Abstract
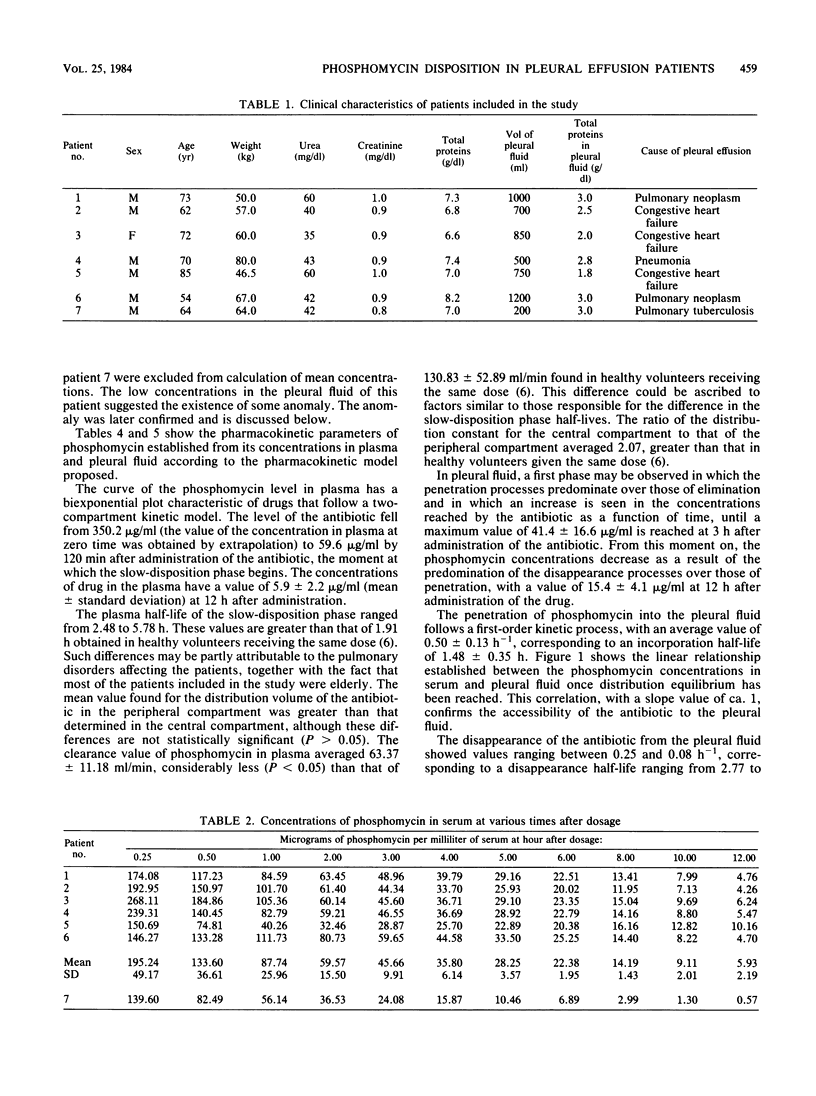
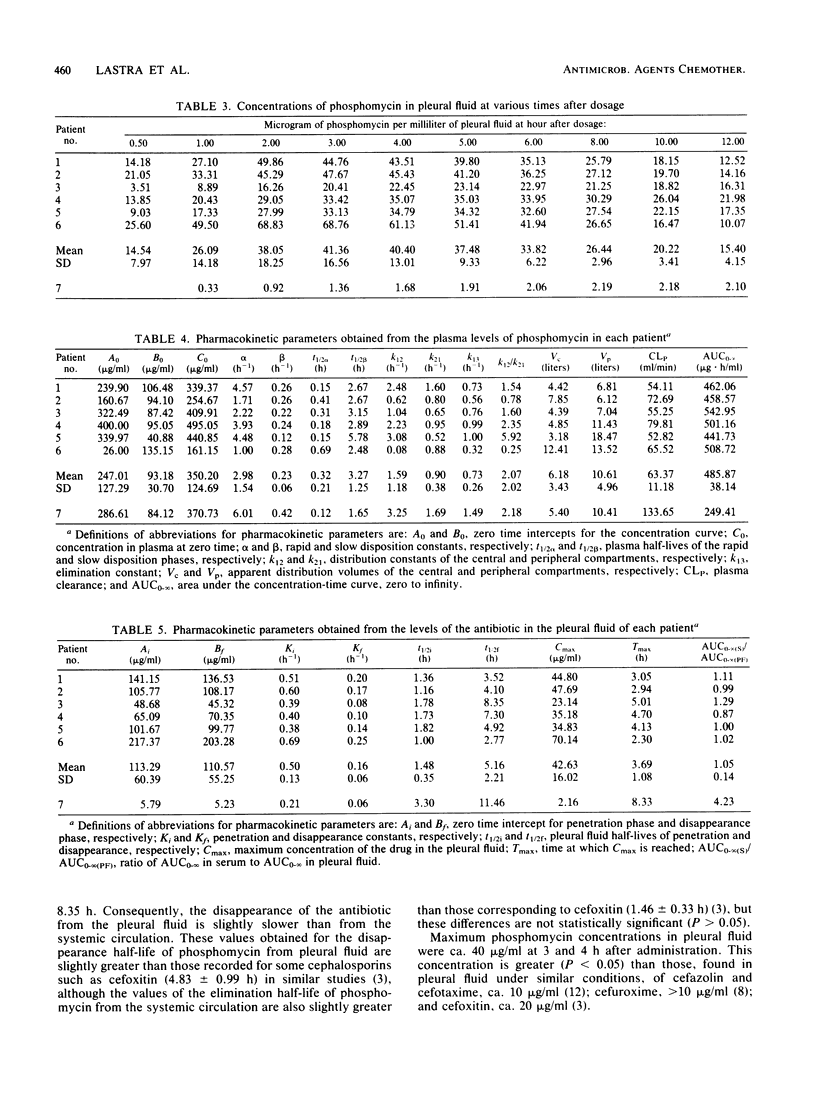
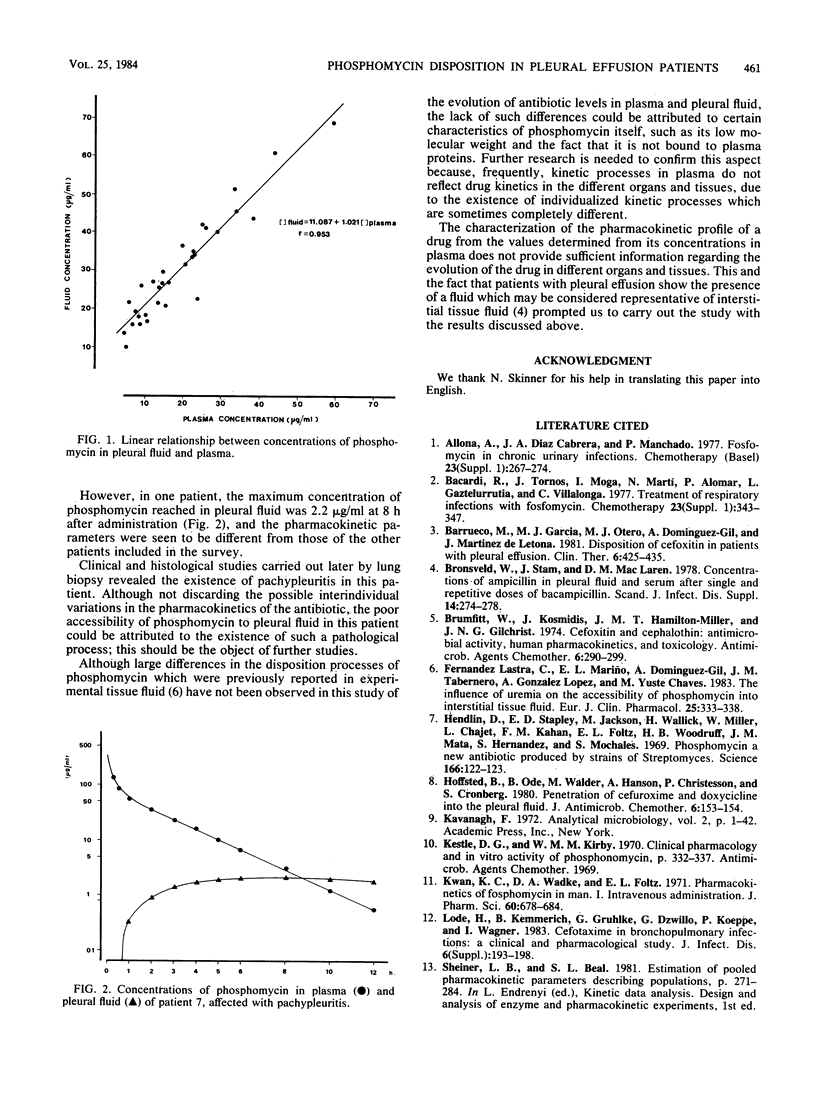
The pharmacokinetics of phosphomycin were studied in seven patients with pleural effusion of varied etiologies. All patients received a single intravenous bolus of 30 mg of antibiotic per kg. Phosphomycin levels in plasma and pleural fluid were determined simultaneously. Antibiotic levels in plasma followed a two-compartment open kinetic model. In the pleural fluid, maximum concentrations of phosphomycin, 42.63 +/- 16.03 micrograms/ml (mean +/- standard deviation), were reached at 3.69 +/- 1.08 h after administration of the antibiotic. The disappearance constant of the antibiotic from the pleural fluid was significantly smaller (0.16 +/- 0.06 h-1) than the elimination constant determined from the levels of drug in plasma (0.73 +/- 0.26 h-1). Phosphomycin persisted in antibacterial concentrations in the pleural fluid for a considerable period of time. The low accessibility of phosphomycin observed in one of the patients in the study, with a maximum concentration value of 2.16 micrograms of phosphomycin per ml of pleural fluid, could be due to the existence of pachypleuritis in that patient; this was later confirmed in clinical and histological studies done after the research described here.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allona A., Díaz Cabrera J. A., Manchado P. Fosfomycin in chronic urinary infections. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):267–274. doi: 10.1159/000222059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacardí R., Tornos J., Moga I., Martí N., Alomar P., Gaztelurrutia L., Villalonga C. Treatment of respiratory infections with fosfomycin. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):343–347. doi: 10.1159/000222074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrueco M., Garcia M. J., Otero M. J., Dominguez-Gil A., de Letona J. M. Disposition of cefoxitin in patients with pleural effusion. Clin Ther. 1981;3(6):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsveld W., Stam J., MacLaren D. M. Concentrations of ampicillin in pleural fluid and serum after single and repetitive doses of bacampicillin. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Kosmidis J., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gilchrist J. N. Cefoxitin and cephalothin: antimicrobial activity, human pharmacokinetics, and toxicology. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):290–299. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez Lastra C., Mariño E. L., Dominguez-Gil A., Tabernero J. M., Gonzalez Lopez A., Yuste Chaves M. The influence of uremia on the accessibility of phosphomycin into interstitial tissue fluid. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;25(3):333–338. doi: 10.1007/BF01037944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendlin D., Stapley E. O., Jackson M., Wallick H., Miller A. K., Wolf F. J., Miller T. W., Chaiet L., Kahan F. M., Foltz E. L. Phosphonomycin, a new antibiotic produced by strains of streptomyces. Science. 1969 Oct 3;166(3901):122–123. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3901.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstedt B., Ode B., Walder M., Hanson A., Christensson P., Cronberg S. Penetration of cefuroxime and doxycycline into the pleural fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jan;6(1):153–154. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan K. C., Wadke D. A., Foltz E. L. Pharmacokinetics of phosphonomycin in Man. I. Intravenous administration. J Pharm Sci. 1971 May;60(5):678–685. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600600504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Kemmerich B., Gruhlke G., Dzwillo G., Koeppe P., Wagner I. Cefotaxime in bronchopulmonary infections--a clinical and pharmacological study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):193–198. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. G., Mascarós E., Román J., Paz M., Santos M., Muñoz A., Gobernado M. Enteropathogenic E. coli gastroenterocolitis in neonates treated with fosfomycin. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):310–314. doi: 10.1159/000222068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


