Abstract
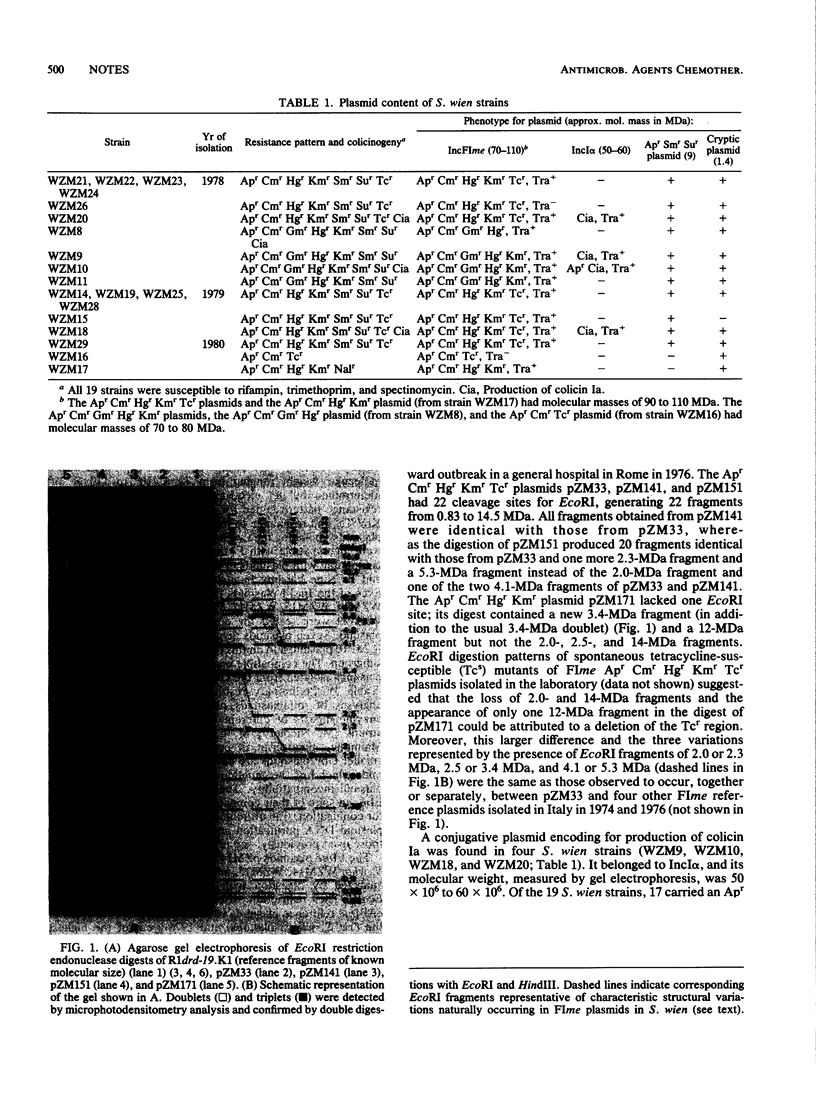
Prevalence, genetic characteristics, and EcoRI cleavage analysis of plasmids identified in clinical strains of Salmonella wien isolated in recent years showed that the plasmid content in this serotype has remained uniform and stable over more than a decade and also late in the epidemic history. No correlation between decrease in S. wien isolations and naturally occurring systematic changes in the DNA of its most common FIme plasmid was structurally detectable.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Threlfall E. J., Carr J. M., McConnell M. M., Smith H. R. Clonal distribution of resistance plasmid-carrying Salmonella typhimurium, mainly in the Middle East. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):425–448. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avril J. L., Dabernat H. J., Gerbaud G. R., Horodniceanu T., Lambert-Zechovsky N., Le Minor S., Mendez B., Chabbert Y. A. Groupes d'incompatibilité des plasmides r chez les souches de Salmonella épidémiques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Aug-Sep;128(2):165–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H. Translocation of a discrete piece of deoxyribonucleic acid carrying an amp gene between replicons in Eschericha coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.1-6.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blohm D., Goebel W. Restriction map of the antibiotic resistance plasmid R1drd-19 and its derivatives pKN102 (R1drd-19B2) and R1drd-16 for the enzymes BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI and SalI. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 29;167(2):119–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00266905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Ling J., Threlfall E. J., Im S. W. Genetic instability of R plasmids in relation to the shift of drug resistance patterns in Salmonella johannesburg. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Feb;128(2):239–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget M., Chandler M., Caro L. The structure of R1drd19: a revised physical map of the plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):183–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00268425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Le Minor S. Origine et répartition en sérotypes des souches isolées en France et reçues au Centre national des Salmonella de 1977 à 1979. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 1981;29(1):45–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maimone F., Colonna B., Bazzicalupo P., Oliva B., Nicoletti M., Casalino M. Plasmids and transposable elements in Salmonella wien. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.369-375.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell M. M., Smith H. R., Leonardopoulos J., Anderson E. S. The value of plasmid studies in the epidemiology of infections due to drug-resistant Salmonella wien. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):178–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mered B., Benhassine M., Papa F., Khati B., Kheddari M., Rahal A., Sari L. Epidémie à "Salmonella wien" et "Salmonella typhi murium" dans un service de pédiatrie. Etude bactériologique et épidémiologique. Arch Inst Pasteur Alger. 1970;48:41–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of FIme resistance plasmids, particularly in epidemic Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Feb 7;159(1):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00401755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]