Abstract
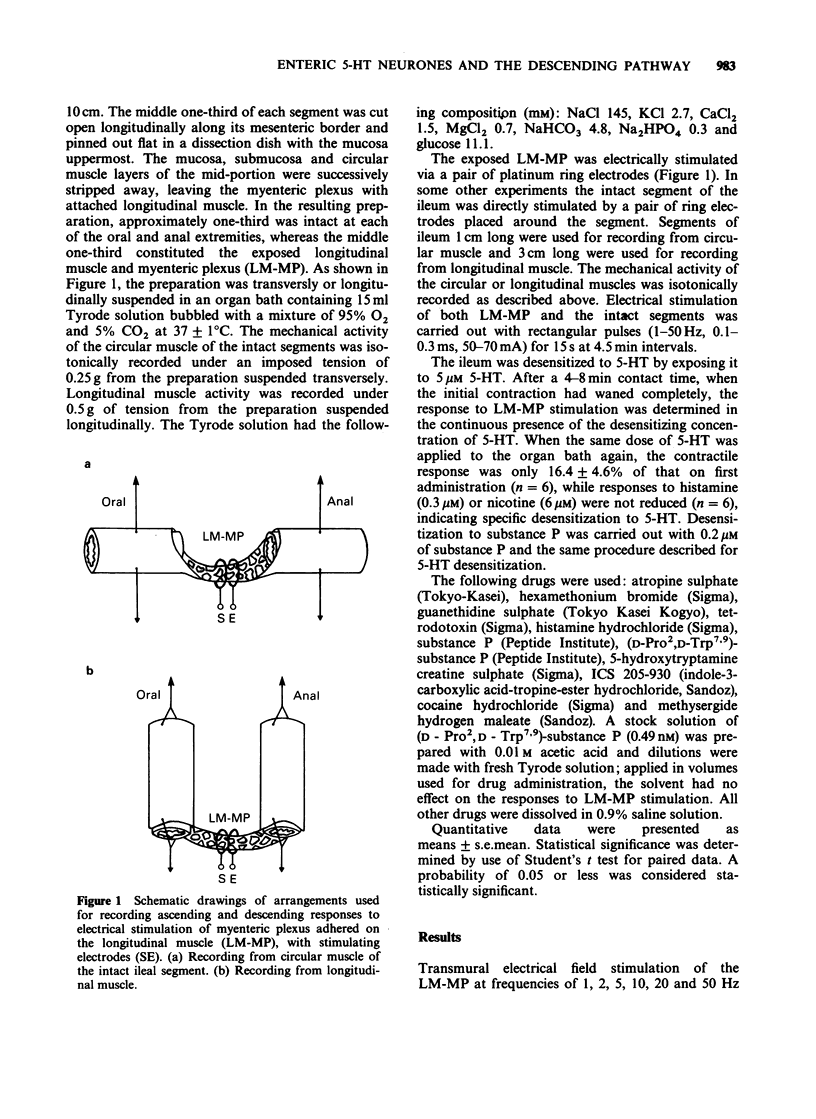
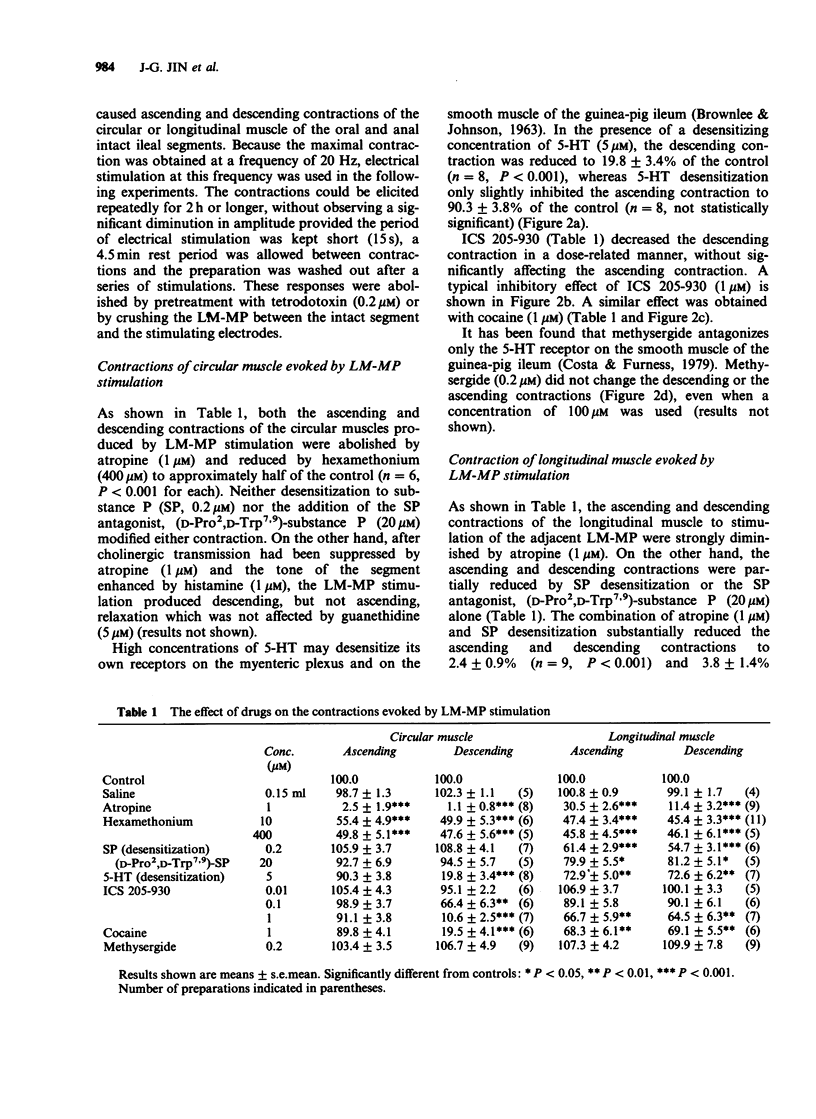
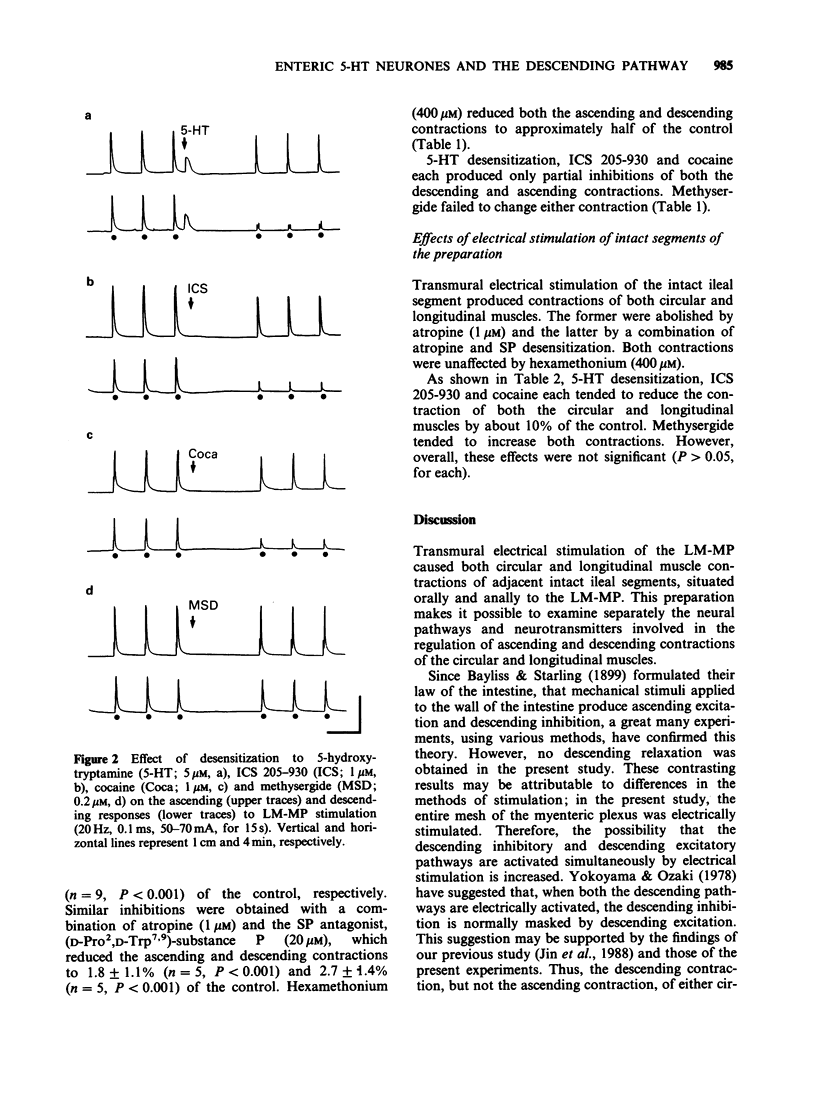
1. Participation of myenteric 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-containing neurones in the ascending and descending pathways of the guinea-pig isolated ileum was investigated in a new preparation. Transmural electrical stimulation of the longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus (LM-MP) portion of the preparation caused ascending and descending contractions of circular or longitudinal muscle in the attached, intact segments situated orally or anally to the point of stimulation. 2. All contractions of LM-MP stimulation were abolished by tetrodotoxin (0.2 microM). The ascending and descending contractions of circular muscles were also abolished by atropine and inhibited to about 50% by hexamethonium. They were not affected by desensitization to substance P (SP) or by the SP antagonist, (D-Pro2,D-Trp7,9)-substance P. The contractions of longitudinal muscles were inhibited by about 45% by hexamethonium and abolished by a combination of atropine with SP desensitization or the SP antagonist, (D-Pro2,D-Trp7,9)-substance P. 3. Desensitization to 5-HT, ICS 205-930 (1 microM) or cocaine (1 microM) reduced the descending contraction of circular muscle by 80-90%, without significantly affecting the ascending contraction. Methysergide (0.2 microM) failed to alter either contraction. 4. 5-HT desensitization, ICS 205-930 and cocaine only partially reduced the descending contraction of longitudinal muscle. A similar reduction of the ascending contraction (20-30%) was also observed. Methysergide had no effects on either contraction. 5. Contractions of either circular or longitudinal muscle produced by field stimulation of the intact segment were not significantly affected by any of the 5-HT receptor antagonists tested.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWNLEE G., JOHNSON E. S. THE SITE OF THE 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE RECEPTOR ON THE INTRAMURAL NERVOUS PLEXUS OF THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED ILEUM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Oct;21:306–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The movements and innervation of the small intestine. J Physiol. 