Abstract
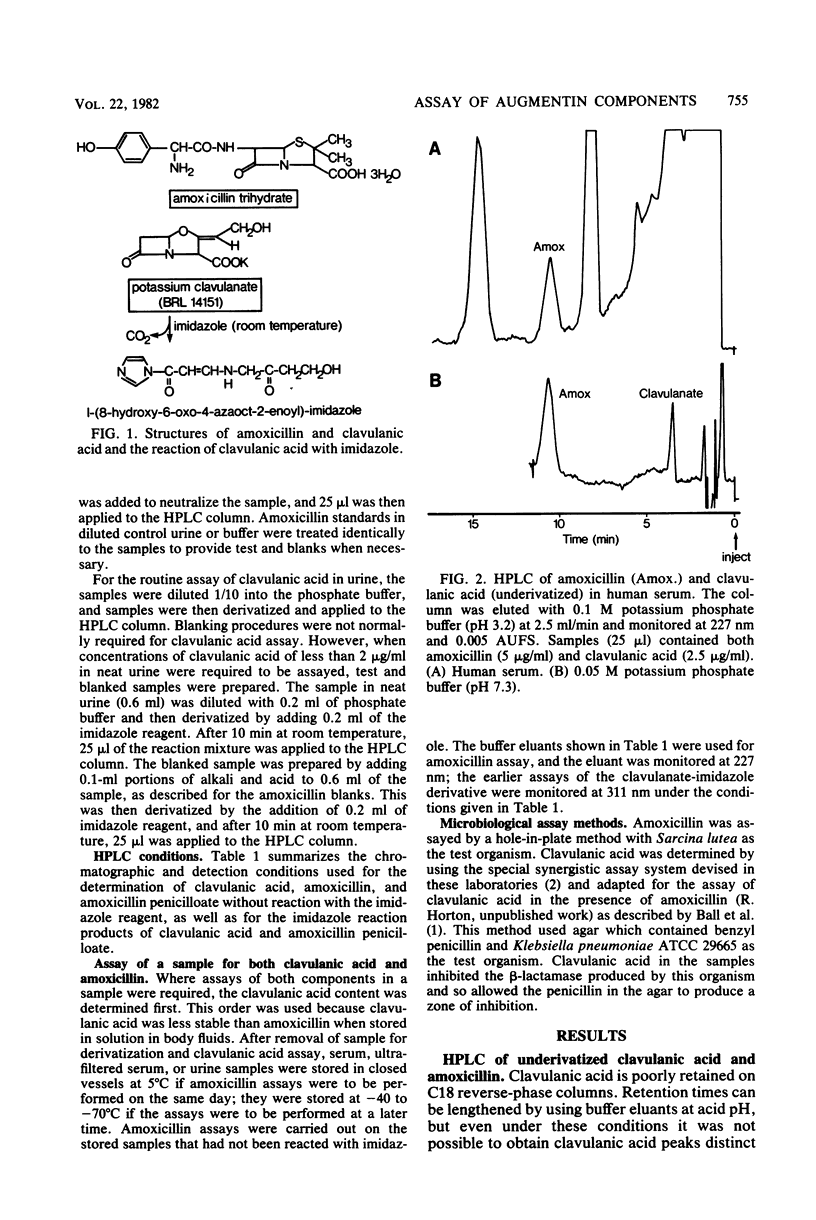
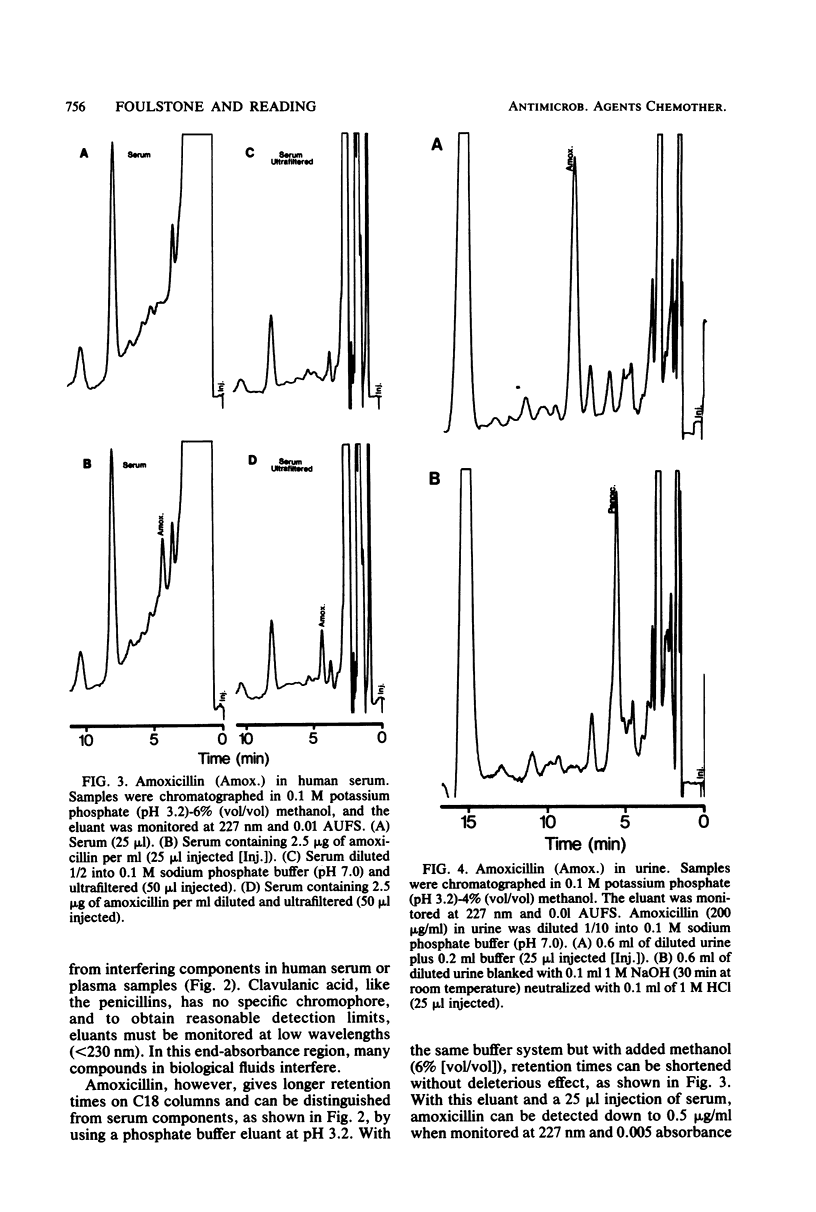
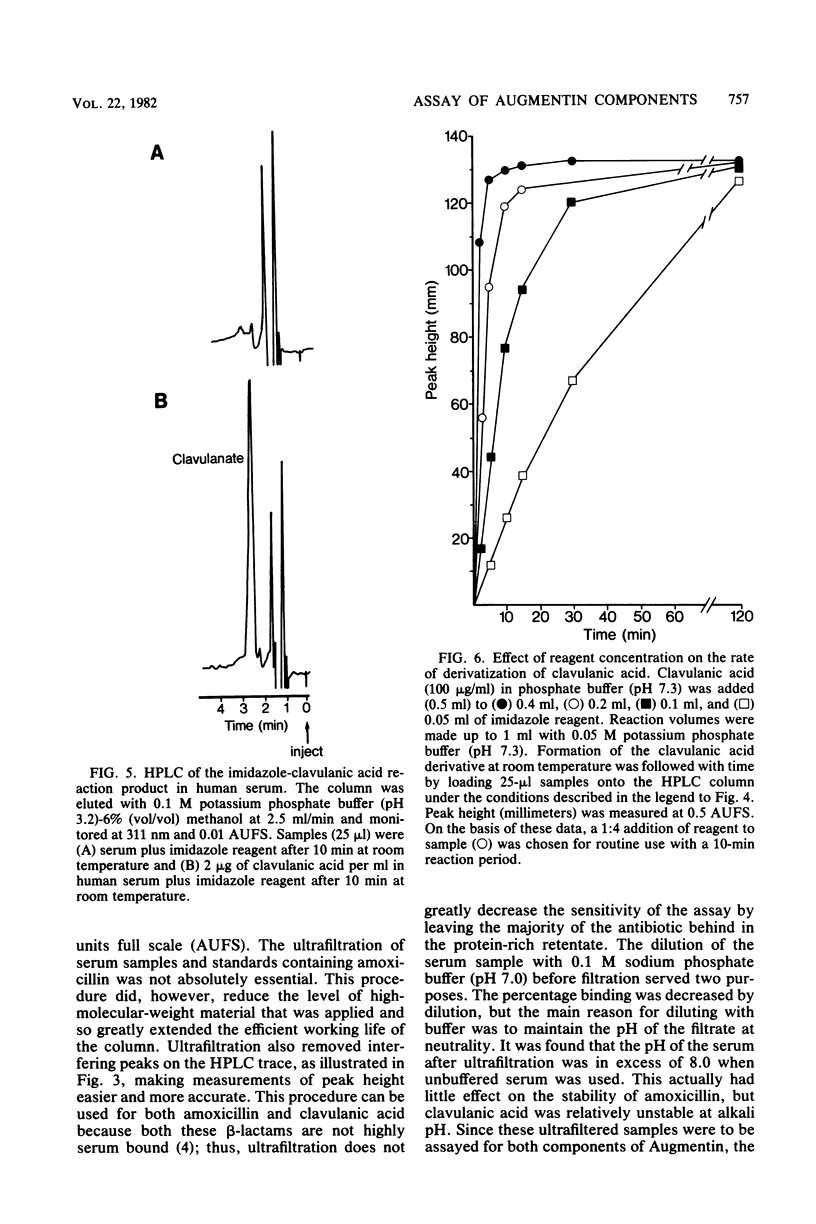
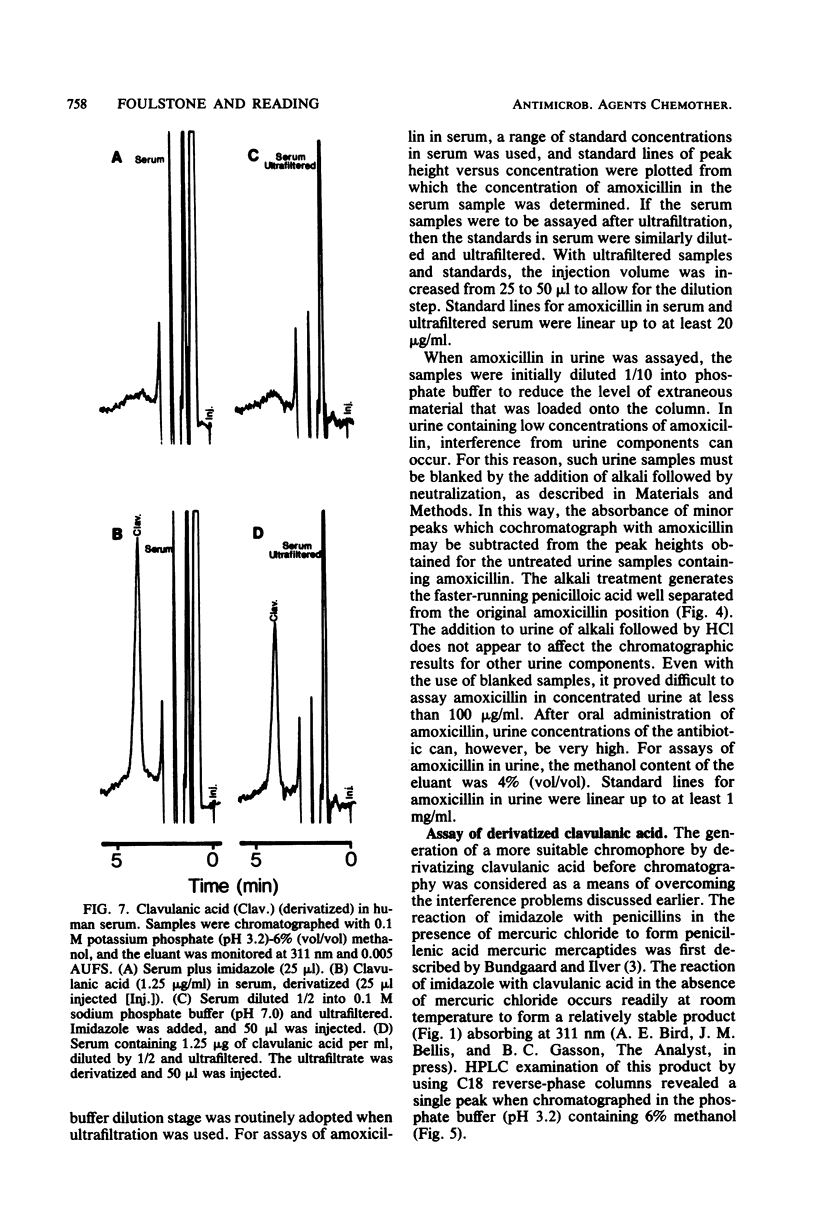
Augmentin is a new antibacterial formulation comprised of amoxicillin and the beta-lactamase inhibitor clavulanic acid. In the present paper, the use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to provide a rapid assay of the components of Augmentin in body fluids is described. Clavulanic acid was assayed by reacting the sample with imidazole, which readily produces a