Abstract
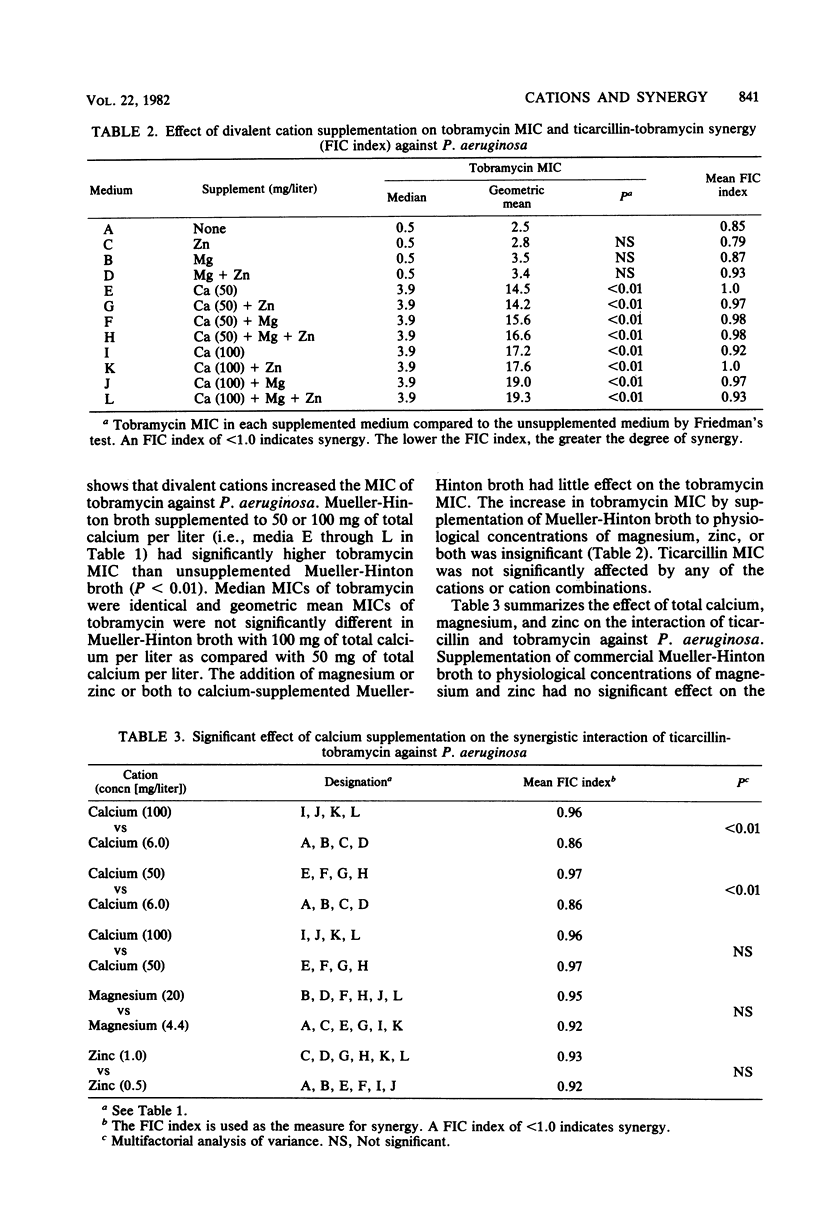
Correlation between in vitro and in vivo test results for synergy between carboxypenicillins and aminoglycosides against Pseudomonas aeruginosa is poor. Although the divalent cation content of culture media is known to affect aminoglycoside susceptibility testing for P. aeruginosa, this effect of divalent cations has not been examined for synergy testing of carboxypenicillin-aminoglycoside interaction against P. aeruginosa. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of tobramycin and ticarcillin and the interaction of these drugs in combination were studied by a microtitration method for 36 strains of P. aeruginosa in Mueller-Hinton broth with varying supplements of calcium, magnesium, and zinc. The supplementation of Mueller-Hinton broth to 50 or 100 mg of calcium per liter had a significant effect in increasing the tobramycin MIC (P less than 0.01), as well as decreasing the degree of synergy between ticarcillin and tobramycin (P less than 0.01). Supplementation to 20 mg of magnesium per liter, 1.0 mg of zinc per liter, or both did not significantly affect tobramycin MIC or the interaction of tobramycin and ticarcillin. Supplementation to 50 or 100 mg of calcium per liter rendered any additional effect of magnesium and zinc on aminoglycoside MIC and aminoglycoside-carboxypenicillin interaction negligible. If these results for ticarcillin and tobramycin are confirmed for other carboxypenicillins and aminoglycosides, then the Mueller-Hinton broth used for P. aeruginosa aminoglycoside susceptibility and synergy testing may need to be supplemented only with calcium at a concentration of 50 mg/liter.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. L., Gramling P. K., Vestal P. R., Farrar W. E., Jr Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tobramycin or gentamicin alone and combined with carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):300–304. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casillas E., Kenny M. A., Minshew B. H., Schoenknecht F. D. Effect of ionized calcium and soluble magnesium on the predictability of the performance of Mueller-Hinton agar susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):987–992. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'amato R. F., Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Kirven L. A. Effect of calcium and magnesium ions on the susceptibility of Pseudomonas species to tetracycline, gentamicin polymyxin B, and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):596–600. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Iannetta A., Wedgwood R. J. Activity of colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inhibition by calcium. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):610–612. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovick R., Bayan A. P., Canales P., Pansy F. The Influence of Certain Substances on the Activity of Streptomycin: III. Differential Effects of Various Electrolytes on the Action of Streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):125–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Barnishan J. Effect of divalent cation concentrations on the antibiotic susceptibilities of nonfermenters other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):434–438. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felegie T. P., Yu V. L., Rumans L. W., Yee R. B. Susceptibility of Pseudomonas maltophilia to antimicrobial agents, singly and in combination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):833–837. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Effect of medium composition on the apparent sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. A., Pollock H. M., Minshew B. H., Casillas E., Schoenknecht F. D. Cation components of Mueller-Hinton agar affecting testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptibility to gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M., Standiford H. C., Tatem B., Young V. M., Greene W. H., Schimpff S. C., Calia F. M., Hornick R. B. Comparative activity of tobramycin, amikacin, and gentamicin alone and with carbenicillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):442–446. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane protein H1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in adaptive and mutational resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, polymyxin B, and gentamicin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.872-878.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostenson R. C., Fields B. T., Nolan C. M. Polymyxin B and rifampin: new regimen for multiresistant Serratia marcescens infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):655–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Schoenknecht F. D., Kenny M. A., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: selection of a control strain and criteria for magnesium and calcium content in media. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):454–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonne M., Jawetz E. Combined action of carbenicillin and gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):893–896. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.893-896.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Snyder R. J., Kohner P. C., Wiltse C. G., Ilstrup D. M., McCall J. T. Effect of cation content of agar on the activity of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):103–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J. J. Comparative susceptibilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to 1-oxacephalosporin (LY 127935) and eight other antipseudomonal antimicrobial agents (old and new). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):96–98. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics aganst Pseudomonas aeruginosa: specificity and site of calcium and magnesium antagonism. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):663–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



