Abstract
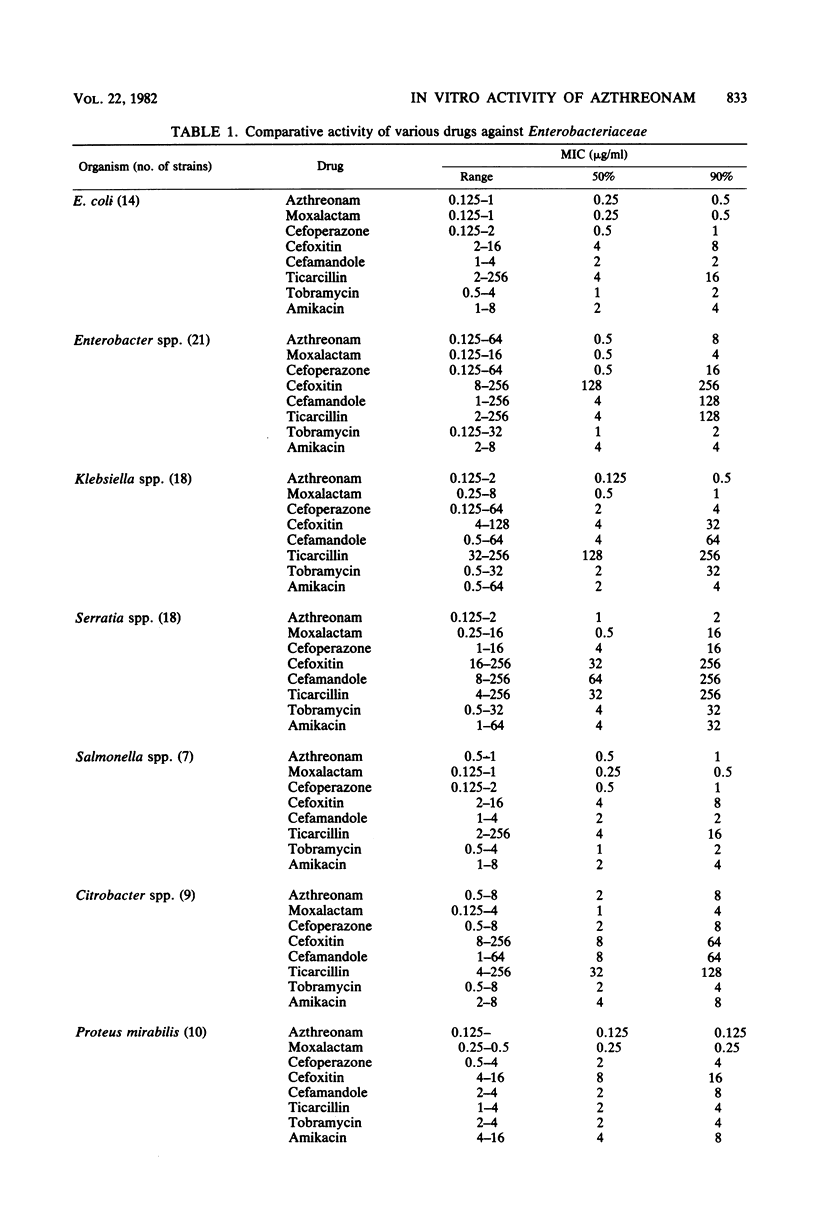
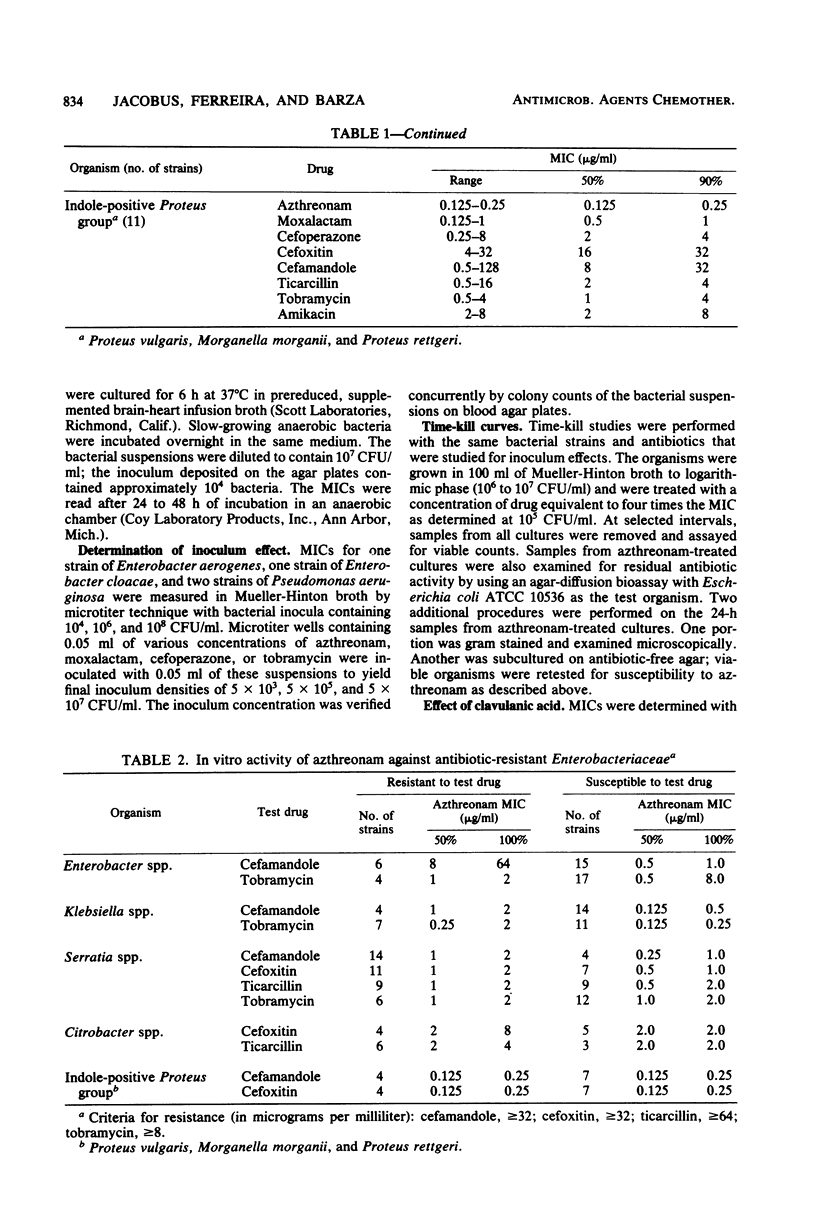
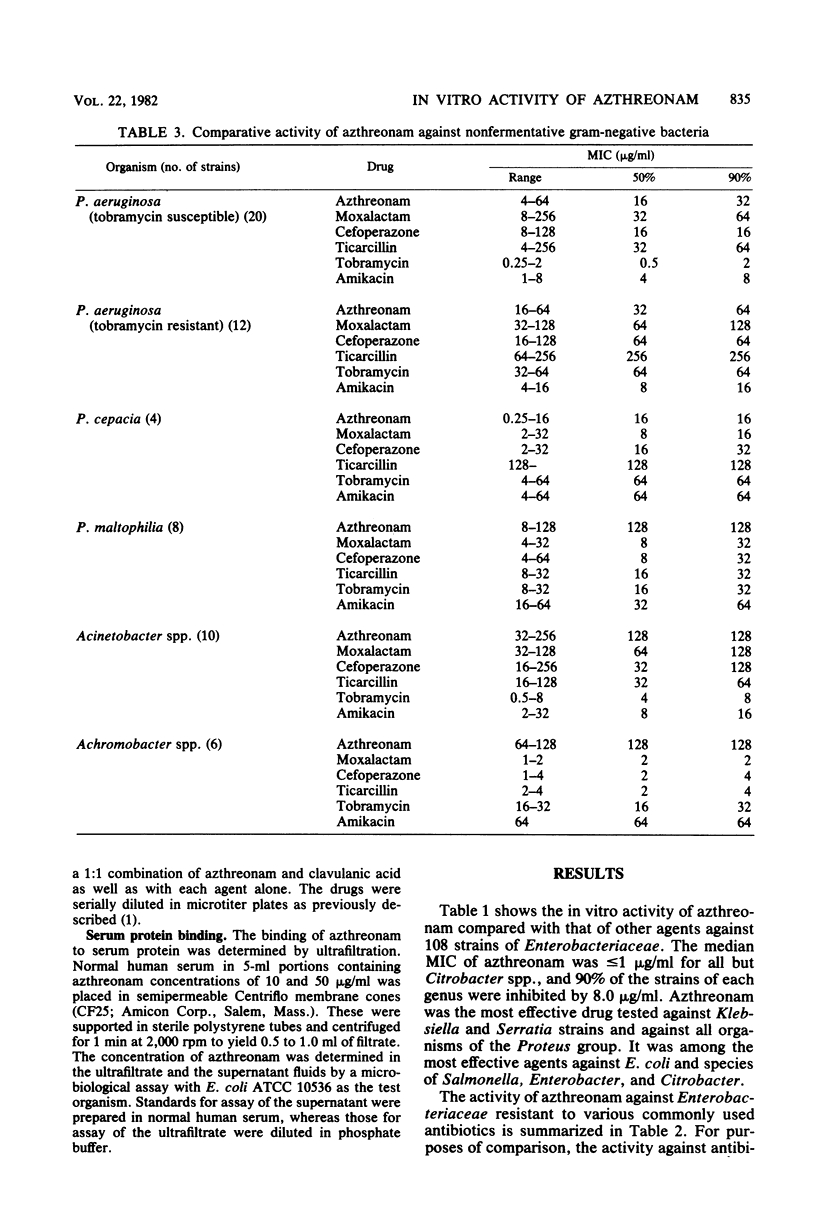
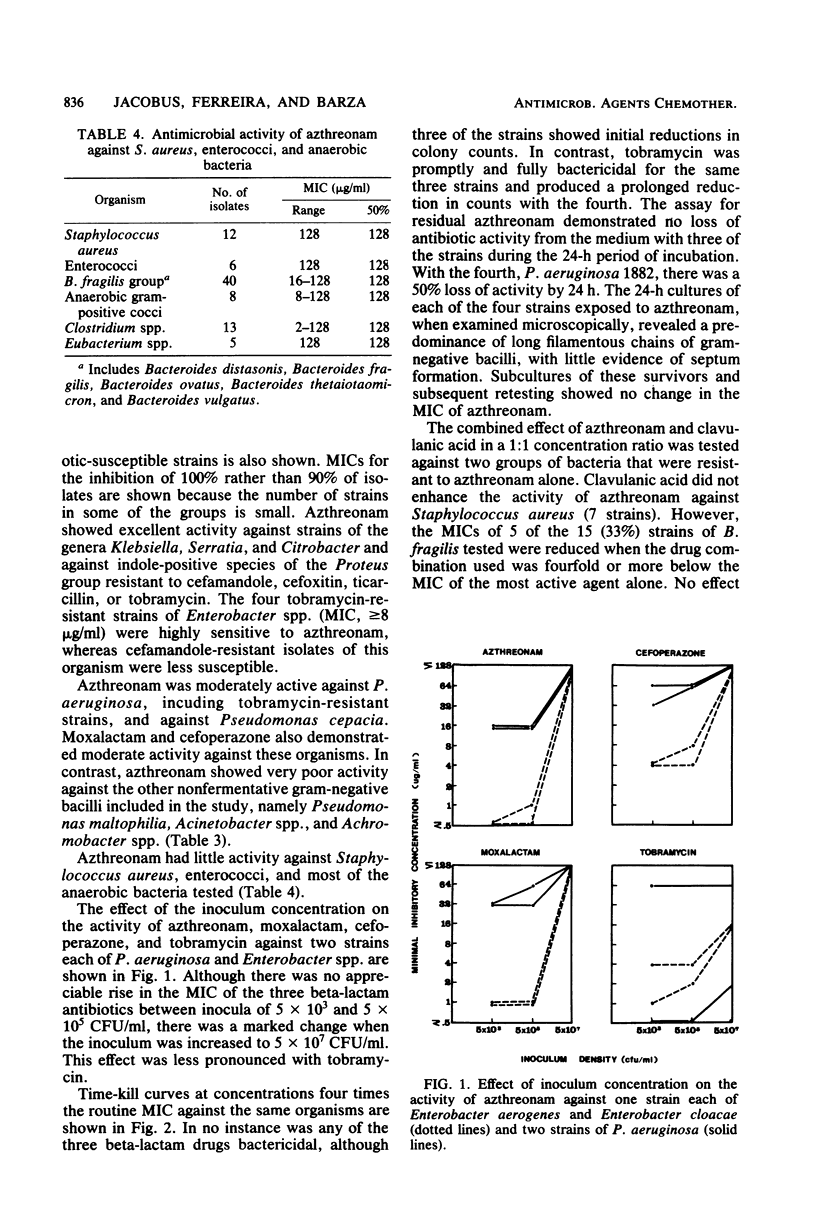
We studied the activity of azthreonam (SQ 26,776), a novel monocyclic beta-lactam compound, against a variety of clinical isolates. It was more potent than moxalactam, cefoperazone, cefamandole, cefoxitin, ticarcillin, tobramycin, or amikacin against strains of Klebsiella spp., Serratia spp., and the Proteus group. It was highly effective against Escherichia coli and strains of Salmonella spp. The median minimal inhibitory concentration for all species of Enterobacteriaceae was less than or equal to 2 micrograms/ml. Azthreonam was moderately active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including tobramycin-resistant strains, and against Pseudomonas cepacia (median minimal inhibitory concentration, 16 to 32 micrograms/ml), but was weakly active against Pseudomonas maltophilia and strains of Acinetobacter spp. and Achromobacter spp. The drug showed little activity against Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci, and