Abstract
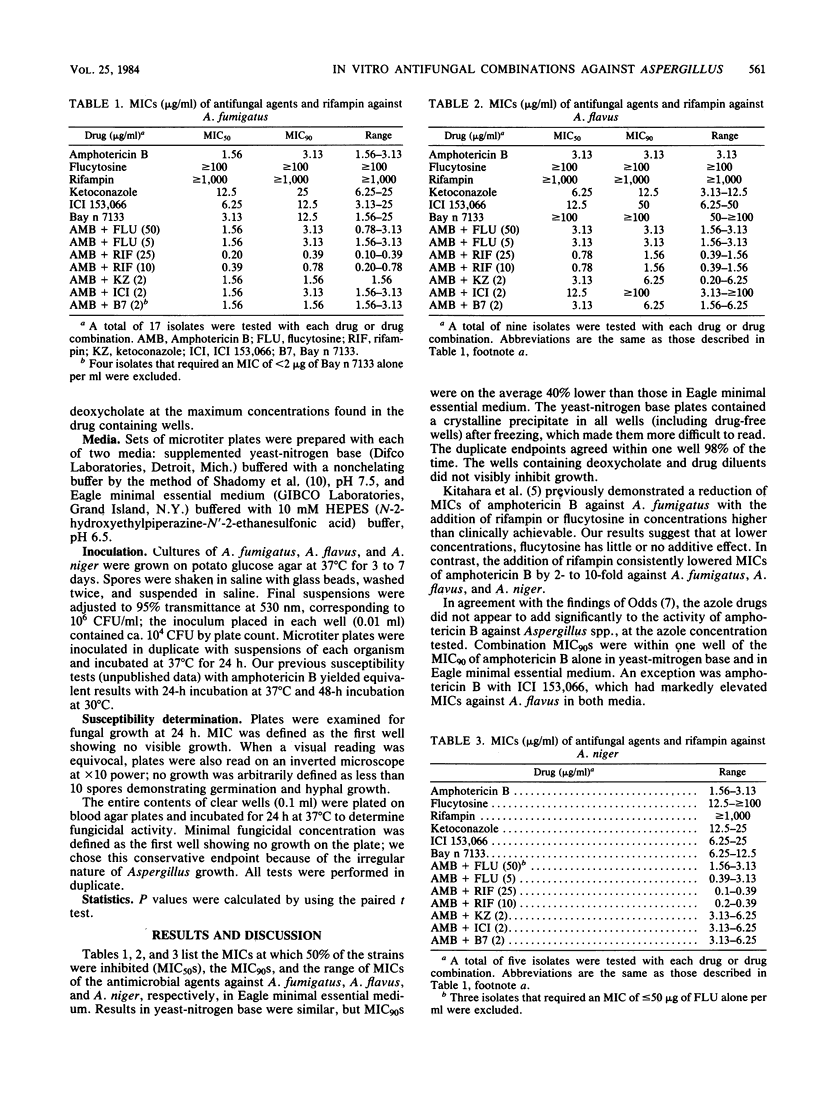
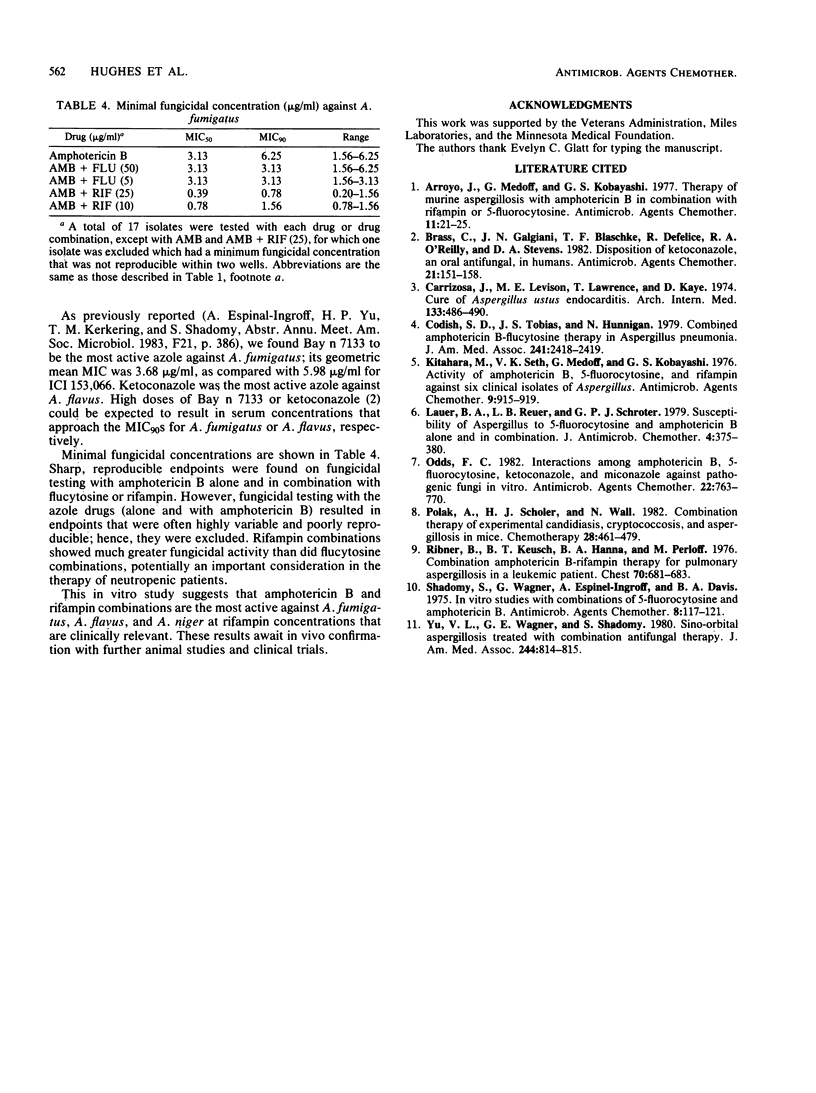
Strains of Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, and Aspergillus niger were tested for in vitro susceptibility with a microtiter plate system in buffered yeast-nitrogen base and in buffered minimal essential medium. Isolates were tested against amphotericin B, flucytosine, rifampin, ketoconazole, ICI 153,066, and Bay n 7133 and against combinations of amphotericin B with each of the other five drugs. Combinations of amphotericin B and rifampin were the most active against all three species of Aspergillus. Flucytosine combined with amphotericin B produced little or no reduction of the MICs at which 90% of the strains were inhibited compared with amphotericin B alone. With one exception, the addition of ketoconazole, ICI 153,066, or Bay n 7133 to amphotericin B did not consistently alter the MICs. The addition of ICI 153,066 markedly increased the MICs of amphotericin B against the A. flavus isolates in both media. When the azoles were tested alone, Bay n 7133 was the most active against A. fumigatus, but was two- to fivefold less active against A. flavus. Ketoconazole was the most active azole against A. flavus.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Therapy of murine aspergillosis with amphotericin B in combination with rifampin of 5-fluorocytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass C., Galgiani J. N., Blaschke T. F., Defelice R., O'Reilly R. A., Stevens D. A. Disposition of ketoconazole, an oral antifungal, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):151–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrizosa J., Levison M. E., Lawrence T., Kaye D. Cure of Aspergillus ustus endocarditis on a prosthetic valve. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Mar;133(3):486–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codish S. D., Tobias J. S., Hannigan M. Combined amphotericin B-flucytosine therapy in Aspergillus pneumonia. JAMA. 1979 Jun 1;241(22):2418–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara M., Seth V. K., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Activity of amphotericin B, 5-fluorocytosine, and rifampin against six clinical isolates of Aspergillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):915–919. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer B. A., Reller L. B., Schröter G. P. Susceptibility of Aspergillus to 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B alone and in combination. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(4):375–380. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.4.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Interactions among amphotericin B, 5-fluorocytosine, ketoconazole, and miconazole against pathogenic fungi in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):763–770. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak A., Scholer H. J., Wall M. Combination therapy of experimental candidiasis, cryptococcosis and aspergillosis in mice. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(6):461–479. doi: 10.1159/000238138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribner B., Keusch G. T., Hanna B. A., Perloff M. Combination amphotericin B-rifampin therapy for pulmonary aspergillosis in a leukemic patient. Chest. 1976 Nov;70(5):681–683. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Wagner G., Espinel-Ingroff E., Davis B. A. In vitro studies with combinations of 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):117–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L., Wagner G. E., Shadomy S. Sino-orbital aspergillosis treated with combination antifungal therapy. Successful therapy after failure with amphotericin B and surgery. JAMA. 1980 Aug 22;244(8):814–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



