Abstract
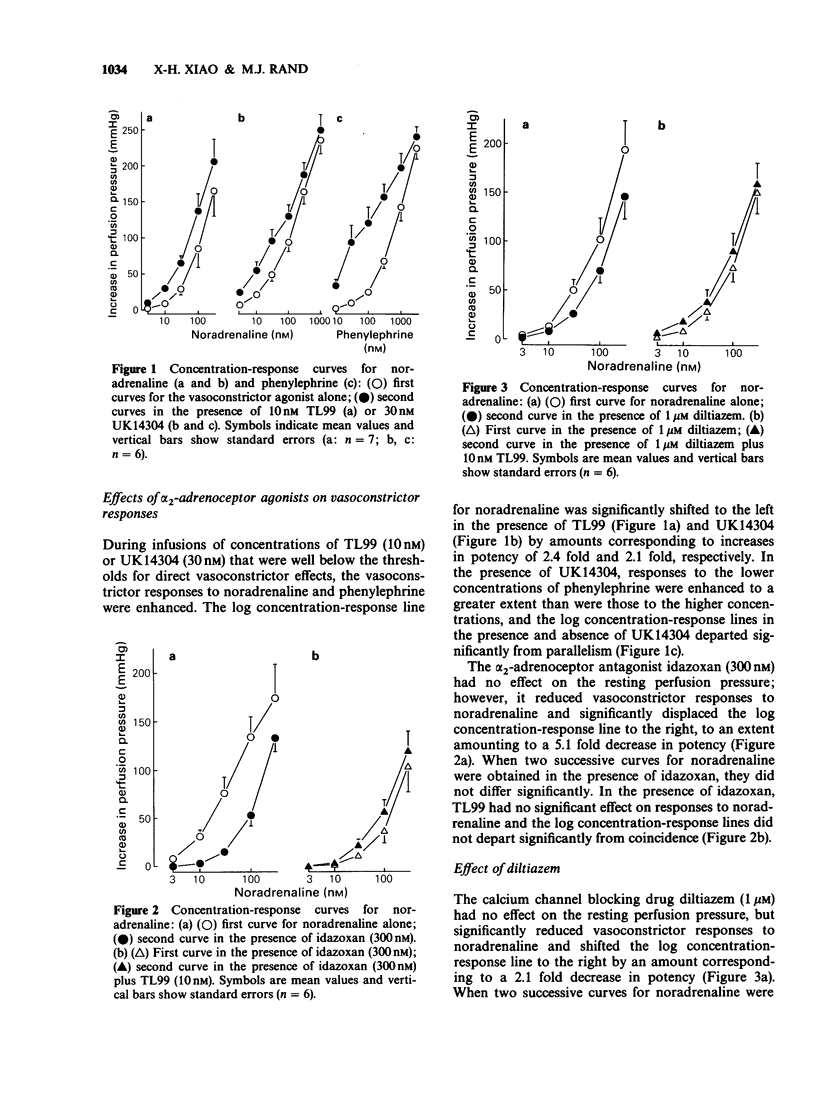
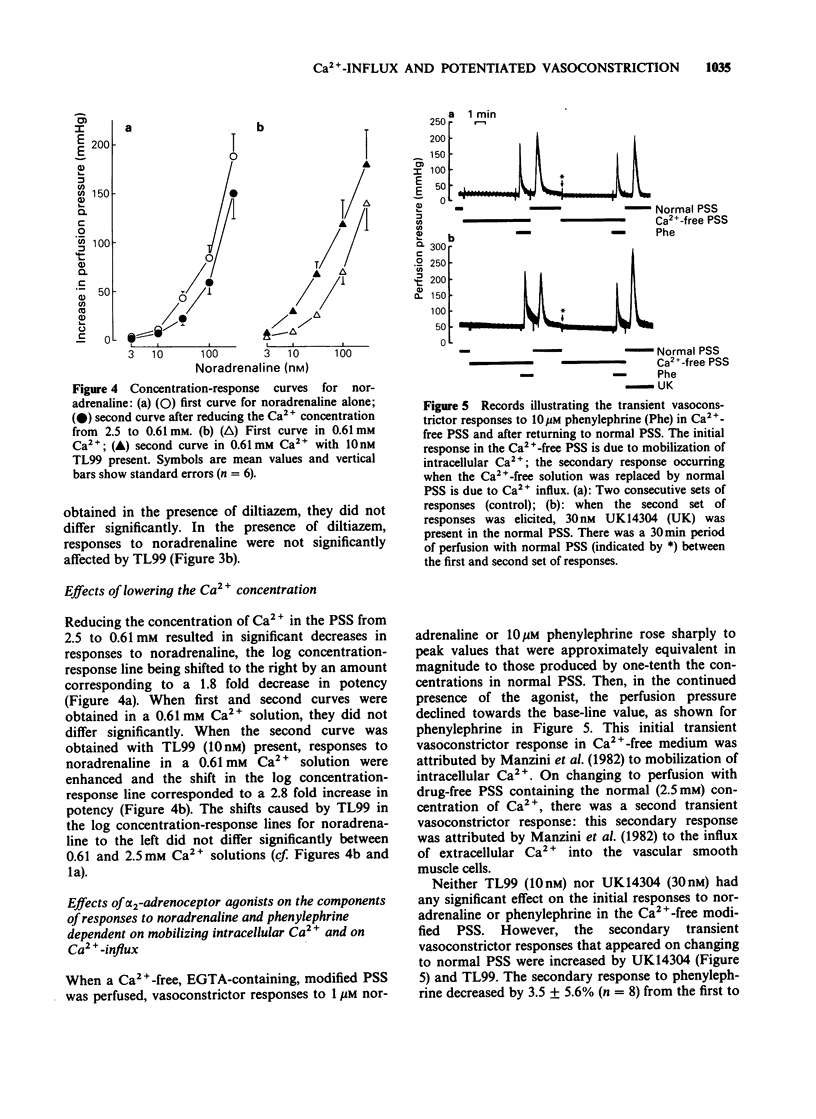
1. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists TL99 (2-(N N-dimethyl)amino-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) and UK14304 (5-bromo-6-[2-imidazoline-2-yl-aminol]-quinoxaline), in concentrations that are less than 1% of those producing vasoconstriction, enhance vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline and phenylephrine in isolated perfused preparations of the rat tail artery. 2. The enhancing effect was abolished when Ca2+ was absent and by the calcium channel blocking drug diltiazem. 3. alpha 2-Adrenoceptor agonists had no effect on the component of the responses to noradrenaline and phenylephrine that is attributable to mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, but enhanced the component attributable to influx of extracellular Ca2+. 4. These results suggest that the enhancing effect of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists on responses of the rat tail artery to alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonists involves an increase in Ca2+-influx into smooth muscle cells through Ca2+ channels that are opened when alpha 2-adrenoceptors are activated.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Matsuki N., Kasuya Y. Pharmacological and electrophysiological discrimination of contractile responses to selective alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in rat tail artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;45(2):249–261. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor binding and contraction of rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):678–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D. UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterisation of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Droogmans G. Exchange characteristics of the noradrenaline-sensitive calcium store in vascular smooth muscle cells or rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:263–279. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. J., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. Pharmacological analysis of postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors mediating contractions to (-)-noradrenaline in the rabbit isolated lateral saphenous vein can be explained by interacting responses to simultaneous activation of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):485–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dashwood M., Jacobs M. Autoradiographic study of the alpha-adrenoceptors of rat aorta and tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 10;115(1):129–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90597-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant J. A., Scrutton M. C. Interaction of selective alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists with human and rabbit blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(1):121–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks P. E., Cannon J. G. Cardiovascular effects of 2-(NN-dimethyl)amino-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4 tetrahydronaphthalene in pithed rats: differential antagonism by yohimbine and prazosin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;32(11):786–788. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb13068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks P. E., Tierney C., Langer S. Z. Preferential antagonism by diltiazem of alpha 2-adrenoceptor mediated vasoconstrictor responses in perfused tail arteries of spontaneous hypertensive rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):388–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00692906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jim K. F., Matthews W. D. Role of extracellular calcium in contractions produced by activation of postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the canine saphenous vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jul;234(1):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Maggi C. A., Meli A. A simple procedure for assessing norepinephrine-induced cellular and extracellular Ca++ mobilization in rabbit ear artery. J Pharmacol Methods. 