Abstract
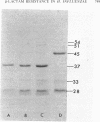
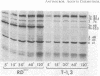
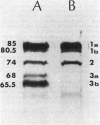
The mechanism of non-beta-lactamase-mediated beta-lactam resistance in a clinical isolate of Haemophilus influenzae type b was studied. This clinical isolate showed up to a 32-fold increase in MICs of a wide variety of beta-lactams, including moxalactam and cefotaxime, although no beta-lactamase activity was detected, even after attempted induction. Transformation of broad-spectrum beta-lactam resistance into ampicillin-susceptible H. influenzae RDnov was accomplished. Examination of the outer membrane protein profile of the resistant parent by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of Triton X-100-extracted membranes revealed an unusual major outer membrane protein band at a molecular weight of 45,000. This outer membrane protein profile did not transform with beta-lactam resistance. Permeability differences were noted between the resistant strain and the nonisogenic susceptible strain of H. influenzae, although these penetration differences were not transformed. Comparison of the penicillin-binding protein profile of a resistant transformant with that of a susceptible parent with both whole-membrane preparations and whole-cell labeling, revealed a major reduction in binding affinity to penicillin-binding proteins 3a and 3b (molecular weights, 68,000 and 65,000, respectively). Thus, alteration in penicillin-binding proteins 3a and 3b correlated with the beta-lactam resistance.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Bendler J. W., Setlow J. K. Plasmid transformation in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1099-1101.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Outer-membrane protein subtypes of Haemophilus influenzae type b and spread of disease in day-care centers. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):210–217. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. M., Plowman D. Mechanisms of ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae from respiratory tract. Lancet. 1980 Feb 9;1(8163):279–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90778-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E. Transferable chloramphenicol and ampicillin resistance in a strain of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):154–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Boulton M. G., Ross G. W. Penicillin-binding proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Comparison of two strains differing in their resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Feb;7(2):127–136. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar F. A., Farrell W., Howard A. J., Hince C., Leung T., Williams J. D. Activity of HR 756 against Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis and Gram-negative rods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):445–450. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Bryan L. E., Rabin H. R. beta-Lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with modified penicillin-binding proteins emerging during cystic fibrosis treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):705–711. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W., Reynolds A. V. Cefotoxime (HR 756) a new cephalosporin with exceptional broad-spectrum activity in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):437–444. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. L., Collier A. M., Pendergrass E., King S. H. Methods for serotyping nasopharyngeal isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: slide agglutination, Quellung reaction, countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis, latex agglutination, and antiserum agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):570–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.570-574.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Crawford S. A., Alexander G. A. In vitro activities of moxalactam and cefotaxime against aerobic gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):937–942. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Janik A. Transformation of Acinetobacter calco-aceticus (Bacterium anitratum). J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.281-288.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Isburg C. D., Michaels R. H. Meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae type b resistant to both ampicillin and chloramphenicol. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):14–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesman S. H., Corrado M. L., Shah P. M., Armengaud M., Barza M., Cherubin C. E. Past and current roles for cephalosporin antibiotics in treatment of meningitis. Emphasis on use in gram-negative bacillary meningitis. Am J Med. 1981 Oct;71(4):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman S. J., Brunken J. M., Bollinger M. Prevalence of ampicillin-resistant strains of Haemophilus influenzae causing systemic infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):474–475. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makover S. D., Wright R., Telep E. Penicillin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M. Isolation of an ampicillin-resistant, non-beta-lactamase-producing strain of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):80–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D. The increasing frequency of beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae B. JAMA. 1980 Jul 18;244(3):239–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Campos J. M., Plotkin S. A. Ampicillin-resistant, beta-lactamase-negative haemophilus influenzae type b. Pediatrics. 1982 Feb;69(2):230–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. H., Lopez J. S., Cook C. B. Acidometric agar plate method for ampicillin susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):318–320. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheifele D. W. Ampicillin-resistant Hemophilus influenzae in Canada: nationwide survey of hospital laboratories. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Jul 21;121(2):198–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R., Rodriguez W., Khan W., Ross S. The increasing incidence of Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. A cause of otitis media. JAMA. 1978 Jan 23;239(4):320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syriopoulou V., Scheifele D., Smith A. L., Perry P. M., Howie V. Increasing incidence of ampicillin resistance in Hemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1978 Jun;92(6):889–892. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega R., Sadoff H. L., Patterson M. J. Mechanisms of ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae type B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):164–168. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]