Abstract
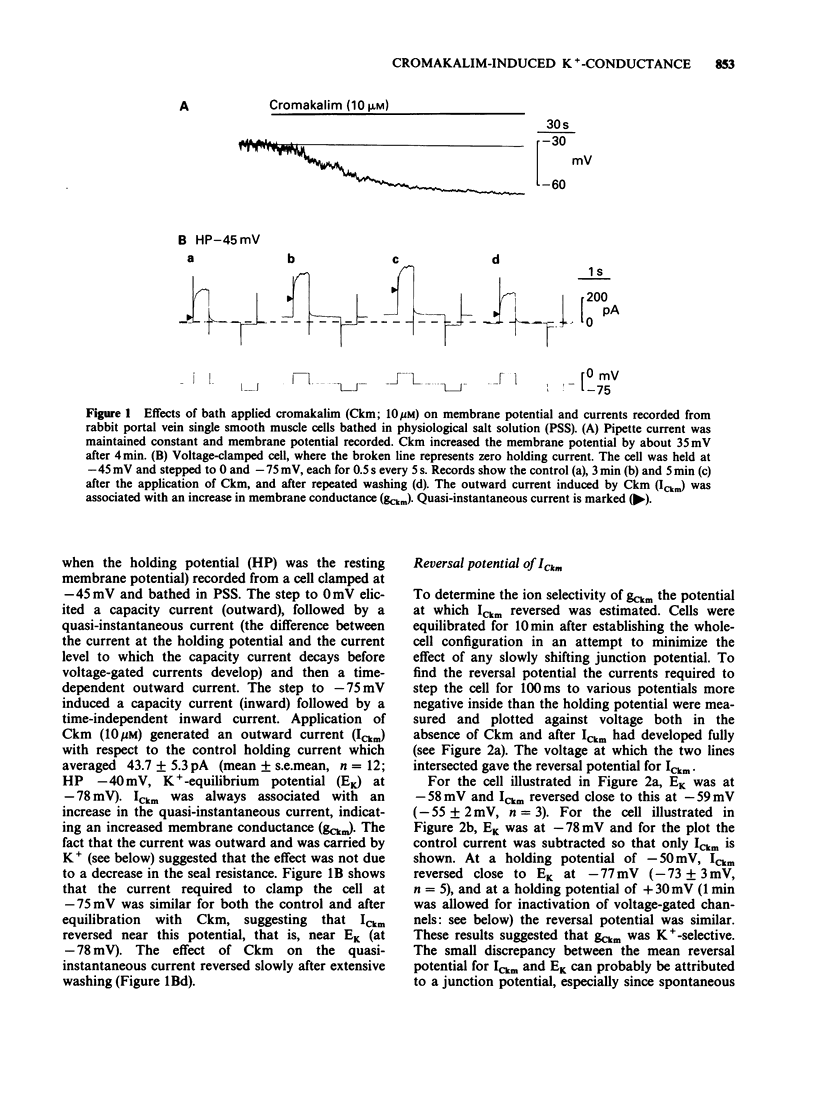
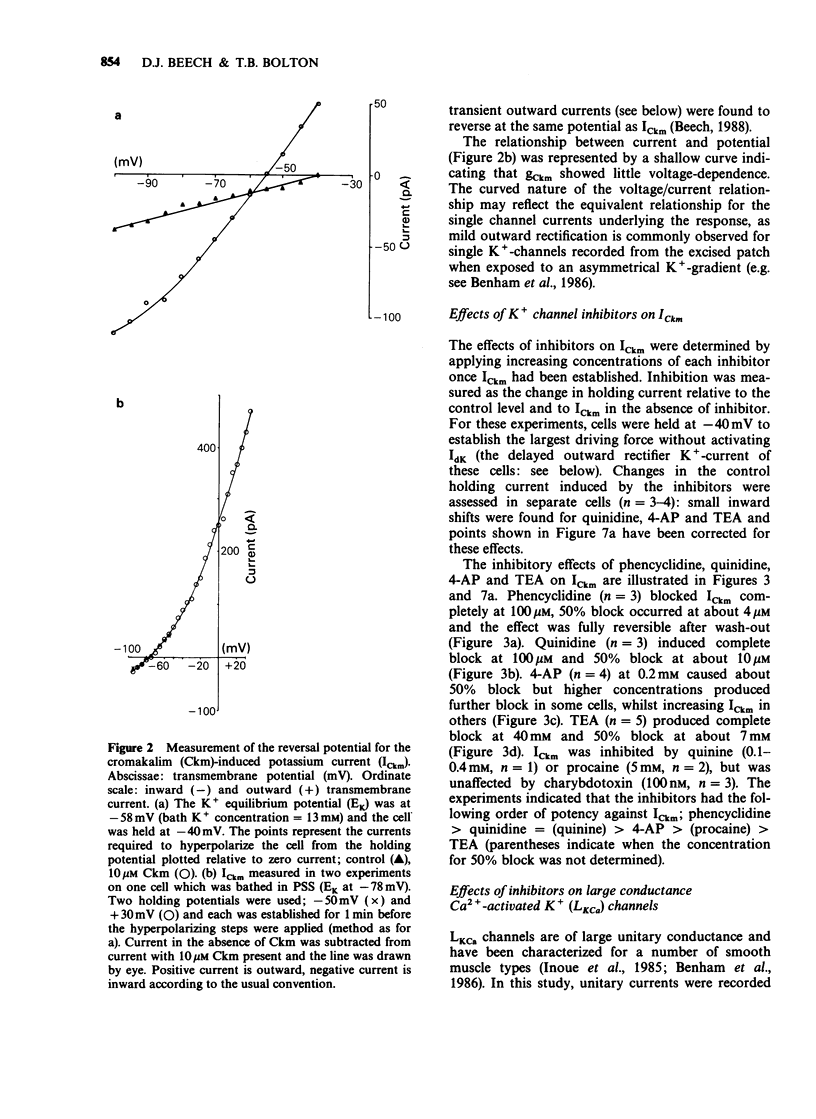
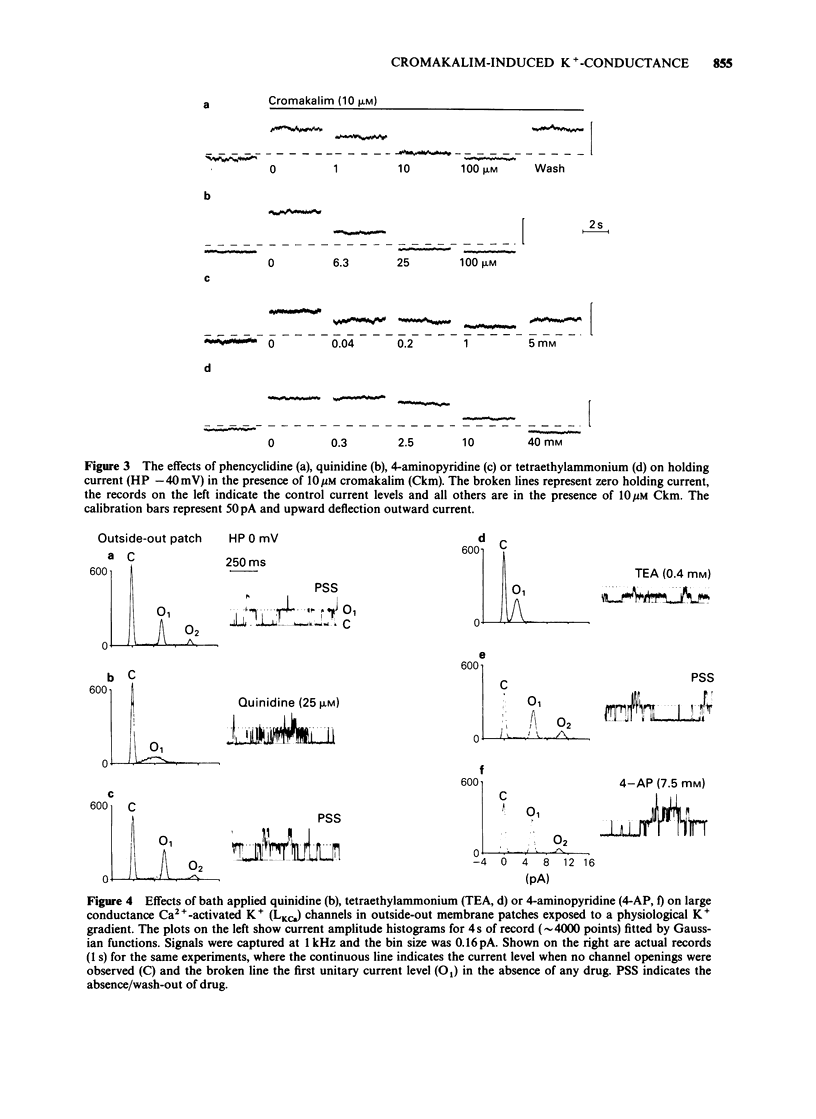
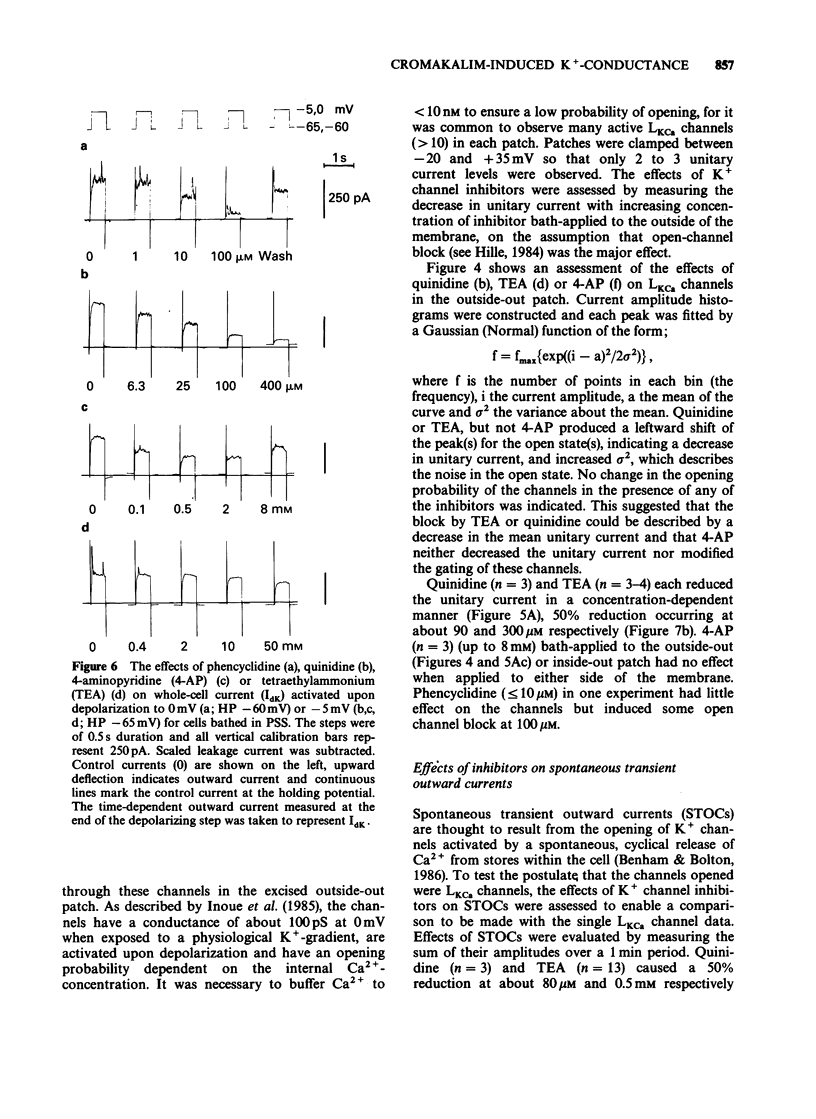
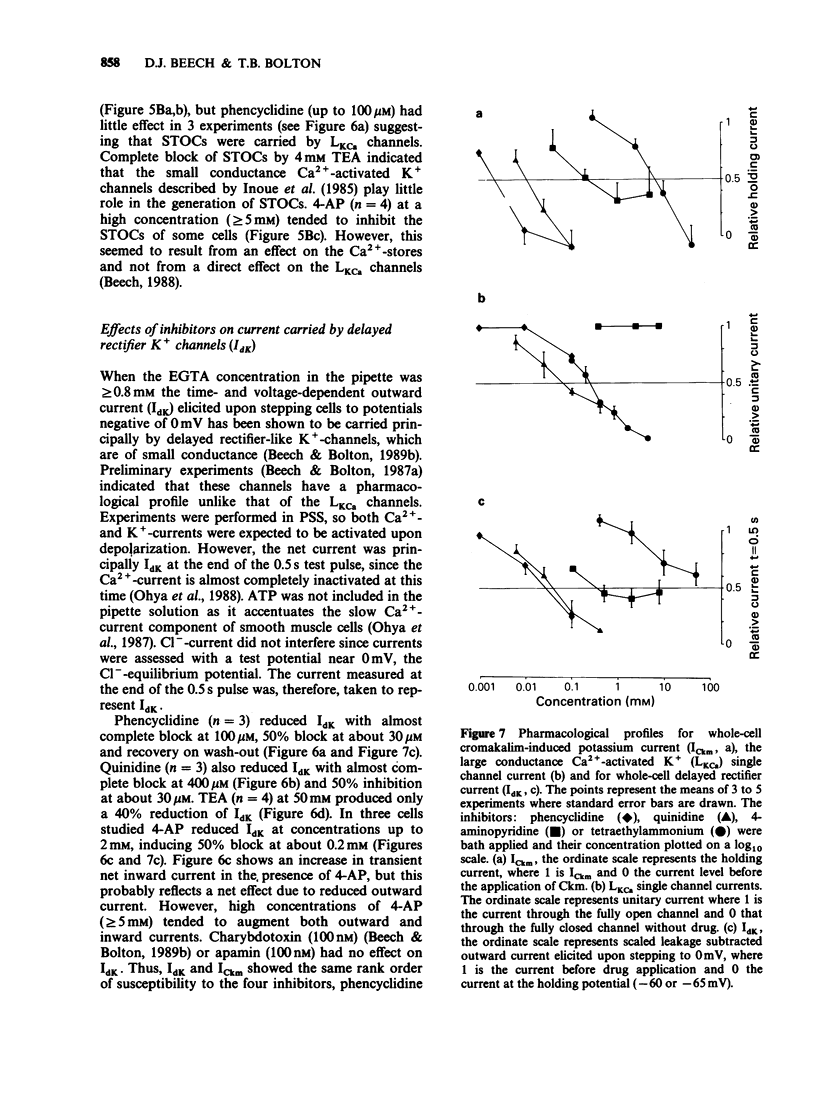
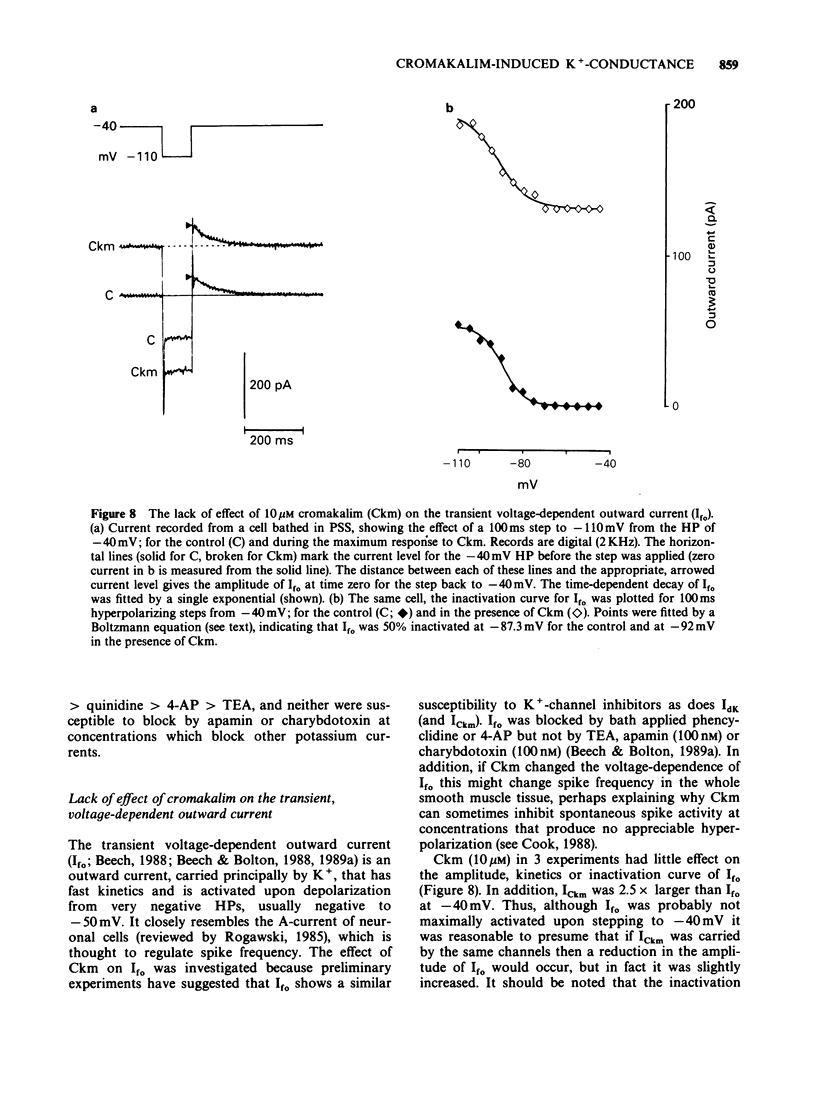
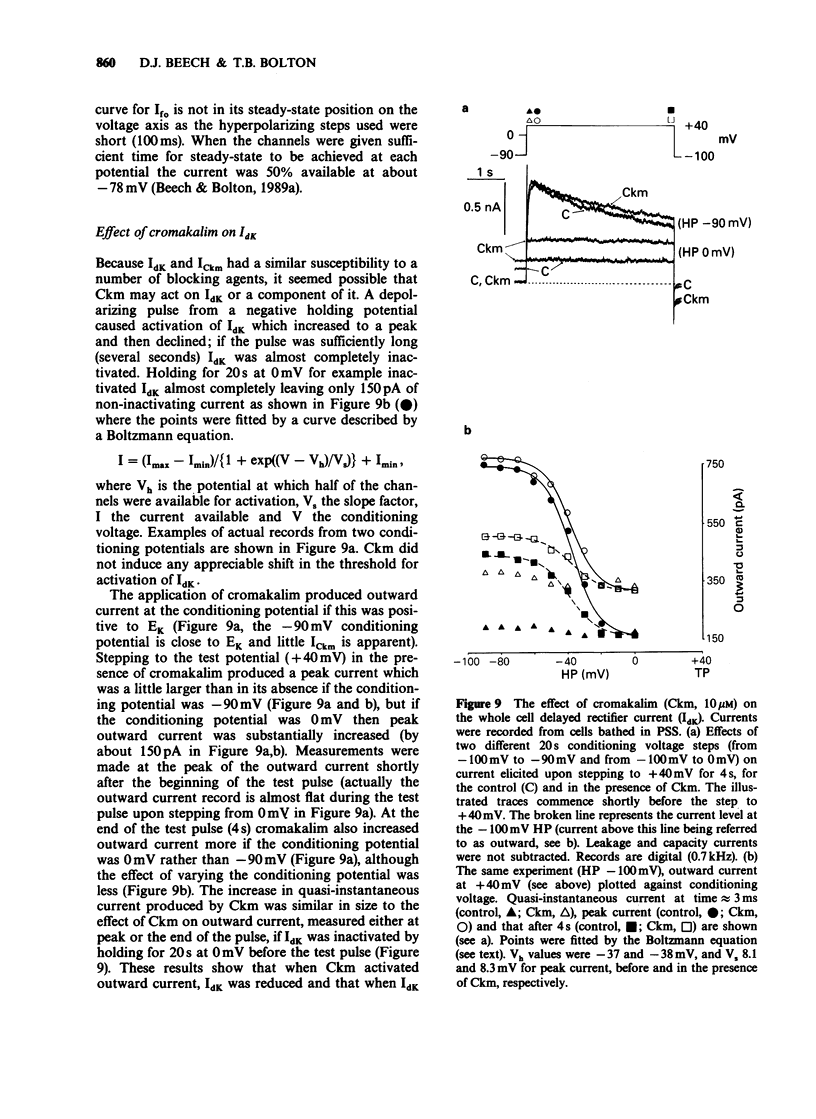
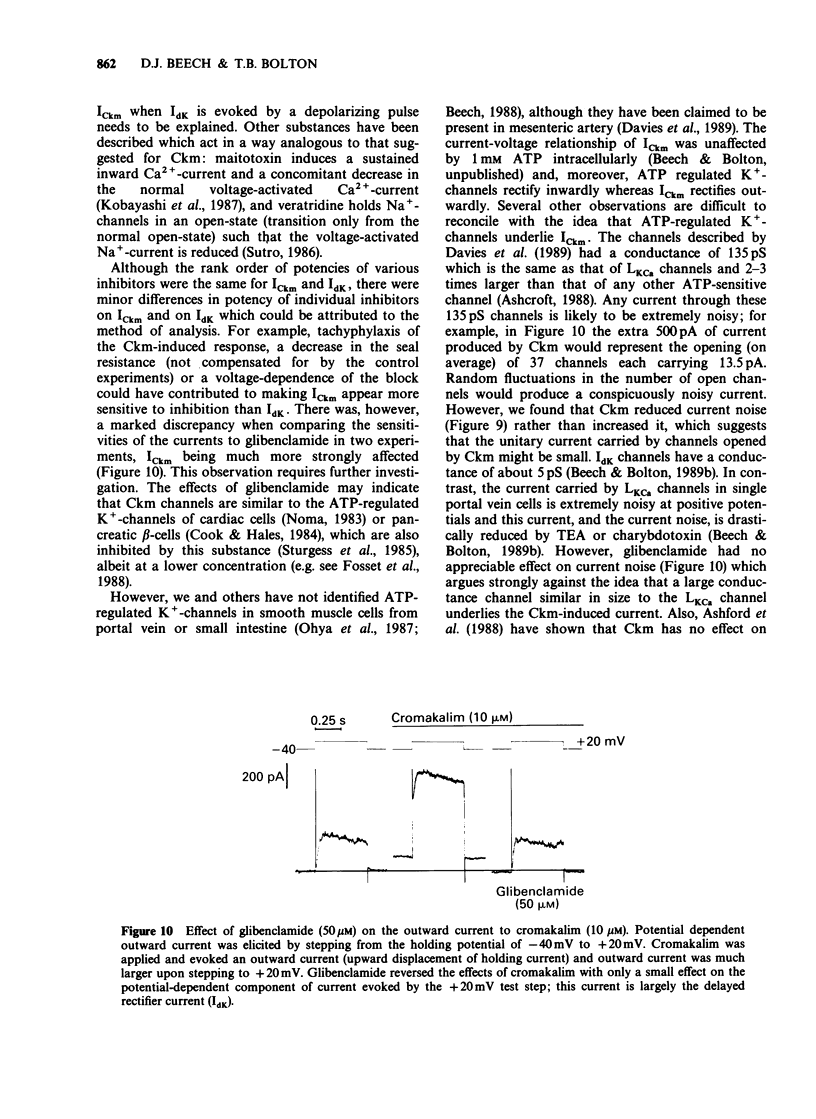
1. Single smooth muscle cells were isolated freshly from the rabbit portal vein and membrane currents were recorded by the whole-cell or excised patch configurations of the patch-clamp technique at room temperature. 2. Cromakalim (Ckm, 10 microM) induced a potassium current (ICkm) that showed no pronounced voltage-dependence and had low current noise. 