anaerobic bacteria, including Bacteroides fragilis, Clostridium spp., and gram-positive cocci. Like moxalactam and cefoperazone, azthreonam exhibited a considerable inoculum effect with strains of Enterobacter spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Combination with clavulanic acid did not increase the activity of azthreonam against S. aureus but was synergistic for 5 of 15 strains of B. fragilis. Azthreonam is about 50% bound to human serum protein. The selective range of activity of this compound could be of clinical benefit.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer H., Cimarusti C. M., Denzel T., Koster W. H., Slusarchyk W. A., Treuner U. D. Monobactams--structure-activity relationships leading to SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):21–28. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., Weaver S., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of SQ26,776. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):294–298. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Williams J. D. In-vitro activity of the monobactam, SQ 26,776, against Gram-negative bacteria and its stability to their beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):29–37. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Antibacterial activity of a monocyclic beta-lactam SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):111–122. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., King A., Shannon K., Warren C. SQ 26,776: in-vitro antibacterial activity and susceptibility to beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):103–110. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. D. In-vitro studies on SQ 26,776, a new monobactam antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):81–88. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H., Wells J. S. Monobactams--monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):1–16. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Hancox J. SQ 26,776, a novel beta-lactam: an in-vitro comparison with other antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):39–47. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



