Abstract
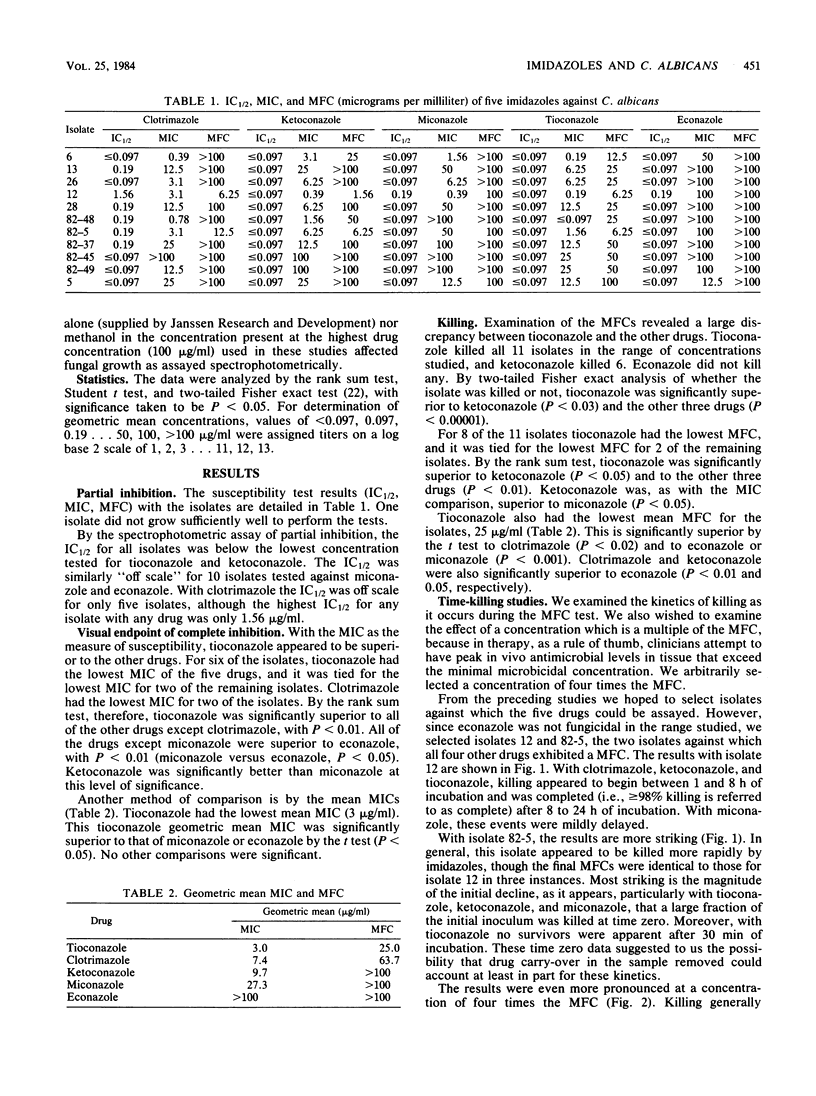
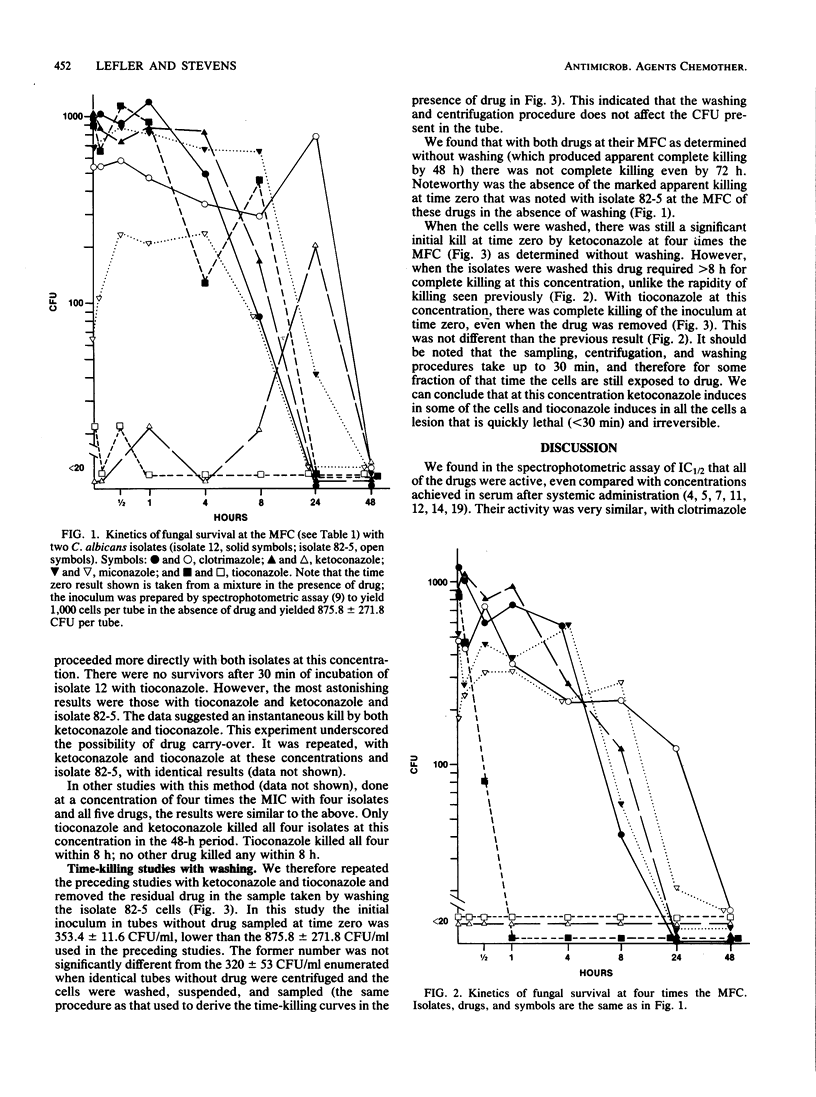
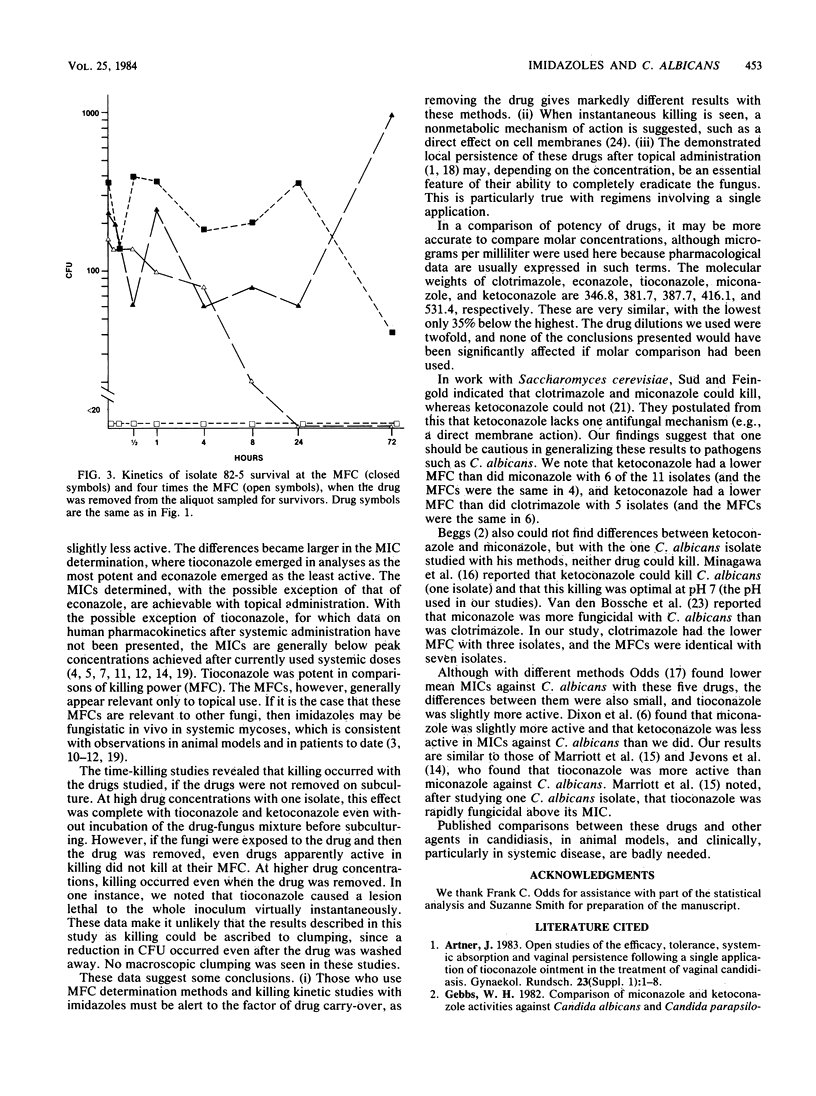
Five imidazoles (clotrimazole, econazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, and tioconazole) in clinical use were compared for their ability to inhibit and kill Candida albicans. Eleven isolates were obtained from patients before therapy. By spectrophotometric determination of 50% growth inhibition, all isolates were inhibited at low concentrations, with clotrimazole slightly less active than the other four drugs. By the conventional MIC determination, tioconazole was more active than all of the others (P less than 0.01) except clotrimazole. In killing (minimum fungicidal concentration [MFC] assay), tioconazole was the most active by several analyses. Studies of the kinetics of killing indicated that the drugs studied could kill under conditions used for the MFC determination and that tioconazole and ketoconazole could kill particularly rapidly. If the drug was washed from the cells before subculturing, concentrations above the MFC were required to kill, but tioconazole could produce a lethal lesion in all cells virtually instantaneously. These findings are pertinent to MFC and killing kinetics methodology and to the observation of drug persistence after topical application. The results differ from some previous in vitro comparisons made with different methods. They are relevant to conclusions about drug mechanisms based on their abilities to inhibit and to kill, and they underscore the need to study various assay methods and fungal species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. E. Clotrimazole: new drug for systemic mycoses? Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):653–654. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass C., Galgiani J. N., Blaschke T. F., Defelice R., O'Reilly R. A., Stevens D. A. Disposition of ketoconazole, an oral antifungal, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):151–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. A., Bodey G. P. Clotrimazole (Bay b 5097): in vitro and clinical pharmacological studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon D., Shadomy S., Shadomy H. J., Espinel-Ingroff A., Kerkering T. M. Comparison of the in vitro antifungal activities of miconazole and a new imidazole, R41,400. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):245–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhet E., Dupont B. Preliminary studies on the pharmacology and therapeutic activity of oral and intravenous econazole. Mykosen Suppl. 1978;1:192–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Stevens D. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of yeasts: a turbidimetric technique independent of inoculum size. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):721–728. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heel R. C., Brogden R. N., Carmine A., Morley P. A., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Ketoconazole: a review of its therapeutic efficacy in superficial and systemic fungal infections. Drugs. 1982 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):1–36. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198223010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heel R. C., Brogden R. N., Pakes G. E., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Miconazole: a preliminary review of its therapeutic efficacy in systemic fungal infections. Drugs. 1980 Jan;19(1):7–30. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198019010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Finn P. D. Obfuscation of the activity of antifungal antimicrobics by culture media. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):353–361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevons S., Gymer G. E., Brammer K. W., Cox D. A., Leeming M. R. Antifungal activity of tioconazole (UK-20,349), a new imidazole derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):597–602. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa H., Kitaura K., Nakamizo N. Effects of pH on the activity of ketoconazole against Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):105–107. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., MacDonald F. Persistence of miconazole in vaginal secretions after single applications. Implications for the treatment of vaginal candidosis. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Dec;57(6):400–401. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.6.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. A., Levine H. B., Deresinski S. C. Miconazole in coccidiodomycosis. II. Therapeutic and pharmacologic studies in man. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller R. L., Bennett J. E., Scholer H. J., Wall M., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility to 5-fluorocytosine and prevalence of serotype in 402 Candida albicans isolates from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):482–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Heterogeneity of action of mechanisms among antimycotic imidazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):71–74. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Van Cutsem J. M. The action of miconazole of the growth of Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Mar;13(Pt 1):63–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H. Antagonistic action of lipid components of membranes from Candida albicans and various other lipids on two imidazole antimycotics, clotrimazole and miconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jul;12(1):16–25. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


