Abstract
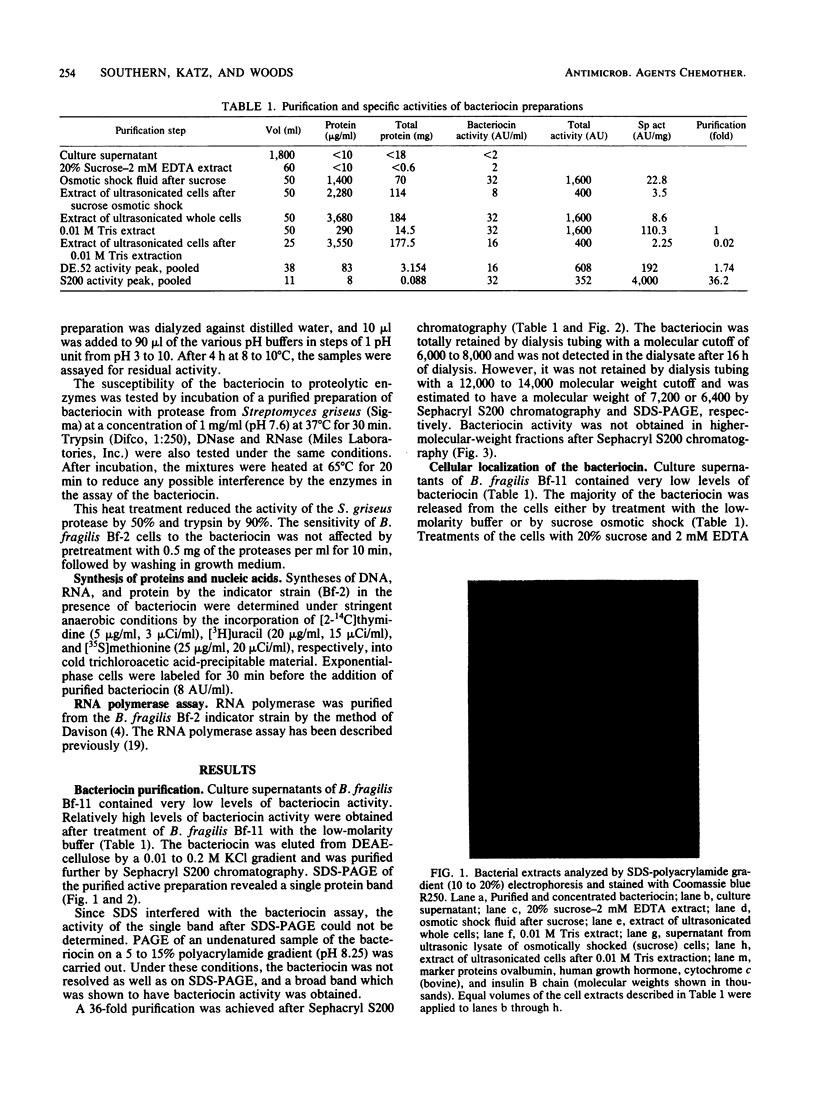
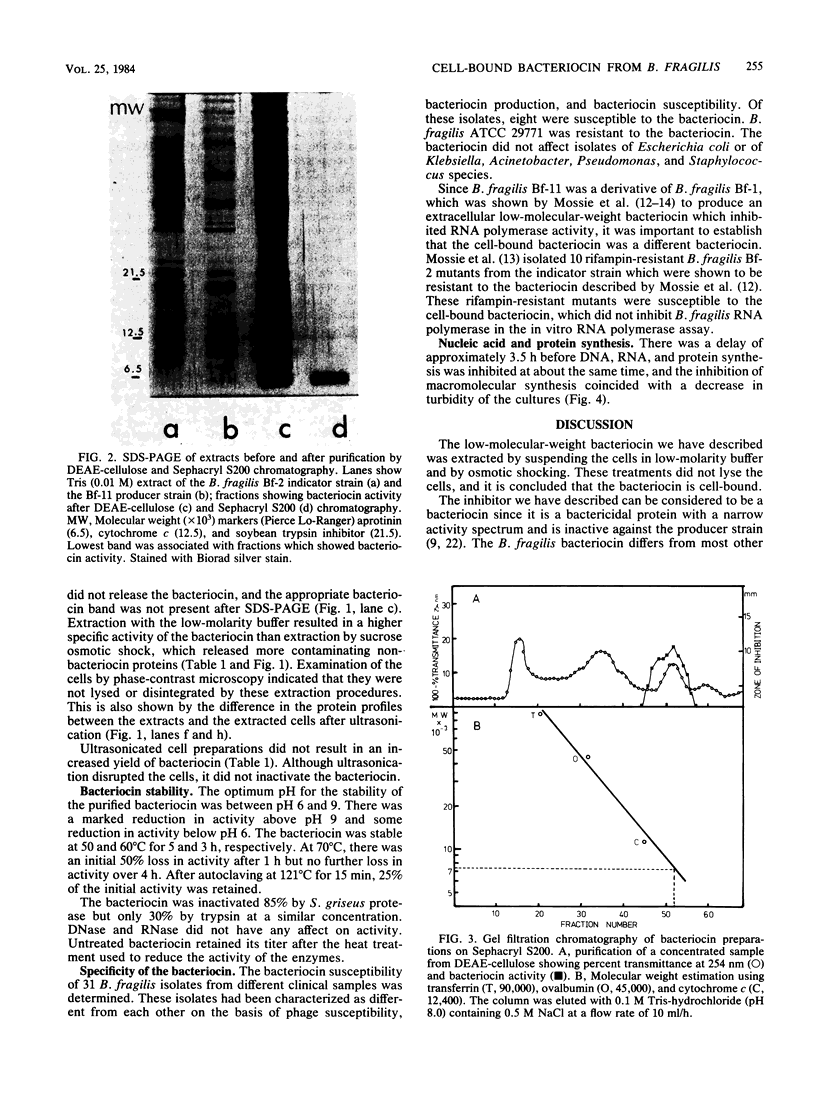
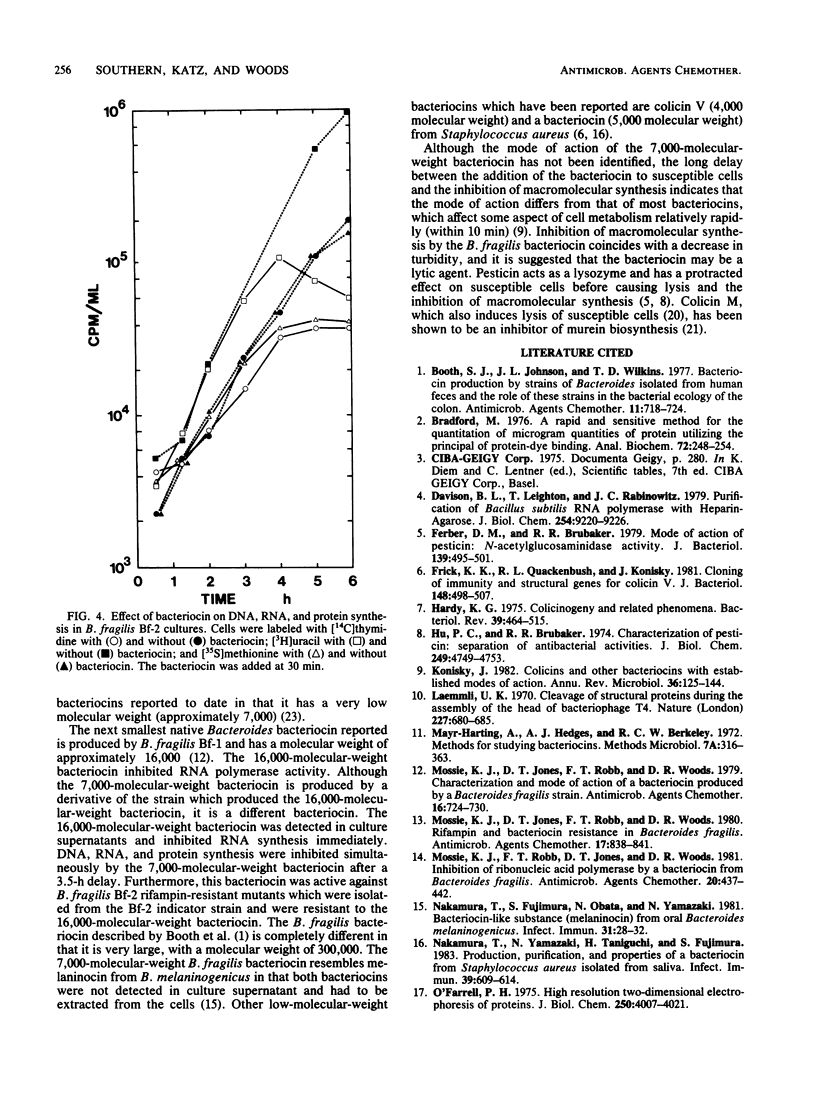
A cell-bound bacteriocin was extracted from a Bacteroides fragilis BF-11 strain by treating the cells with a low-molarity buffer (0.01 M Tris-hydrochloride, pH 8.0). Sucrose osmotic shock experiments and ultrasonic lysis of whole cells indicated that the majority of the bacteriocin was located at the cell surface. Culture supernatants contained no significant bacteriocin activity. The bacteriocin was purified by DEAE-cellulose and Sephacryl S200 chromatography and had an apparent molecular weight of approximately 7,000. It was relatively heat stable and was inactivated by proteases. There was a delay of approximately 3.5 h before DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis were inhibited by the bacteriocin. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis coincided with lysis of the susceptible indicator strain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschlimann A., Freyvogel T., Geigy R. Jean-G. Baer (1902-1975) Acta Trop. 1975;32(4):279–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth S. J., Johnson J. L., Wilkins T. D. Bacteriocin production by strains of Bacteroides isolated from human feces and the role of these strains in the bacterial ecology of the colon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):718–724. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Mode of action of pesticin: N-acetylglucosaminidase activity. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):495–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.495-501.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick K. K., Quackenbush R. L., Konisky J. Cloning of immunity and structural genes for colicin V. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):498–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.498-507.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G. Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):464–515. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.464-515.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Brubaker R. R. Characterization of pesticin. Separation of antibacterial activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4749–4753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossie K. G., Jones D. T., Robb F. T., Woods D. R. Characterization and mode of action of a bacteriocin produced by a Bacteroides fragilis strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):724–730. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossie K. G., Jones D. T., Robb F. T., Woods D. R. Rifampin and bacteriocin resistance in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):838–841. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossie K. G., Robb F. T., Jones D. T., Woods D. R. Inhibition of ribonucleic acid polymerase by a bacteriocin from Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):437–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Fujimura S., Obata N., Yamazaki N. Bacteriocin-like substance (melaninocin) from oral Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.28-32.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yamazaki N., Taniguchi H., Fujimura S. Production, purification, and properties of a bacteriocin from Staphylococcus aureus isolated from saliva. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.609-614.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., Emslie-Smith A. H., Senior B. W. Agar diffusion method for the assay of colicins. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1468–1474. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1468-1474.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb S. M., Woods D. R., Robb F. T., Struthers J. K. Rifampicin-resistant mutant supporting bacteriophage growth on stationary phase Achromobacter cells. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):117–123. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K., Dreher R., Braun V. Structural and functional properties of colicin M. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):54–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.54-63.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K., Höltje J. V., Braun V. Colicin M is an inhibitor of murein biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):994–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.994-1000.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P. Nutritional features of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.251-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]