3. This current, ICkm, was inhibited by (in order of potency): phencyclidine greater than quinidine greater than 4-aminopyridine greater than tetraethylammonium ions (TEA). These drugs inhibited the delayed rectifier current, IdK, which is activated by depolarization of the cell, with the same order of potency. 4. Large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (LKCa) in isolated membrane patches were blocked by (in order of potency) quinidine greater than TEA approximately phencyclidine. 4-Aminopyridine was ineffective. A similar order of potency was found for block of spontaneous transient outward currents thought to represent bursts of openings of LKCa channels. 5. The low current noise of ICkm at positive potentials, and its susceptibility to inhibitors indicated that it was not carried by LKCa channels, and that it may be carried by channels which underlie IdK. It was observed that when ICkm was activated, IdK was reduced. However, in two experiments, ICkm was much more susceptible to glibenclamide than IdK; possible reasons for this are discussed.
Full text
PDF

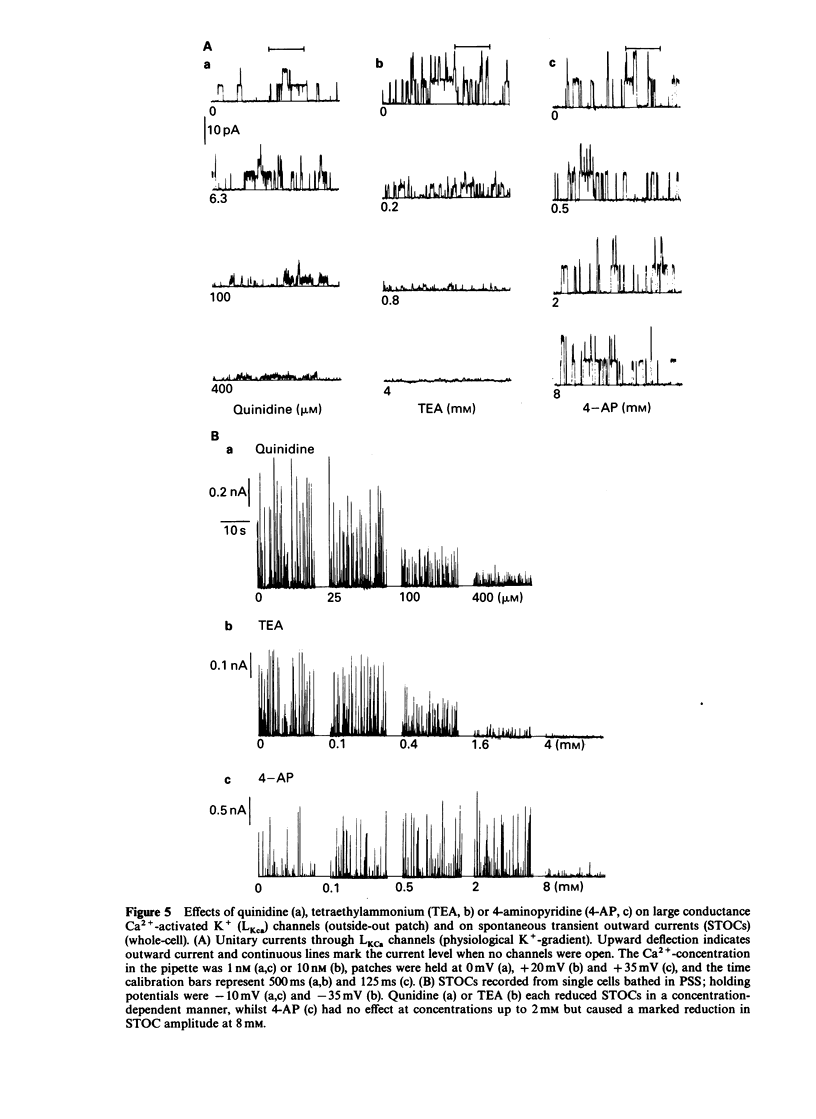



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen S. L., Boyle J. P., Cortijo J., Foster R. W., Morgan G. P., Small R. C. Electrical and mechanical effects of BRL34915 in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):395–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer C., ten Bruggencate G. Actions of BRL 34915 (Cromakalim) upon convulsive discharges in guinea pig hippocampal slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;337(4):429–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00169535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. A voltage-dependent outward