1982 Aug;8(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(82)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medgett I. C., Langer S. Z. Heterogeneity of smooth muscle alpha adrenoceptors in rat tail artery in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jun;229(3):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medgett I. C., Rajanayagam M. A. Effects of reduced calcium ion concentration and of diltiazem on vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline and sympathetic nerve stimulation in rat isolated tail artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;83(4):889–898. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan A. G., Medgett I. C., Story D. F. Involvement of Ca2+ mobilization in the amplifying effect of serotonin on responses of rabbit isolated ear artery to exogenous noradrenaline. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):500–503. doi: 10.1007/BF00182722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri A., Barakeh J. F., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Reserpine-induced postjunctional supersensitivity in rat vas deferens and caudal artery without changes in alpha adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Aug;234(2):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajanayagam M. A., Medgett I. C. Greater activation of smooth muscle alpha-2 adrenoceptors by epinephrine in distal than in proximal segments of rat tail artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):989–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümann H. J., Lues I. Postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in the isolated saphenous vein of the rabbit. Characterization and influence of angiotensin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;323(4):328–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00512471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepperson N. B. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists potentiate responses mediated by alpha 1-adrenoceptors in the cat nictitating membrane. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):463–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. M., Swamy V. C., Triggle D. J. Postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor characterization and Ca2+ channel antagonist and activator actions in rat tail arteries from normotensive and hypertensive animals. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;64(7):909–921. doi: 10.1139/y86-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulpizio A., Hieble J. P. Demonstration of alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated contraction in the isolated canine saphenous artery treated with Bay K 8644. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 3;135(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Mathy M. J., Thoolen M. J., de Jonge A., Wilffert B., van Zwieten P. A. Invariable susceptibility to blockade by nifedipine of vasoconstriction to various alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in pithed rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;36(11):772–775. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meel J. C., De Jonge A., Kalkman H. O., Wilffert B., Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. Vascular smooth muscle contraction initiated by postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation is induced by an influx of extracellular calcium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 16;69(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meel J. C., de Jonge A., Kalkman H. O., Wilffert B., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Organic and inorganic calcium antagonists reduce vasoconstriction in vivo mediated by postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;316(4):288–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00501359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. J., Webb R. C., Smith C. B. Alpha-2 adrenoreceptors on arterial smooth muscle: selective labeling by [3H]clonidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):599–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao X. H., Medgett I. C., Rand M. J. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists clonidine, TL99 and DPI enhance vasoconstrictor responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation and noradrenaline in the rat tail artery preparation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1987 Nov-Dec;14(11-12):903–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao X. H., Rand M. J. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance responses to certain other vasoconstrictor agonists in the rat tail artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


