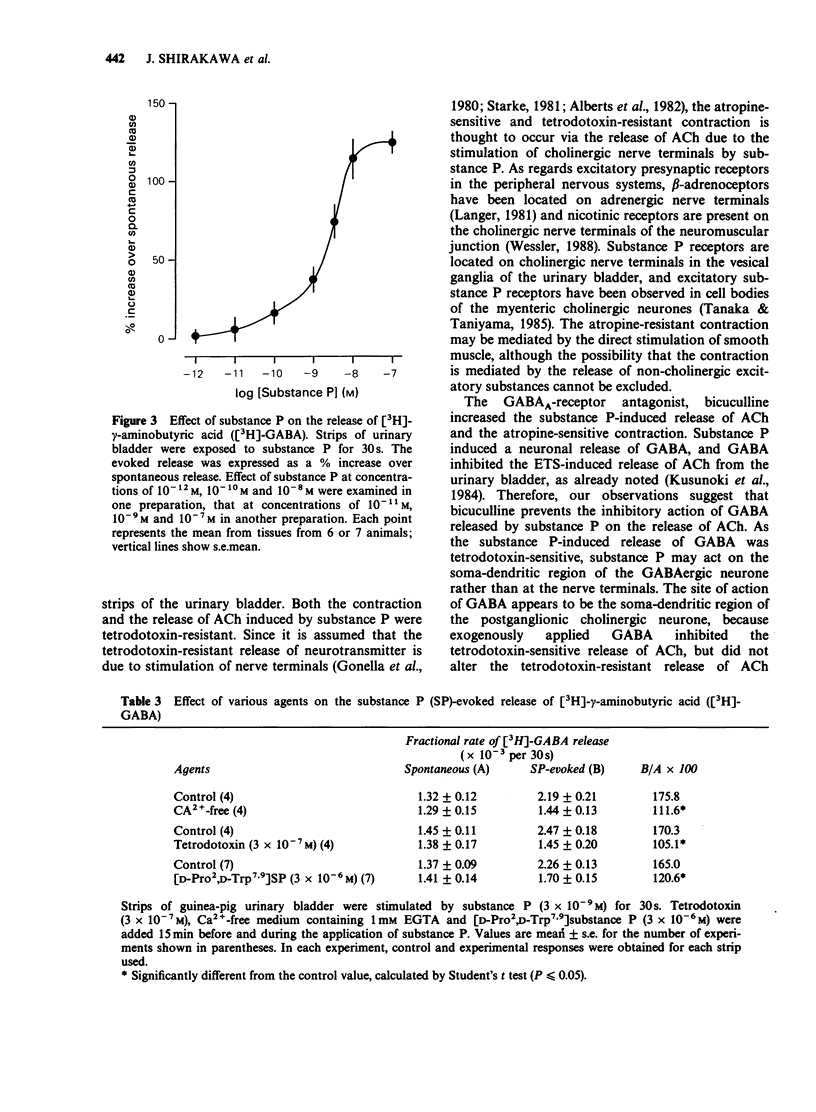
1. The action of substance P (SP) on the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and acetylcholine (ACh) and on contraction were studied in strips of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Substance P induced a dose-dependent contraction of strips of guinea-pig urinary bladder (EC50 = 1.2 x 10(-9) M). This contraction was not altered by tetrodotoxin, but with a dose of 10(-9) M and less, there was a complete inhibition by 10(-6) M) atropine. Contractions initiated by 3 x 10(-9) M) SP or more were partly inhibited by atropine. The EC50 value of substance P in the presence of atropine was 7.0 x 10(-9) M. 2. Substance P induced a Ca2+-dependent and tetrodotoxin-resistant release of [3H]-acetylcholine (ACh) from strips of urinary bladder preloaded with [3H]-choline (EC50 = 4.9 x 10(-10) M), and this release was antagonized by [D-Pro2,D-Trp7,9] substance P. 3. Bicuculline increased the substance P-induced contraction and the release of [3H]-ACh from the strips. 4. Substance P induced a Ca2+-dependent and tetrodotoxin-sensitive release of [3H]-gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from strips preloaded with [3H]-GABA (EC50 = 2.6 x 10(-9) M), and this release was antagonized by [D-Pro2,D-Trp7,9] substance P. 5. Therefore, substance P appears to exert excitatory effects on the contractility of urinary bladder predominantly by stimulating its own receptor located on the cholinergic nerve terminals. GABA released by substance P inhibits stimulation of the cholinergic neurone. However, the direct action of substance P on the cholinergic neurone is more potent that the indirect action via GABA release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts P., Bartfai T., Stjärne L. The effects of atropine on [3H]acetylcholine secretion from guinea-pig myenteric plexus evoked electrically or by high potassium. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:93–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm P., Alumets J., Brodin E., Håkanson R., Nilsson G., Sjöberg N. O., Sundler F. Peptidergic (substance P) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm P., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Peptidergic (vasoactive intestinal peptide) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):751–754. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Cocks T., Crowe R., Kasakov L. Purinergic innervation of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):125–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Gosling J. A. The distribution of noradrenergic nerves and small, intensely fluorescent (SIF) cells in the cat urinary bladder. A light and electron microscope study. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Jul 12;150(2):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00222166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbadawi A., Schenk E. A. A new theory of the innervation of bladder musculature. 3. Postganglionic synapses in uretero-vesico-urethral autonomic pathways. J Urol. 1971 Mar;105(3):372–374. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K. Evidence for adenosine triphosphate as an excitatory transmitter in guinea-pig, rabbit and pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:39–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonella J., Niel J. P., Roman C. Mechanism of the noradrenergic motor control on the lower oesophageal sphincter in the cat. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:251–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted S., Sjögren C., Andersson K. E. Substance P and somatostatin and excitatory neurotransmission in rabbit urinary bladder. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 Jul;252(1):72–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Schultzberg M., Elde R., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Said S., Goldstein M. Peptide neurons in peripheral tissues including the urinary tract: immunohistochemical studies. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978;43 (Suppl 2):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki M., Taniyama K., Tanaka C. Neuronal GABA release and GABA inhibition of ACh release in guinea pig urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):R502–R509. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.4.R502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Dec;32(4):337–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(1):1–43. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Santicioli P., Grimaldi G., Meli A. The effect of peripherally administered GABA on spontaneous contractions of rat urinary bladder in vivo. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(4):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell J., Benson G. S., Wood J. G. Autonomic innervation of the urogenital system: adrenergic and cholinergic elements. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):679–694. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Murphy W. Electrophoresis of acetylcholine, choline and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jul 7;16(7):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Meli A. GABAB receptor mediated inhibition of field stimulation-induced contractions of rabbit bladder muscle in-vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;36(6):378–381. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Booth A. M., Thor K. B., Ostrowski N. L., Nagel J. R., de Groat W. C. Parasympathetic ganglia: naloxone antagonizes inhibition by leucine-enkephalin and GABA. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 25;271(2):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren C., Andersson K. E., Husted S. Contractile effects of some polypeptides on the isolated urinary bladder of guinea-pig, rabbit, and rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1982 Mar;50(3):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1982.tb00960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka C., Taniyama K. Substance P provoked gamma-aminobutyric acid release from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:319–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama K., Kusunoki M., Tanaka C. gamma-aminobutyric acid inhibits motility of the isolated guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler I. Neurotransmission at the NMJ. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):125–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Youther M. L. Direct evidence for a release of acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus of guinea pig small intestine by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):665–668. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Booth A. M. Inhibition and facilitation in parasympathetic ganglia of the urinary bladder. Fed Proc. 1980 Oct;39(12):2990–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C. The actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related amino acids on mammalian autonomic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Apr;172(2):384–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


