Abstract
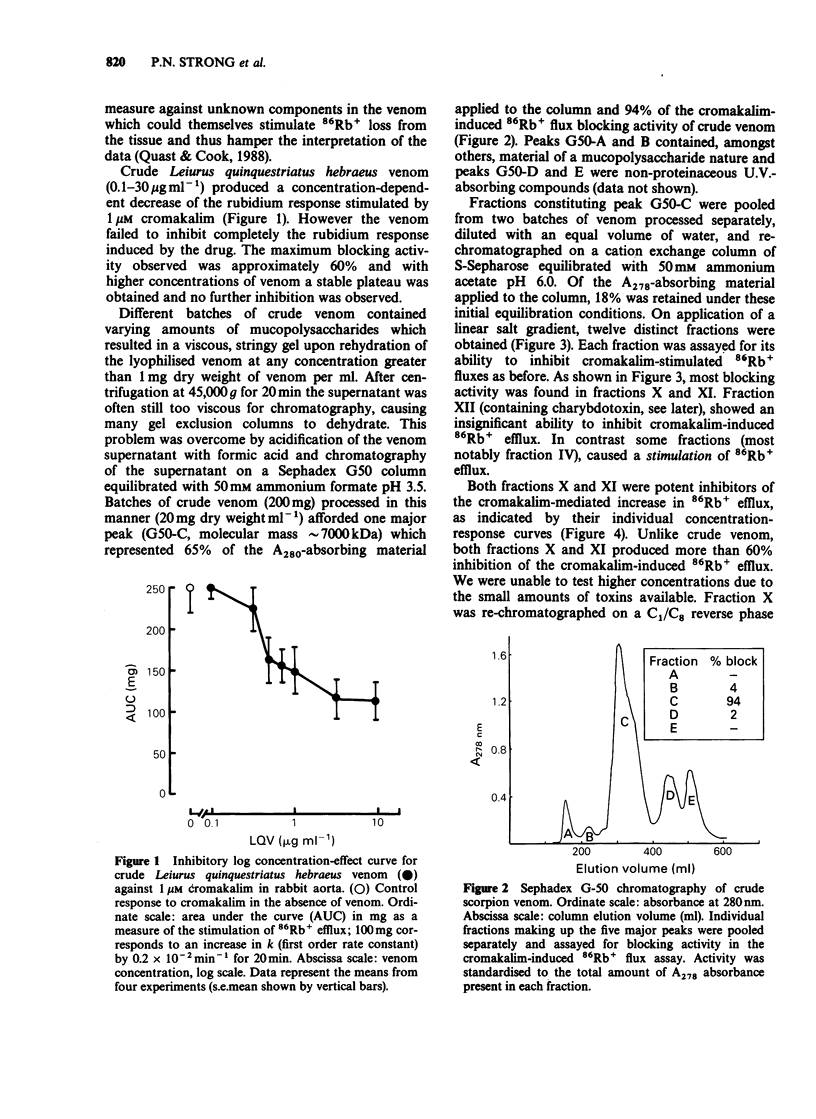
1. The effects of fractionated Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus venom on cromakalim-induced 86Rb+ efflux in rabbit aortic smooth muscle were examined. 2. Crude venom (0.1-30 micrograms ml-1) produced a concentration-dependent decrease of 1 microM cromakalim-induced 86Rb+ response. The maximum blocking activity attainable was approximately 60%. 3. Fractionation of crude venom by gel permeation chromatography and subsequent chromatography on a cation ion-exchange column, produced two fractions (X and XI), active in the 86Rb+ blocking assay. 4. Fraction XII contained charybdotoxin (approximately 85% pure). After a final high performance liquid chromatography (h.p.l.c.) purification step, the purified toxin failed to inhibit the cromakalim-stimulated 86Rb+ efflux although it was a potent inhibitor of A23187-induced K+ flux in human erythrocytes and the large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle. 5. Subsequent purification of fraction X by h.p.l.c. yielded a minor peak which contained 86Rb+ blocking activity. This subfraction was also capable of inhibiting apamin-sensitive, angiotensin II-stimulated K+ flux in guinea-pig hepatocytes. 6. It is concluded that the potassium channel opened by cromakalim in rabbit aortic smooth muscle is not blocked by charybdotoxin but by another distinct toxin in the venom of Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus.
