Abstract
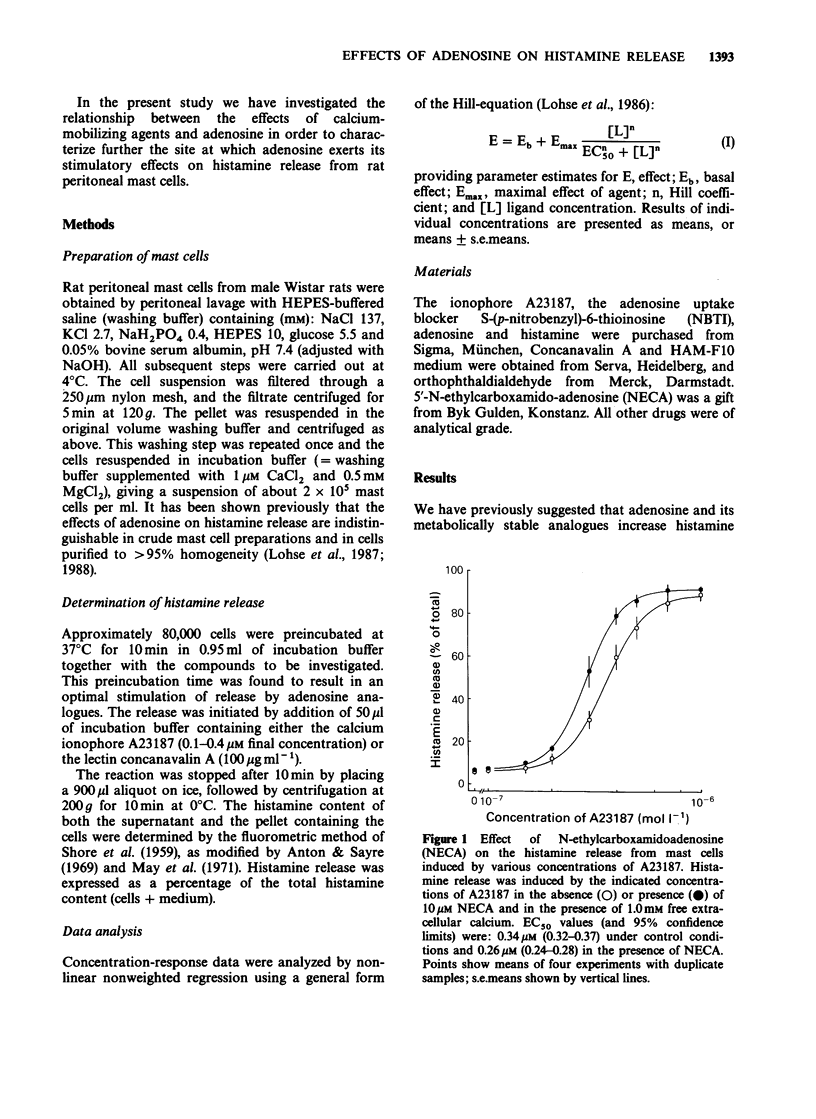
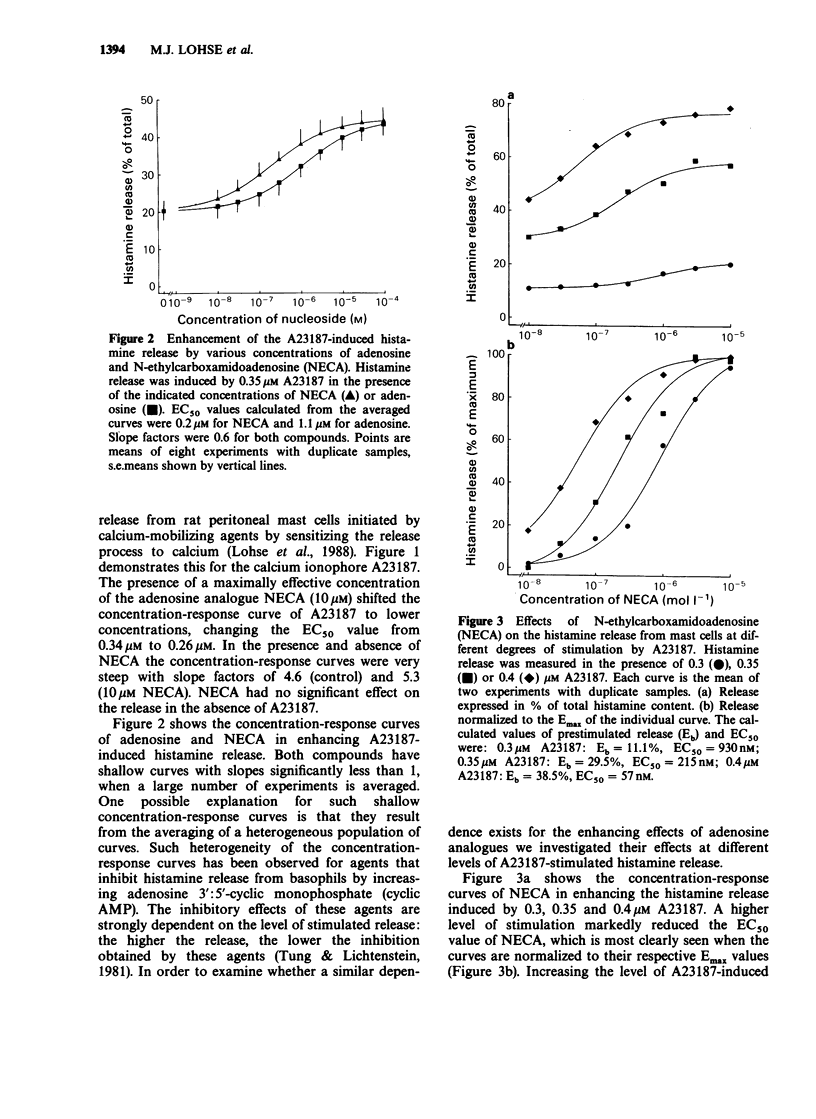
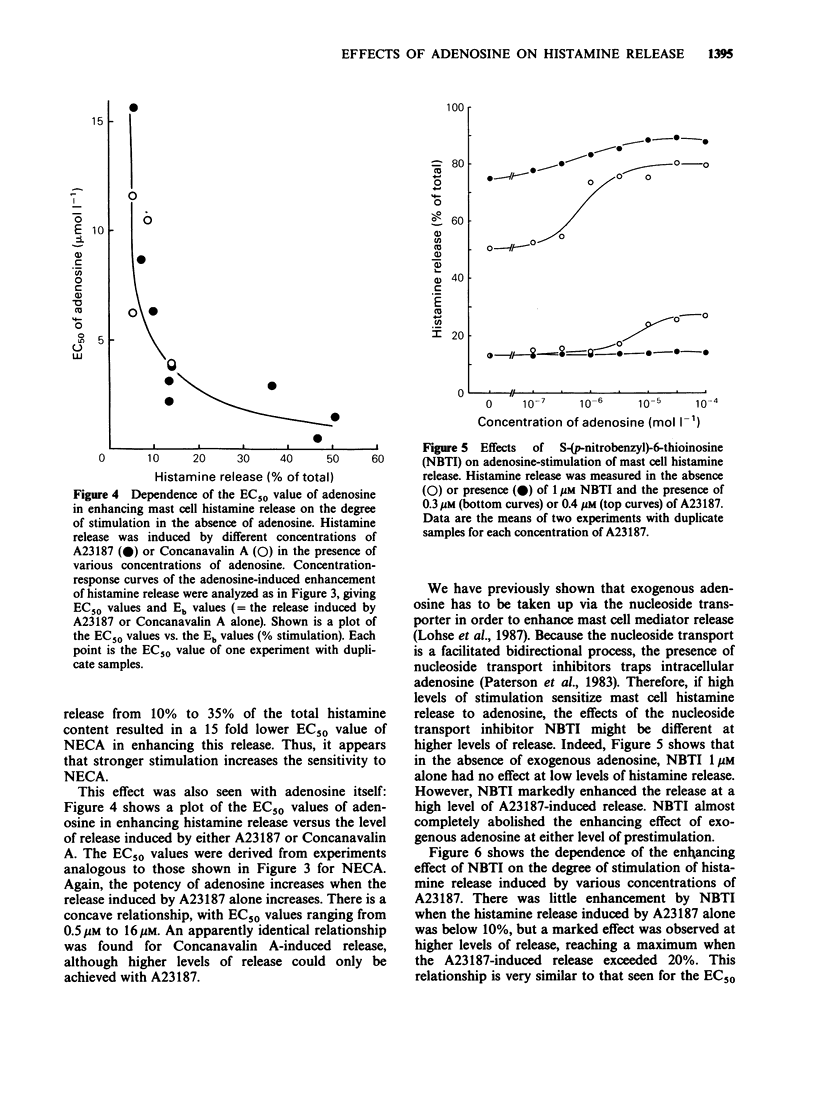
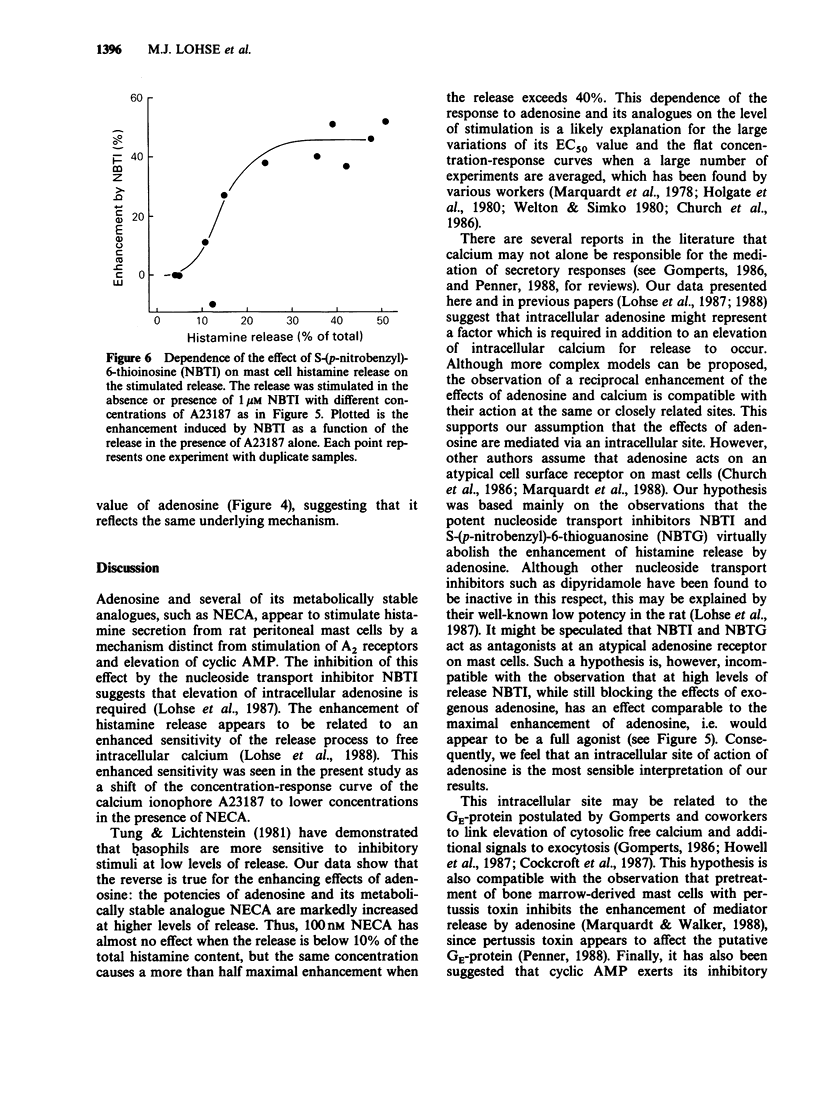
1. Adenosine and its metabolically stable analogue N-ethyl-carboxamidoadenosine (NECA) enhance histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells when these are stimulated by calcium-mobilizing agents. NECA and adenosine shift the concentration-response curve of the calcium ionophore A23187 to lower concentrations. 2. The potencies of NECA or adenosine in enhancing A23187-induced histamine release are dependent on the level of stimulated release in the absence of adenosine analogues. At high levels of release their potencies are up to 20 times higher than at low levels. Consequently, averaged concentration-response curves of adenosine and NECA for enhancing histamine release are shallow. 3. The adenosine transport blocker S-(p-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine (NBTI) has no effect by itself at low levels of stimulated histamine release, but abolishes the enhancing effect of adenosine. At high levels of release, however, NBTI alone enhances the release of histamine. 4. It is concluded that adenosine and calcium reciprocally enhance the sensitivity of the secretory processes to the effects of the other agent. The levels of intracellular adenosine obtained by trapping adenosine inside stimulated mast cells are sufficient to enhance histamine release substantially, suggesting that this effect may play a physiological and pathophysiological role.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton A. H., Sayre D. F. A modified fluorometric procedure for tissue histamine and its distribution in various animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Apr;166(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Guthrie D. F., Moore J. P., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. Synergistic signals in the mechanism of antigen-induced exocytosis in 2H3 cells: evidence for an unidentified signal required for histamine release. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1129–1136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Moore J. P., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. The calcium signal and phosphatidylinositol breakdown in 2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7137–7142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Holgate S. T., Hughes P. J. Adenosine inhibits and potentiates IgE-dependent histamine release from human basophils by an A2-receptor mediated mechanism. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):719–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Hughes P. J., Vardey C. J. Studies on the receptor mediating cyclic AMP-independent enhancement by adenosine of IgE-dependent mediator release from rat mast cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):233–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Two G-proteins act in series to control stimulus-secretion coupling in mast cells: use of neomycin to distinguish between G-proteins controlling polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2745–2750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Role of adenylate cyclase in immunologic release of mediators from rat mast cells: agonist and antagonist effects of purine- and ribose-modified adenosine analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6800–6804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Essential synergy between Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides in exocytotic secretion from permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):191–197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., Church M. K. Separate purinoceptors mediate enhancement by adenosine of concanavalin A-induced mediator release and the cyclic AMP response in rat mast cells. Agents Actions. 1986 Apr;18(1-2):81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01987989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., Holgate S. T., Church M. K. Adenosine inhibits and potentiates IgE-dependent histamine release from human lung mast cells by an A2-purinoceptor mediated mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 1;33(23):3847–3852. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoutsakos A., Pearce F. L. The effect of adenosine and its analogues on cyclic AMP changes and histamine secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells stimulated by various ligands. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1373–1379. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Salzer M. J., Schwabe U. Adenosine regulates the Ca2+ sensitivity of mast cell mediator release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8875–8879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Schwabe U. Agonist photoaffinity labeling of A1 adenosine receptors: persistent activation reveals spare receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;30(4):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Maurer K., Gensheimer H. P., Schwabe U. Dual actions of adenosine on rat peritoneal mast cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 May;335(5):555–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00169124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Gruber H. E., Wasserman S. I. Adenosine release from stimulated mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6192–6196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Parker C. W., Sullivan T. J. Potentiation of mast cell mediator release by adenosine. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):871–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Walker L. L. Alteration of mast cell responsiveness to adenosine by pertussis toxin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 15;37(20):4019–4025. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May C. D., Lyman M., Alberto R., Cheng J. Procedures for immunochemical study of histamine release from leukocytes with small volume of blood. J Allergy. 1970 Jul;46(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(70)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Almers W. Fast calcium transients in rat peritoneal mast cells are not sufficient to trigger exocytosis. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):51–53. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R. Multiple signaling pathways control stimulus-secretion coupling in rat peritoneal mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9856–9860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E. Secretory responses of rat peritoneal mast cells to high intracellular calcium. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung R. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Cyclic AMP agonist inhibition increases at low levels of histamine release from human basophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):642–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Simko B. A. Regulatory role of adenosine in antigen-induced histamine release from the lung tissue of actively sensitized guinea pigs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 15;29(8):1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Sha'afi R. Direct demonstration of increased intracellular concentration of free calcium as measured by quin-2 in stimulated rat peritoneal mast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