derivative absorbing at 311 nm. This derivative chromatographs on reverse-phase HPLC columns clear of interfering components in both human serum and urine. Concentrations of clavulanic acid as low as 0.1 microgram/ml were readily detectable in human serum with this procedure. There was no interference from amoxicillin, amoxicillin penicilloic acid, or the acid and alkali degradation products of clavulanic acid when this assay system was used. Amoxicillin in body fluids was assayed directly by HPLC without derivatization. The same chromatographic conditions were employed for the assay of amoxicillin and the clavulanic acid derivative, simplifying the methodology. Amoxicillin, however, was determined of the antibiotic per ml. An alkali blanking procedure for amoxicillin and clavulanic acid is also described which allows the detection of any underlying peaks which may cochromatograph. The use of ultrafiltration to remove protein from serum samples before HPLC was successfully applied to the assay of clavulanic acid and amoxicillin. Ultrafiltration is not an essential procedure for these assays, but it prolongs column life and reduces interference in the amoxicillin assay. Results obtained by HPLC were compared with those obtained by using microbiological assays.
Full text
PDF

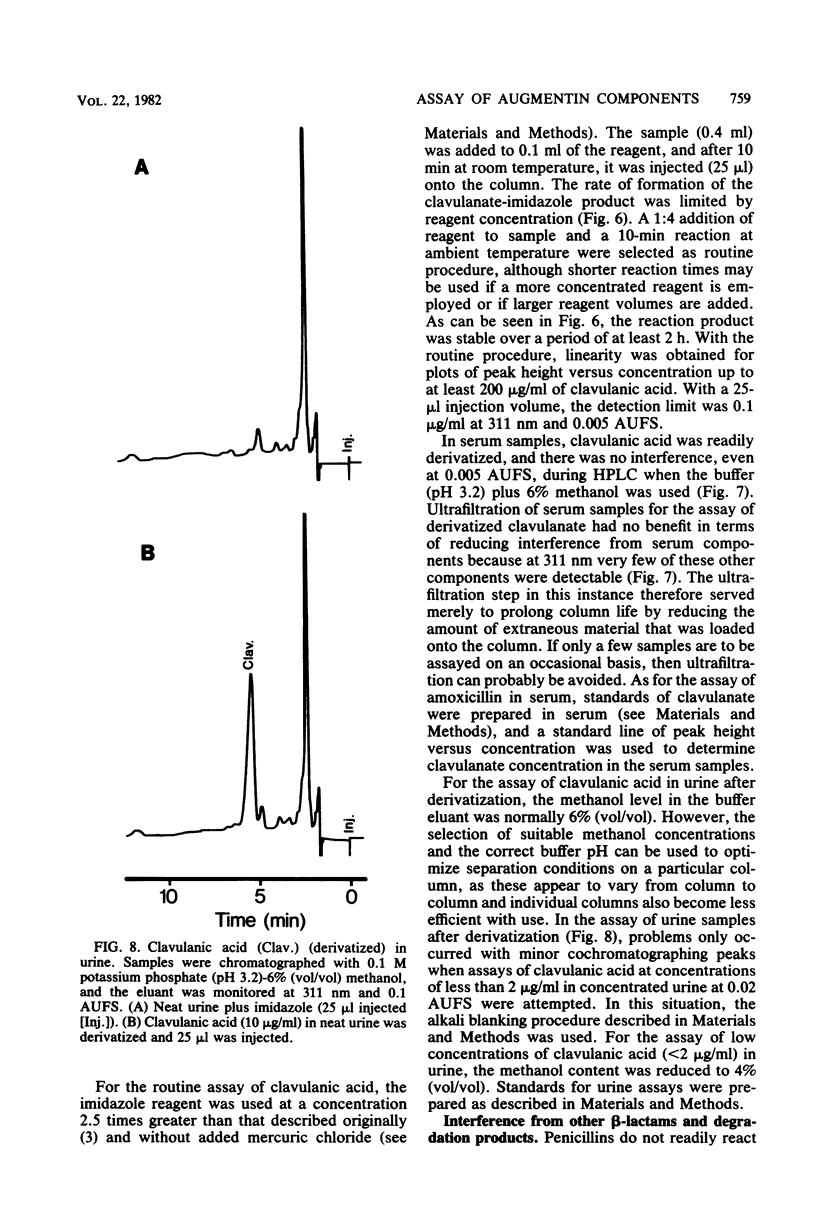
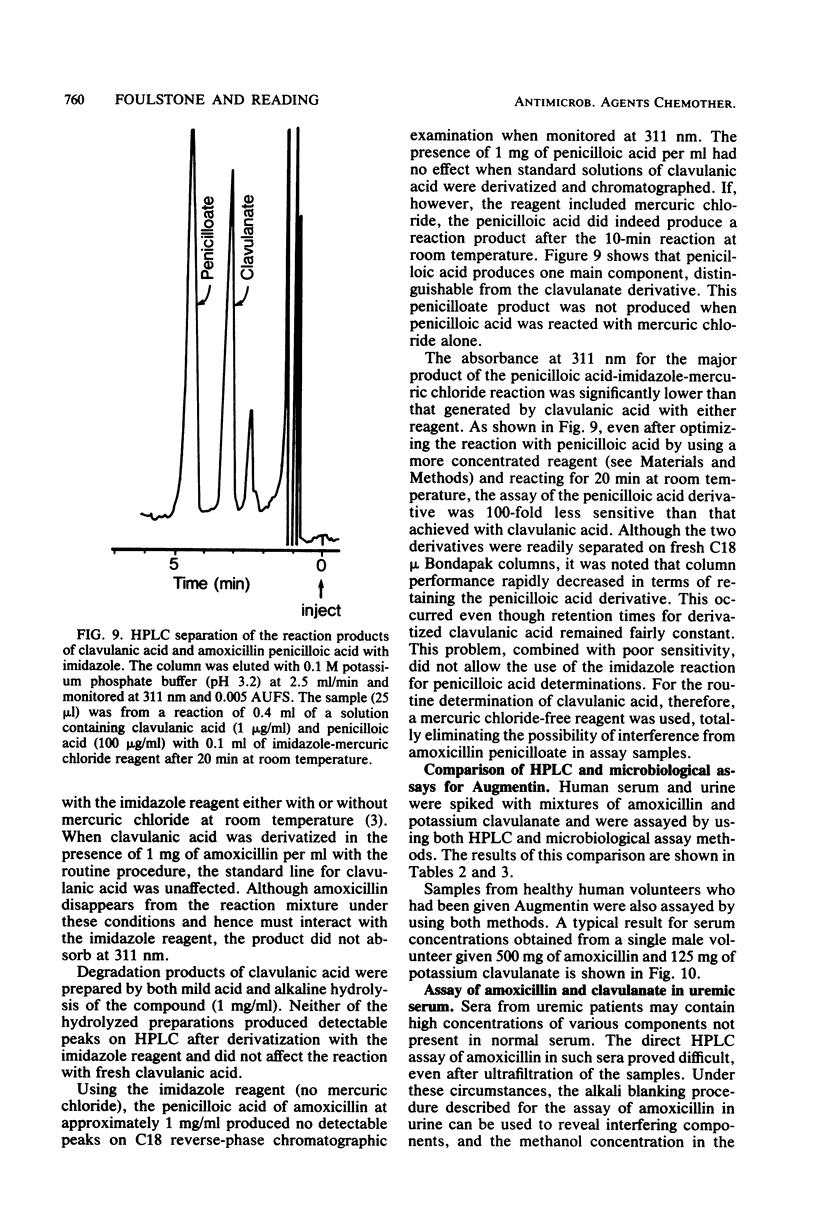
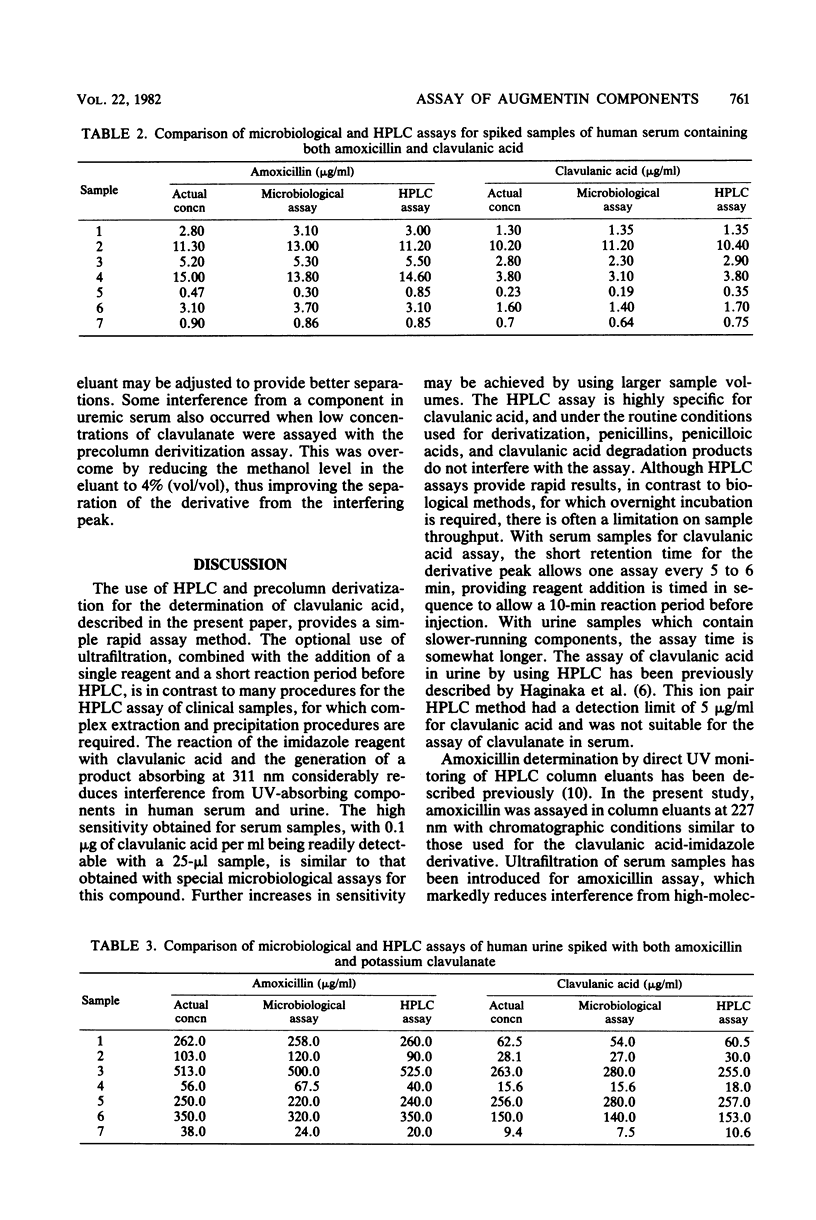
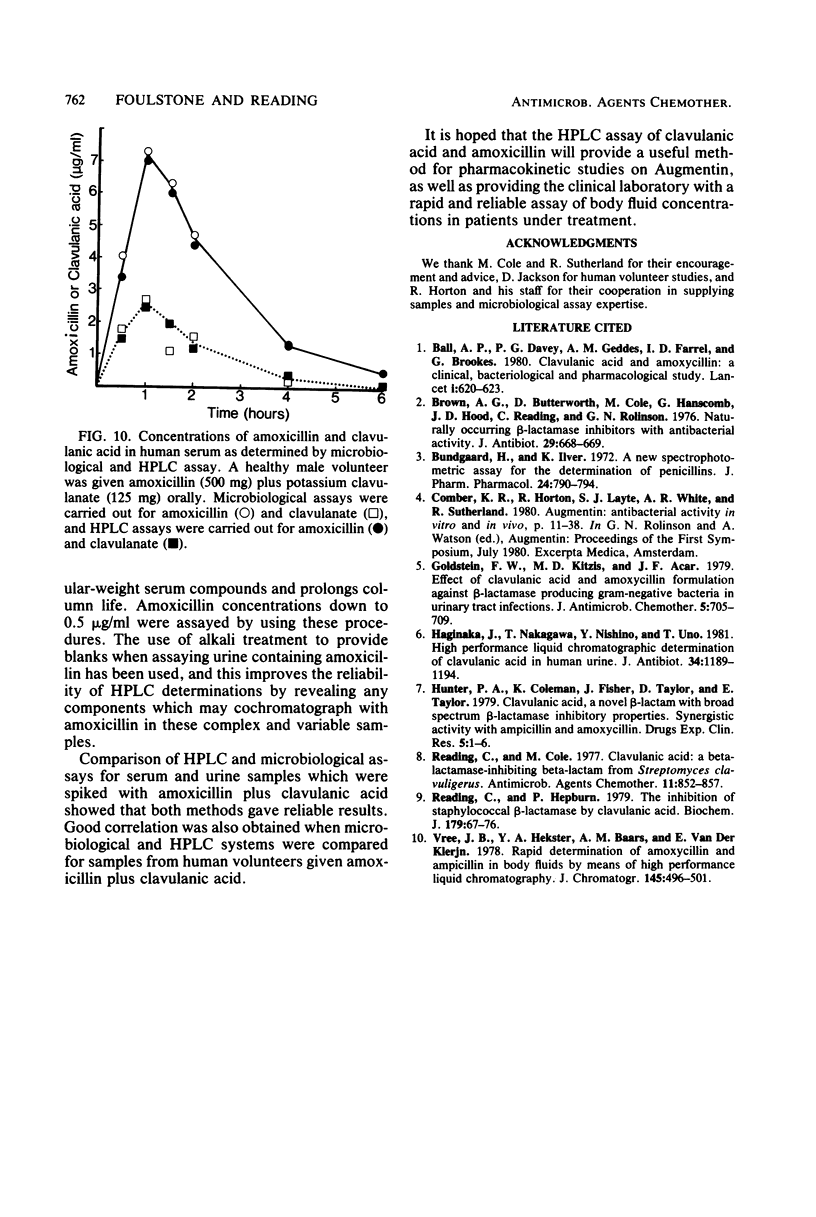
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball A. P., Geddes A. M., Davey P. G., Farrell I. D., Brookes G. R. Clavulanic acid and amoxycillin: a clinical, bacteriological, and pharmacological study. Lancet. 1980 Mar 22;1(8169):620–623. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Butterworth D., Cole M., Hanscomb G., Hood J. D., Reading C., Rolinson G. N. Naturally-occurring beta-lactamase inhibitors with antibacterial activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jun;29(6):668–669. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard H., Ilver K. A new spectrophotometric method for the determination of penicillins. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;24(10):790–794. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Kitzis M. D., Acar J. F. Effect of clavulanic acid and amoxycillin formulation against beta-lactamase producing Gram-negative bacteria in urinary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Nov;5(6):705–709. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.6.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haginaka J., Nakagawa T., Nishino Y., Uno T. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of clavulanic acid in human urine. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Sep;34(9):1189–1194. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Hepburn P. The inhibition of staphylococcal beta-lactamase by clavulanic acid. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):67–76. doi: 10.1042/bj1790067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vree T. B., Hekster Y. A., Baars A. M., Van der Kleijn E. Rapid determination of amoxycillin (clamoxyl) and ampicillin (penbritin) in body fluids of many by means of high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1978 May 1;145(3):496–501. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