1899 May 11;24(2):99–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1899.sp000752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Gershon M. D. 5-hydroxytryptamine participation in the vagal inhibitory innervation of the stomach. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):823–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Properties of the inhibitory potential of smooth muscle as observed in the response to field stimulation of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):299–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Cuello A. C., Verhofstad A. A., Steinbusch H. W., Elde R. P. Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: their visualization and reactions to drug treatment. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. The sites of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in nerve-muscle preparations from the guinea-pig small intestine and colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):237–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drakontides A. B., Gershon M. D. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the mouse duodenum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jul;33(3):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Cory R., Bockaert J. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erde S. M., Sherman D., Gershon M. D. Morphology and serotonergic innervation of physiologically identified cells of the guinea pig's myenteric plexus. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):617–633. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00617.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R., Mobarok Ali A. T., Newgrosh G. Blockade of serotonin receptors on autonomic neurones by (-)-cocaine and some related compounds. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov 16;59(3-4):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. Neuronal 5-HT receptors in the periphery. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12B):1473–1486. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M. Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: their projections in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., PICARELLI Z. P. Two kinds of tryptamine receptor. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):323–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSHON M. D., DRAKONTIDES A. B., ROSS L. L. SEROTONIN: SYNTHESIS AND RELEASE FROM THE MYENTERIC PLEXUS OF THE MOUSE INTESTINE. Science. 1965 Jul 9;149(3680):197–199. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3680.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D. Effects of tetrodotoxin on innervated smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Mar;29(3):259–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D. The enteric nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:227–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland S. J., Tyers M. B. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced depolarization of the rat isolated vagus nerve. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin J. G., Neya T., Takaki M. Polar innervation of enteric non-cholinergic and non-adrenergic neurons in the isolated guinea-pig ileum. Acta Med Okayama. 1988 Jun;42(3):129–136. doi: 10.18926/AMO/31027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Osa T., Toida N. Effect of tetrodotoxin on smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Aug;27(2):366–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman T. P., Ross L. L., Gershon M. D. Separately developing axonal uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine in the fetal ileum of the rabbit. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):437–456. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90360-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger G. J. Increased gut cholinergic activity and antagonism of 5-hydroxytryptamine M-receptors by BRL 24924: potential clinical importance of BRL 24924. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):77–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Slow synaptic excitation mediated by serotonin in Auerbach's plexus. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):836–837. doi: 10.1038/276836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Ozaki T. Polarity of effects of stimulation of Auerbach's plexus on longitudinal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):E345–E353. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.4.E345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