Full text
PDF



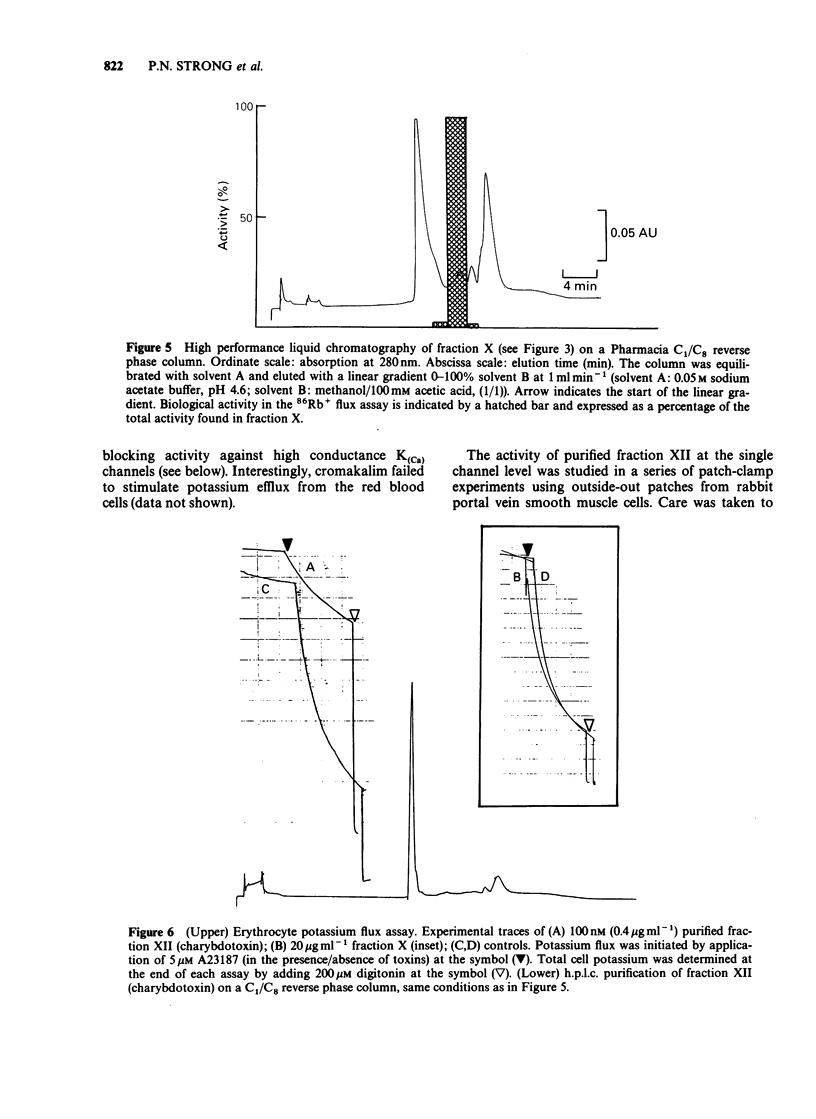
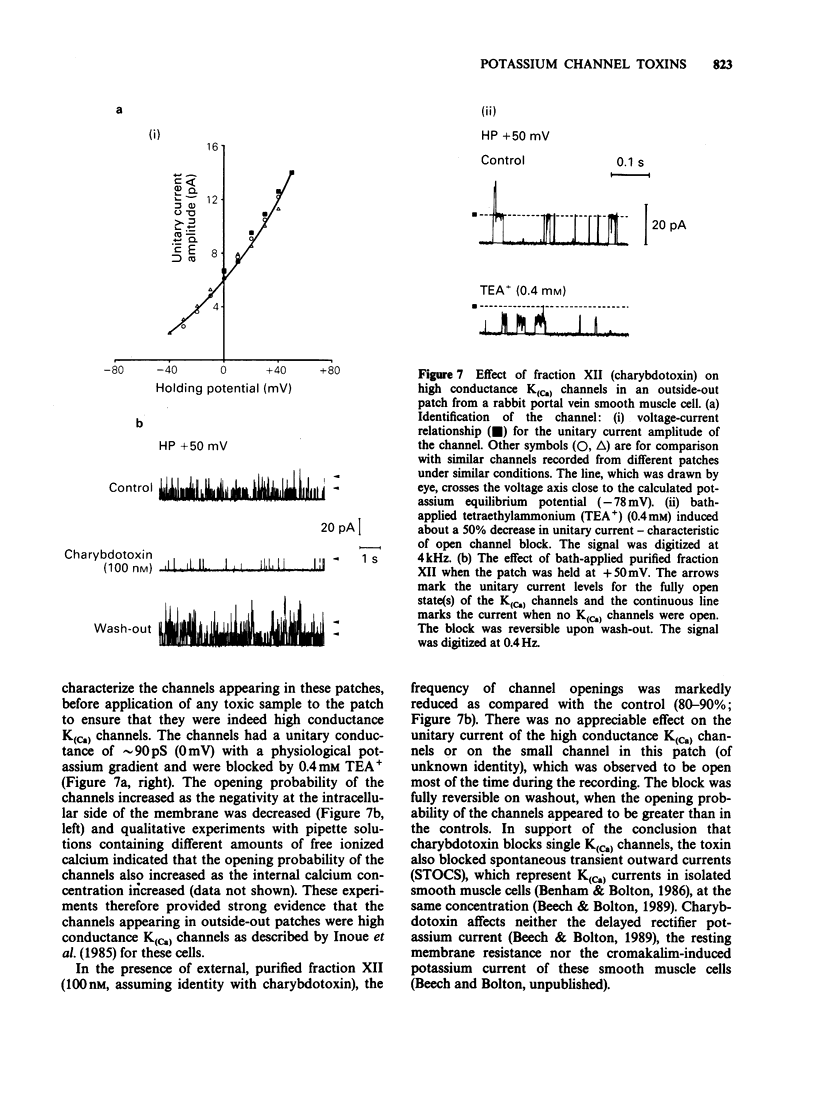



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abia A., Lobatón C. D., Moreno A., García-Sancho J. Leiurus quinquestriatus venom inhibits different kinds of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 14;856(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann A., Grupe A., Ackermann A., Pongs O. Structure of the voltage-dependent potassium channel is highly conserved from Drosophila to vertebrate central nervous systems. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2457–2463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle N. A., Strong P. N. Identification of two toxins from scorpion (Leiurus quinquestriatus) venom which block distinct classes of calcium-activated potassium channel. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicchi G. G., Gimenez-Gallego G., Ber E., Garcia M. L., Winquist R., Cascieri M. A. Purification and characterization of a unique, potent inhibitor of apamin binding from Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus venom. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10192–10197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S., Haylett D. G. Effects of apamin, quinine and neuromuscular blockers on calcium-activated potassium channels in guinea-pig hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:373–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S., Quast U., Hof R. P., Baumlin Y., Pally C. Similarities in the mechanism of action of two new vasodilator drugs: pinacidil and BRL 34915. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;11(1):90–99. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198801000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S., Weir S. W., Danzeisen M. C. Anti-vasoconstrictor effects of the K+ channel opener cromakalim on the rabbit aorta--comparison with the calcium antagonist isradipine. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):741–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Navia M. A., Reuben J. P., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grygorczyk R., Schwarz W., Passow H. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human red cells. Comparison of single-channel currents with ion fluxes. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):693–698. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84211-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggino S. E., Guggino W. B., Green N., Sacktor B. Blocking agents of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cultured medullary thick ascending limb cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C128–C137. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Erxleben C. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels in Aplysia neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):27–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Two Ca-dependent K-channels classified by the application of tetraethylammonium distribute to smooth muscle membranes of the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00582557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Subset-specific expression of potassium channels in developing murine T lymphocytes. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):771–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2448877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene from Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):749–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2441470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Kecskemethy N., Müller R., Krah-Jentgens I., Baumann A., Kiltz H. H., Canal I., Llamazares S., Ferrus A. Shaker encodes a family of putative potassium channel proteins in the nervous system of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1087–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. Leiurus quinquestriatus venom inhibits BRL 34915-induced 86Rb+ efflux from the rat portal vein. Life Sci. 1988;42(7):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U. Effect of the K+ efflux stimulating vasodilator BRL 34915 on 86Rb+ efflux and spontaneous activity in guinea-pig portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Phillips M., Miller C. Purification of charybdotoxin, a specific inhibitor of the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14607–14613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E., Black S. D., Fujita V. S., Coon M. J. Complete amino acid sequence and predicted membrane topology of phenobarbital-induced cytochrome P-450 (isozyme 2) from rabbit liver microsomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6552–6556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):837–839. doi: 10.1038/332837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia H. H., Smith J. S., Martin B. M., Coronado R., Possani L. D. Charybdotoxin and noxiustoxin, two homologous peptide inhibitors of the K+ (Ca2+) channel. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Effect of apamin on responses to BRL 34915, nicorandil and other relaxants in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