current with fast kinetics in single smooth muscle cells isolated from rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:397–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. The effects of tetraethylammonium ions, 4-aminopyridine or quinidine on K+-currents in single smooth muscle cells of the rabbit portal vein. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1987;46(8-9):S673–S676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. Calcium-activated potassium channels in single smooth muscle cells of rabbit jejunum and guinea-pig mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:45–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Patch-clamp studies of slow potential-sensitive potassium channels in longitudinal smooth muscle cells of rabbit jejunum. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:469–486. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle N. A., Strong P. N. Identification of two toxins from scorpion (Leiurus quinquestriatus) venom which block distinct classes of calcium-activated potassium channel. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coldwell M. C., Howlett D. R. Specificity of action of the novel antihypertensive agent, BRL 34915, as a potassium channel activator. Comparison with nicorandil. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 1;36(21):3663–3669. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., De Weille J. R., Green R. D., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas control action potential properties in heart cells via high affinity receptors that are linked to ATP-dependent K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7933–7936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Two Ca-dependent K-channels classified by the application of tetraethylammonium distribute to smooth muscle membranes of the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00582557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Okabe K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. A newly identified Ca2+ dependent K+ channel in the smooth muscle membrane of single cells dispersed from the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):138–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00586674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ochi R., Ohizumi Y. Maitotoxin-activated single calcium channels in guinea-pig cardiac cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):665–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Modulation of ionic currents in smooth muscle balls of the rabbit intestine by intracellularly perfused ATP and cyclic AMP. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00585070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Regulation of calcium current by intracellular calcium in smooth muscle cells of rabbit portal vein. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):375–383. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieder W. Modification of K+ conductance of heart cell membrane by BRL 34915. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;337(1):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00169483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U. Effect of the K+ efflux stimulating vasodilator BRL 34915 on 86Rb+ efflux and spontaneous activity in guinea-pig portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr Cholinergic agonists suppress a potassium current in freshly dissociated smooth muscle cells of the toad. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:503–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Ashford M. L., Cook D. L., Hales C. N. The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):474–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutro J. B. Kinetics of veratridine action on Na channels of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):1–24. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Effect of apamin on responses to BRL 34915, nicorandil and other relaxants in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



